The influence of crosslink characteristics on key properties of dynamically cured NR/PP blends
Vol. 18., No.5., Pages 487-503, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.36
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.36
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

ABSTRACT
Thermoplastic
vulcanizates (TPVs) were prepared by blending natural rubber (NR) and
polypropylene (PP) using dynamic sulfur curing systems with varying
accelerator/sulfur ratios: 0.5/2.5, 1.5/1.5, and 2.5/0.5 phr, categorized as
conventional (CV), semi-efficient (semi-EV), and efficient (EV). The onset of
dynamic vulcanization closely corresponded with scorch time in statically cured
NR compounds. Mixing torque decreased over time, reflecting reversion patterns
in static curing. The CV system exhibited the highest reversion tendency due to
polysulfide linkage breakdown, forming stronger but shorter crosslinks. Dynamic
vulcanization induced higher reversion than static curing, influenced by shear
and extensional forces. Curing systems caused crosslinking rates, reversion,
and crosslink density and distribution variations. Unlike statically cured NR,
PP-extracted TPVs exhibited an inverse trend in total crosslink densities and
distributions; TPVs primarily comprised shorter crosslinks with opposed total
crosslink densities ranked EV > semi-EV > CV. This trend is strongly
correlated with superior mechanical strength, toughness, storage modulus,
viscosity, and rubber elasticity in the EV-cured TPV. EV system also had the
smallest vulcanized NR domains in the PP matrix.
RELATED ARTICLES
Kazem Honarkar, Mohammad Karrabi
