Static and dynamic behaviour of ultra high molecular weight poly-ethylene (UHMWPE) Tensylon® composite
Vol. 18., No.10., Pages 1008-1022, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.77
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.77
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

ABSTRACT
Nowadays, ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), allows the combination of lightweight, high strength and is praised for the design of severely loaded structures. It has become a good option for lightweight armour solutions. It is therefore important to characterise its mechanical behaviour. Up to now, strain rate effects on mechanical behaviour have been poorly explored. In this work, this issue is tackled by studying the strain rate influence on the in-plane deformation, in shear and tension of the Tensylon® HSBD30A, a UHMWPE dedicated to ballistic and blast protection. Two laminates of Tensylon® of respective orientation [0 °/90°]20 and [±45°]20 were subjected to static and split Hopkinson tensile bar (SHTB) tests. A new mounting system was designed, and new specimen shapes were used to match the experimental setup configurations. Digital image correlation (DIC) was used to measure the in-plane strain. A significant strain-rate dependence on the material behaviour.is evidenced. Besides, results exhibit a higher strength for the [0°/90°]20 specimen than for the [±45°]20 one. Despite some limitations, the proposed setup and measurement methods allowed visualisation of strain rate effects on the stress-strain relationship for strain rates ranging from the quasi-static regime to the dynamic one (1500 s–1).
RELATED ARTICLES
Hamza Qayyum, Borhen Louhichi, Malik Hassan, Babar Ashfaq, Muhammad Sulaiman, Muhammad Bilal Khan, Nashmi H. Alrasheedi, Ghulam Hussain
