Research progress of environment-responsive hydrogel applications in agriculture
Wenxu Zhang, Xuyang Mu, Yan Xu, Guofu Ma, Ziqiang Lei
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 193-213, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.14
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.14
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

ABSTRACT
Environment-responsive hydrogels are environmentally friendly polymeric materials that rapidly respond to their environment by changing their volume or strength when the external environment, such as temperature, pH, light, and magnetism, changes. As environment-responsive hydrogels, they are uniquely flexible and sensitive, enabling them to be used in various applications, and are now at the forefront of polymer science research. Scholars have reviewed more environmentresponsive hydrogels in biomedicine, detection sensors, and drug release. We present a detailed description of the reaction mechanism and preparation process of environment-responsive hydrogels, taking temperature-responsive, pH-responsive, and light-responsive hydrogels as examples. Finally, a summary is given at the end: 1) the application of environmentally responsive hydrogels in agriculture, and 2) the problems and future trends of their application in agriculture.
RELATED ARTICLES
Hafsa Ilyas, Syeda Huma H. Zaidi, Salwa D. Al-Malwi, Muhammad Yasir, Muhammad Usman, Seemab Parvaiz, Muhammad Siddiq
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1038-1052, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.78
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1038-1052, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.78
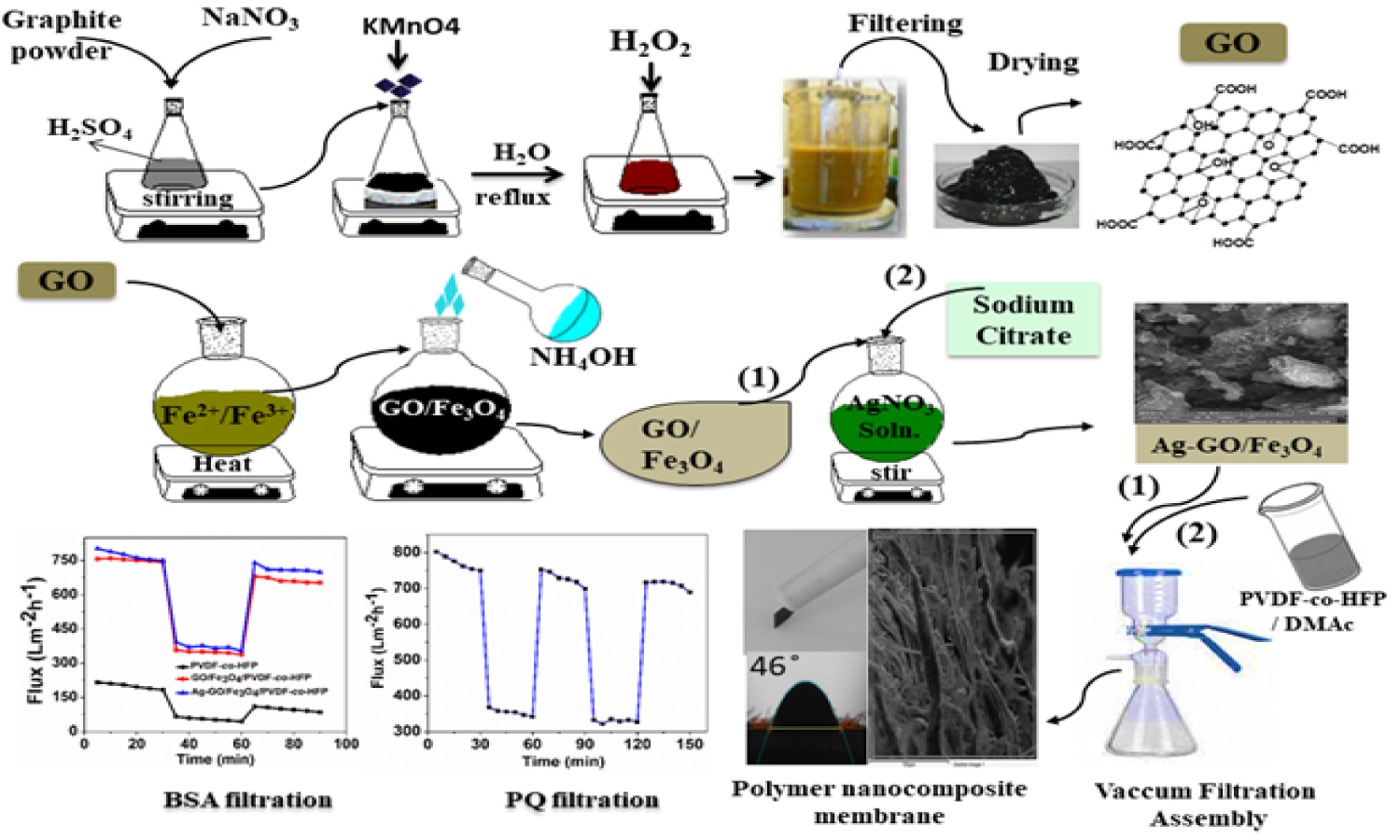
Magnetically active membranes based on GO/Fe3O4and Ag-GO/Fe3O4have been synthesized via the resin-infiltration technique, achieving significant improvements in rejection and antifouling properties, followed by their characterization by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-rays spectroscopy (EDX) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). The increasing demand for efficient water purification technologies is challenged by low separation efficiency, poor resistance to fouling, and limited tunability in dynamic environments, as well as low rejection performance. This study addresses the research gap by developing and evaluating GO/Fe3O4and Ag-GO/Fe3O4membranes to enhance water treatment performance through improved rejection rates and antifouling capabilities. It exhibits separation efficiency, fouling resistance, and high thermomechanical stability with the added advantage of magnetic responsiveness – a combination that addresses multiple persistent issues in membrane-based water treatment. GO/Fe3O4 and Ag-GO/Fe3O4 improved the flux recovery ratio of pristine PVDF-co-HFP membrane from 50.8 to 89.9 and 92.3%, while the rejection % of paraquat (PQ) herbicide increased up to 92.7%. This research is important because magnetically active membranes do not need external magnetic fields to move the magnetic particles to the membrane’s surface.
Nguyen Hoc Thang, Nguyen Van Phuc, Tran Thi Tu Nhi, Dang Xuan Cuong, Do Quang Minh
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 160-192, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.13
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 160-192, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.13

Polymer-based hydrogels are hydrophilic polymer networks with a remarkable capacity to absorb substantial amounts of water and biological fluids, rendering them highly attractive for drug delivery applications. The COVID-19 pandemic has acted as a catalyst for research and innovation in the realm of polymer-based hydrogels for drug delivery, with a particular emphasis on antiviral therapeutics, vaccines, diagnostics, and precision delivery to the respiratory system. The distinctive attributes of hydrogels, such as their biocompatibility, customizable drug release profiles, and ease of functionalization, establish them as versatile platforms for the development of advanced drug delivery systems to combat not only COVID-19 but also a spectrum of other infectious diseases. This study is dedicated to scruti-nizing and evaluating the characteristics of polymer-based hydrogels employed in drug delivery for the treatment of diseases associated with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Furthermore, the investigation introduces a novel classification system for polymer-based hydrogels deployed in drug delivery for SARS-CoV-2-related diseases. Additionally, the paper provides an up-to-date evaluation of the latest developed hydrogels utilized in drug delivery for the treatment of dis-eases linked to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, based on research conducted through the recent months of 2023.