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 311-323, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 311-323, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
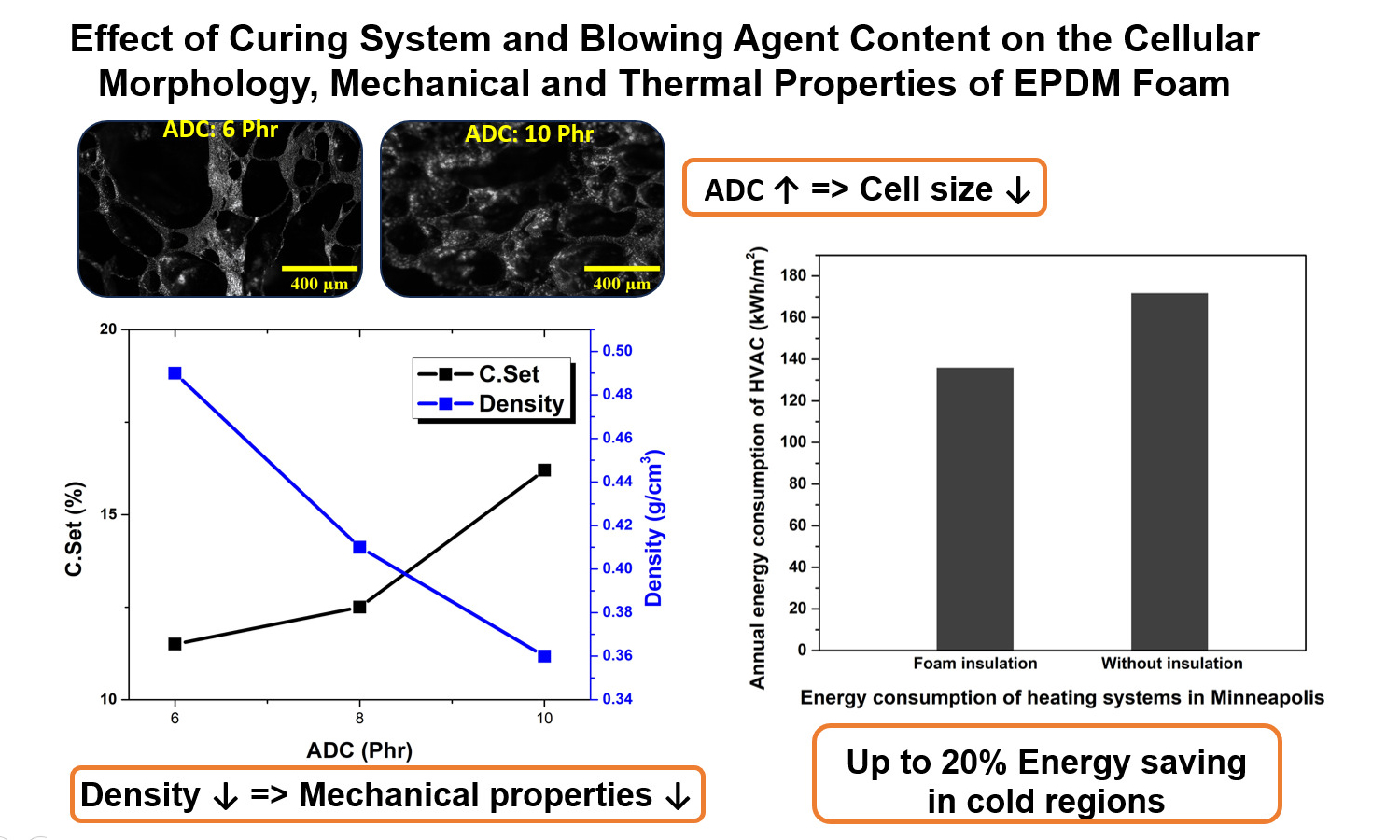
In this study, the effect of the amount of blowing agent and the type of sulfur curing system on the cellular structure, thermal, and mechanical properties of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) foam was investigated. Three types of sulfur curing systems including efficient, semi-efficient and conventional and three variable levels of azodicarbonamide (ADC) were considered; as a result, nine EPDM foam formulations were evaluated. Curing process parameters were measured using cure rheometry and cellular structure was examined by optical microscopy images, determining the average cell size and size distribution. For evaluating physical and mechanical properties, density and compression set tests were performed. Thermal conductivity tests were conducted on selected samples. Building energy modeling was performed using DesignBuilder software to evaluate the thermal insulation performance of the foams. The results showed that the type of curing system and the amount of ADC significantly affect cell morphology, density, and mechanical properties. Overall, a decrease in density leads to reduced mechanical properties. The modeling results indicated that using EPDM foams as building thermal insulation can reduce the energy consumption of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems by up to 20%.
Reinforcing effect of thermo-oxidative reclaimed rubber on NR/SBR blends for tire tread applications