Vol. 19., No.11., Pages 1173-1187, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.86
Vol. 19., No.11., Pages 1173-1187, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.86
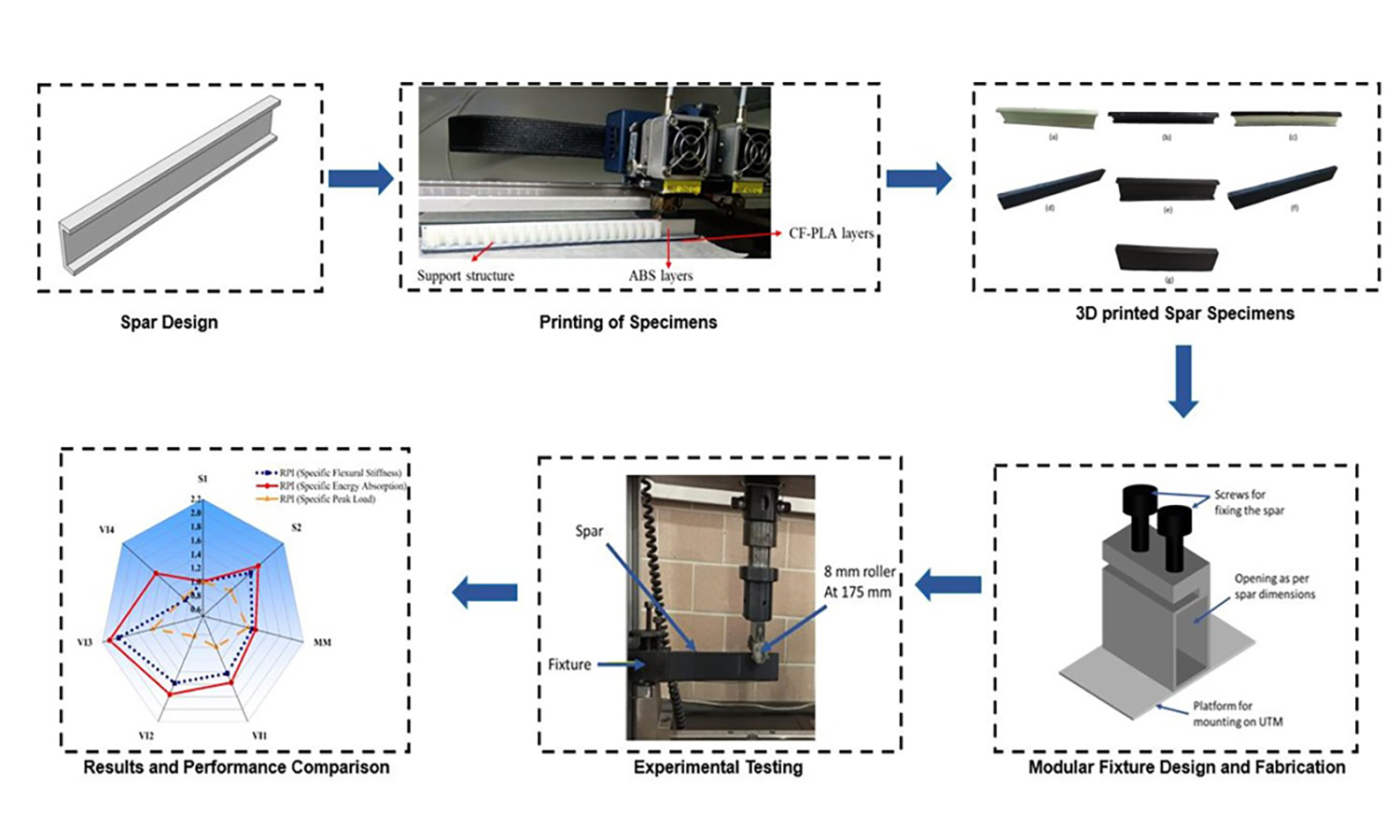
To reduce fuel consumption and extend flight time, the aerospace industry has focused on lightweight design. Achieving this without compromising structural integrity has been challenging. However, innovative additive manufacturing offers new opportunities for practical solutions. This study presents two methods: multi-material additive manufacturing (MMAM) and variable infill density additive manufacturing (VIDAM), aimed at reducing structural weight while maintaining mechanical performance. These methods were applied to a wing spar, a test geometry based on stress distribution principles from laminated beam mechanics. The structures produced with these new approaches showed improved mechanical responses compared to those made with traditional additive manufacturing techniques. A maximum increase of 91% in load-carrying capacity and a 34.8% increase in specific energy absorption were observed. scanning electron microscopy analysis revealed that layer bonding and material diffusion greatly influenced the mechanical performance. Although the study was conducted on small-scale models, the design concepts can be adapted to large-scale industrial applications that benefit from lightweight structures, such as the aerospace and automotive.
Rebeka Lorber, Janez Slapnik, Borut Černe, Andreas Hausberger, Jan Sumfleth
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1073-1089, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.80
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1073-1089, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.80