Yunhui Xu, Zaheer ul Haq, Junrong Li, Hui Tu, Zaixue Wang, Houluo Cong
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
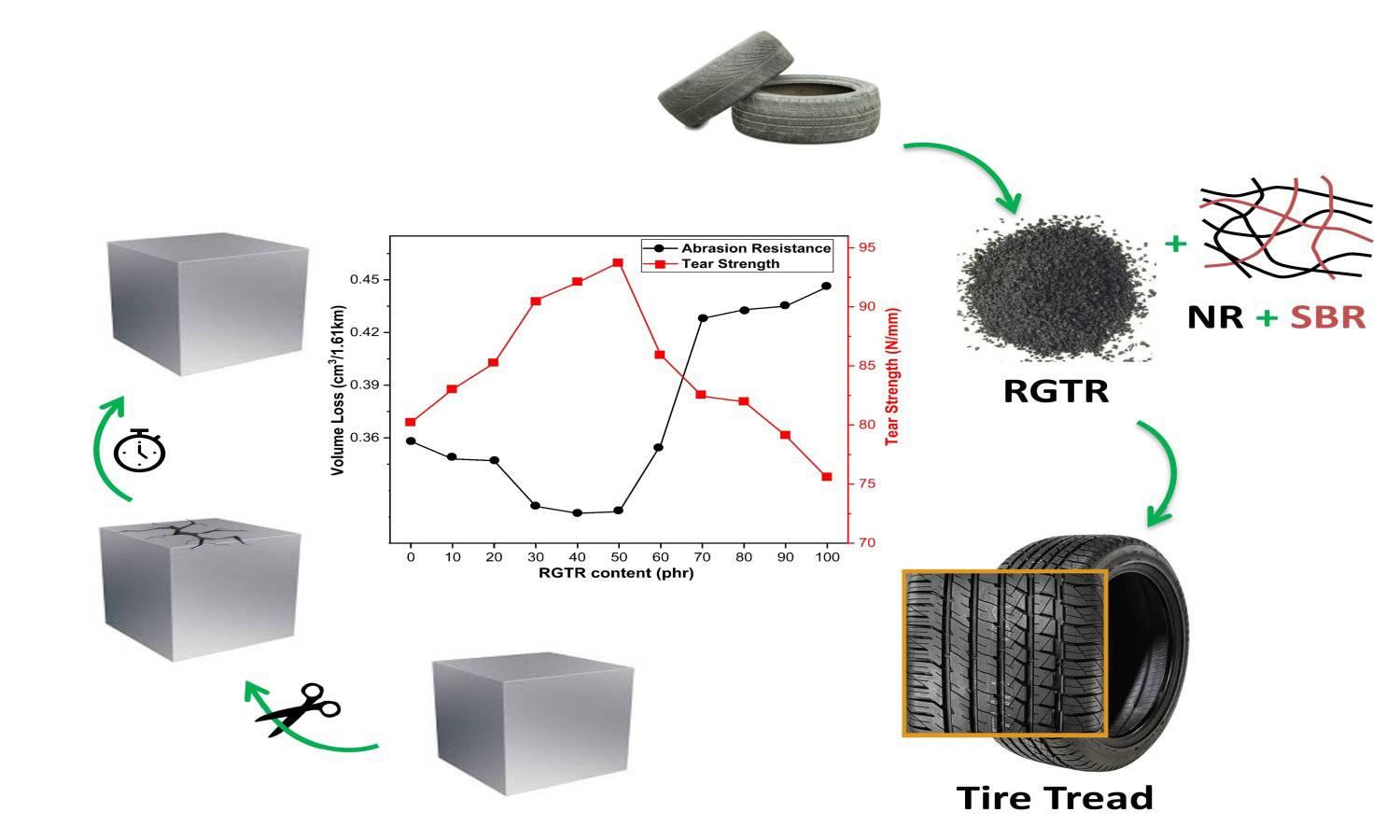
This study explores the application of thermo-oxidative reclaimed ground tire rubber (RGTR) in natural rubber (NR)/styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) composite, focusing on its impact on morphology, mechanical properties, rheological behavior, vulcanization characteristics, aging resistance, tear strength and abrasion resistance. The findings revealed that RGTR enhances the tear strength and abrasion resistance of NR/SBR composites while maintaining comparable tensile strength, elongation at break, and modulus. The incorporation of RGTR reduced Mooney viscosity of the NR/SBR composites and improved flowability. It also shortened the vulcanization time and enhanced vulcanization efficiency. The NR/SBR composites with RGTR loadings below 60 phr exhibited optimal performance, achieved a maximum tear strength of 93.77 N/mm and improved abrasion resistance. However, higher RGTR content led to increased agglomeration, as evidenced by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which showed finer dispersion at lower RGTR contents and larger aggregates at higher loadings. These findings demonstrate the potential of RGTR as a sustainable additive for enhancing specific properties in NR/SBR composites, contributing to both performance optimization and waste tire management.
Dibyendu Dey, Sharmistha Dhar, Barkat Aziz, Sambhu Bhadra, Sujith Nair, Kinsuk Naskar
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 127-141, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.11
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 127-141, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.11
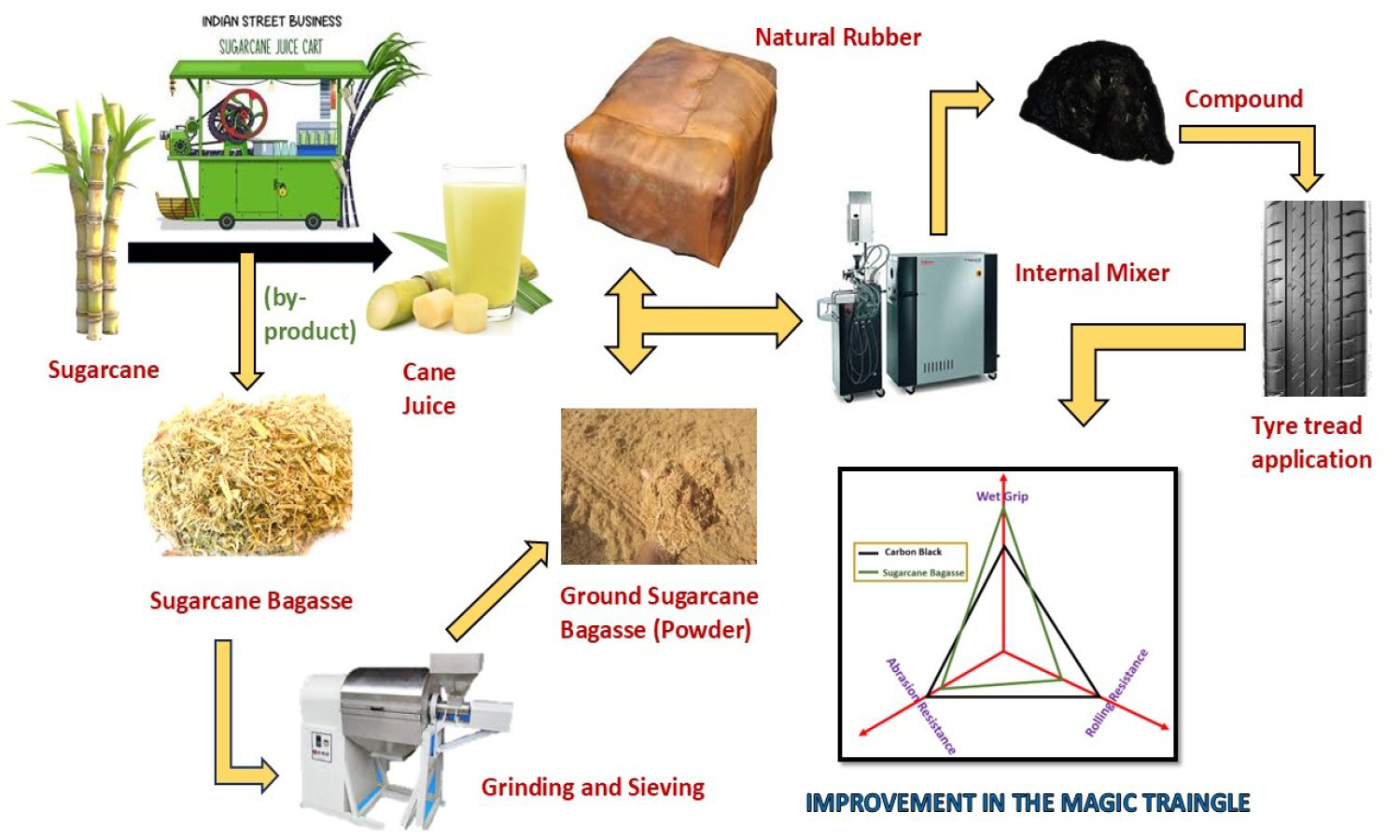
Ground sugarcane bagasse (GSB), an agro-waste rich in lignocellulosic components, was studied as a sustainable bio-filler in natural rubber (NR) tread compounds to lessen reliance on petroleum-derived carbon black (CB). A control formulation with 45 phr CB was compared to hybrid formulations with 40, 35, and 30 phr CB mixed with 5, 10, and 15 phr GSB. Tensile strength 13.1 MPa, elongation at break 700%, and hardness 67 Shore A were all optimally balanced by the compound containing 10 phr GSB (S2), while also exhibiting good cure behavior and thermal stability. Improved tire performance characteristics were confirmed by a dynamic mechanical study, which showed that tan δ at 60 °C decreased by 8.0% (resulting in lower rolling resistance) and increased by 3.9% (improving wet traction) at 0°C. The Payne effect showed improved filler dispersion as a result of GSB partially replacing CB. The results show that appropriately dispersed GSB can partially reinforce NR, enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. However, larger GSB loadings decrease modulus, tear strength, and abrasion resistance due to lower interfacial adhesion and the presence of micro-voids. According to this study, pulverized sugarcane bagasse shows promise as an environmentally friendly filler for green tire applications, promoting the circular economy and lowering the carbon footprint of rubber compounding.
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
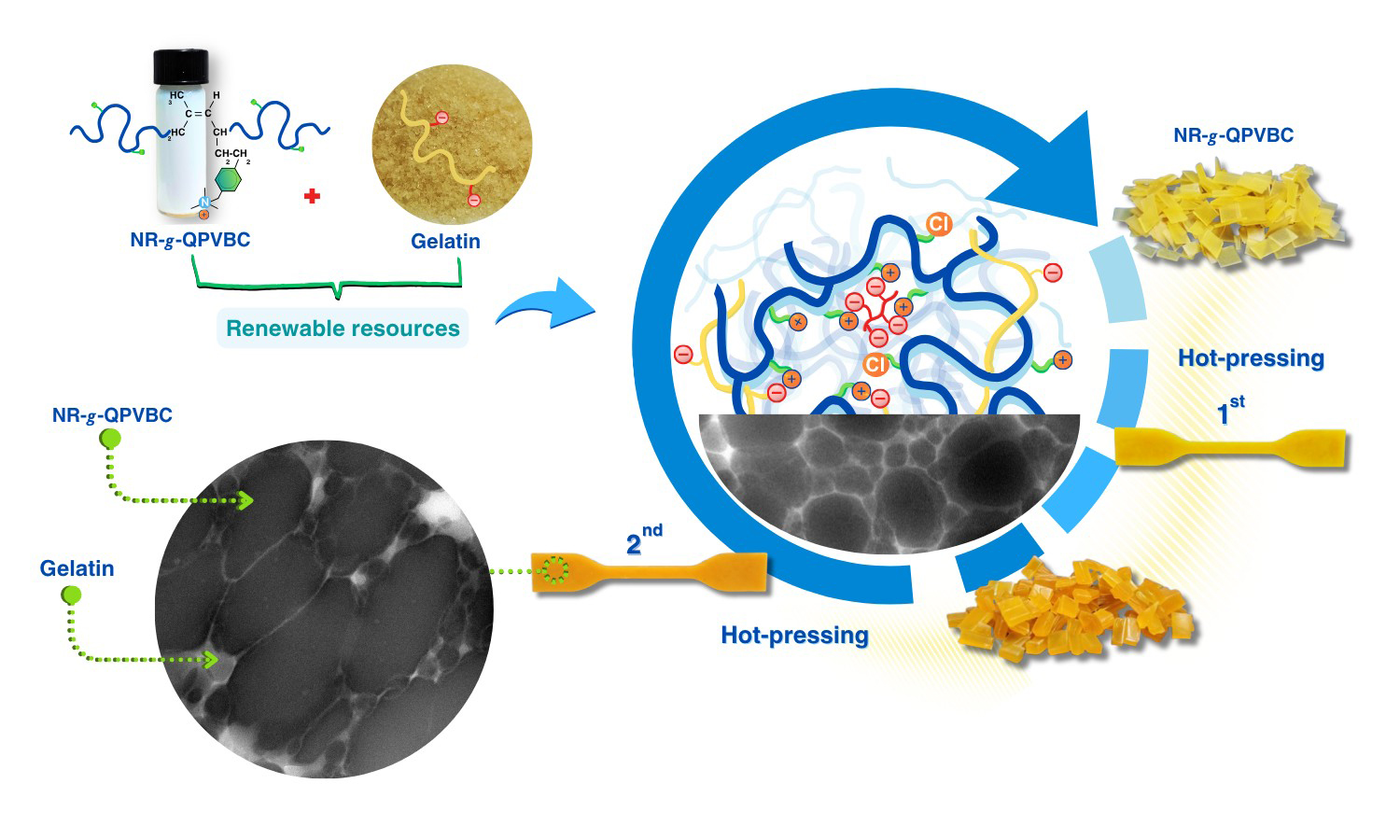
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Jutatip Makmanee Treitler, Diew Saijun, Kritsada Phatcharasit, Suwat Rattanapan
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1310-1319, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.96
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1310-1319, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.96
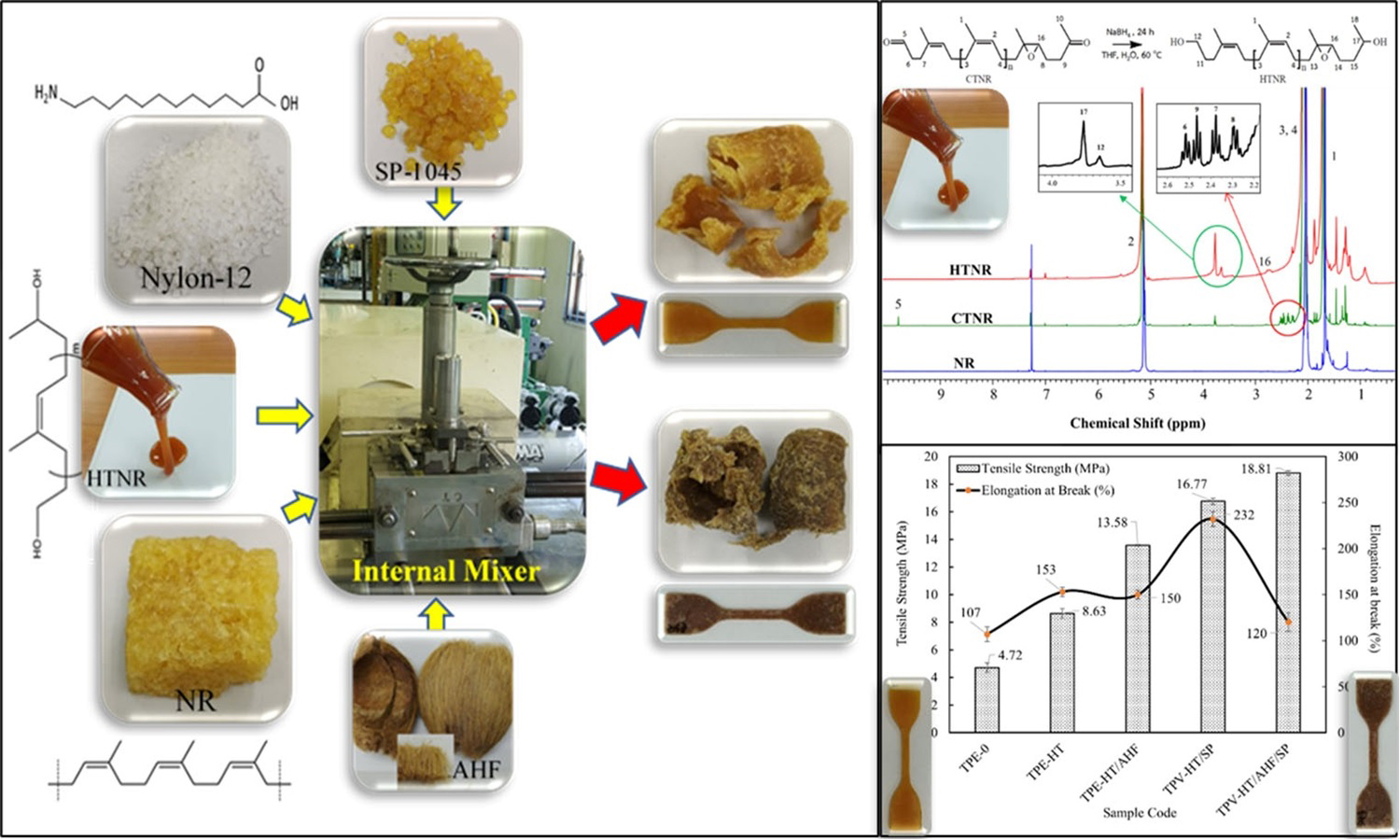
This work introduces an innovative method to enhance the compatibility of nylon-12/natural rubber thermoplastic elastomers by utilizing hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber as a reactive compatibilizer and natural fibers as reinforcement. Hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber was synthesized from natural rubber via oxidative cleavage to carbonyl telechelic natural rubber, followed by reduction with sodium borohydride. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) verified the structure. Incorporating hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber into nylon-12/natural rubber (40/60 wt%) blends significantly enhanced interfacial adhesion, improving tensile strength and elongation at break compared to the uncompatibilized mix. Dynamic vulcanization using phenolic resin achieved an optimal balance of strength and ductility. The incorporation of areca husk fiber enhanced tensile strength, hardness, and solvent resistance, with a slight decrease in ductility and tear strength. Rheological analysis indicated that hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber increased melt viscosity due to improved phase interactions, while dynamic vulcanization reduced the melt flow index through network formation. Solvent uptake experiments confirmed that hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber, areca husk fiber, and SP-1045 vulcanizing agent minimized swelling in isooctane, toluene, and diesel oil.