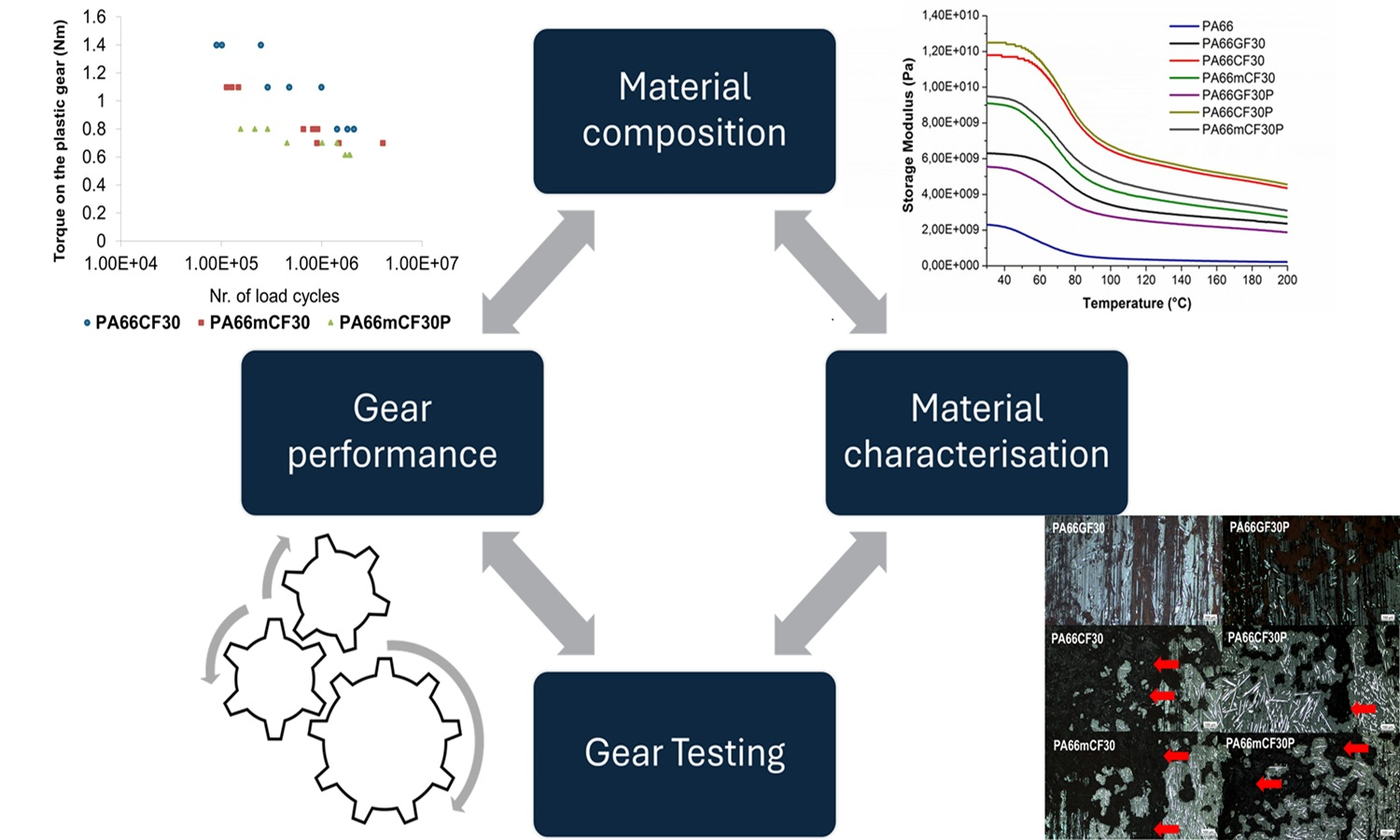
The study investigates the use of repurposed milled carbon fibre (mCF) as reinforcement for polyamide 66 (PA66) in gear applications, addressing environmental and cost concerns of virgin carbon fibres. Neat PA66 and PA66 composites reinforced with mCF, glass fibres (GF), and carbon fibres (CF), with and without polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), were injection moulded and evaluated for microstructure (fibre length), thermal, mechanical, surface, and tribological properties, as well as gear performance under VDI 2736 guidelines. CF reinforced composites showed the highest modulus and tensile strength, followed by mCF and GF. PTFE reduced modulus and strength in binary composites. All reinforced composites significantly lowered the coefficient of friction (COF) and wear rate compared to neat PA66, with mCF showing the most notable improvements. PTFE slightly improved tribological performance only for GF (wear) and CF (COF) composites. In gear testing, binary composites outperformed neat PA66, with CF performing best, followed by mCF and GF. Ternary composites had slightly lower performance than their binary equivalents. Correlation analysis showed that gear performance is closely linked to structural integrity. Failure analysis revealed higher crack susceptibility in mCF reinforced gears due to shorter fibre length. The findings highlight mCF reinforced PA66 as a sustainable, cost-effective material for durable polymer gears.
Xue Xu, Rujie Li, Li Gao, Beibei Sun, Hongming Liu, Shiai Xu
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 959-976, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.72
Vol. 19., No.9., Pages 959-976, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.72
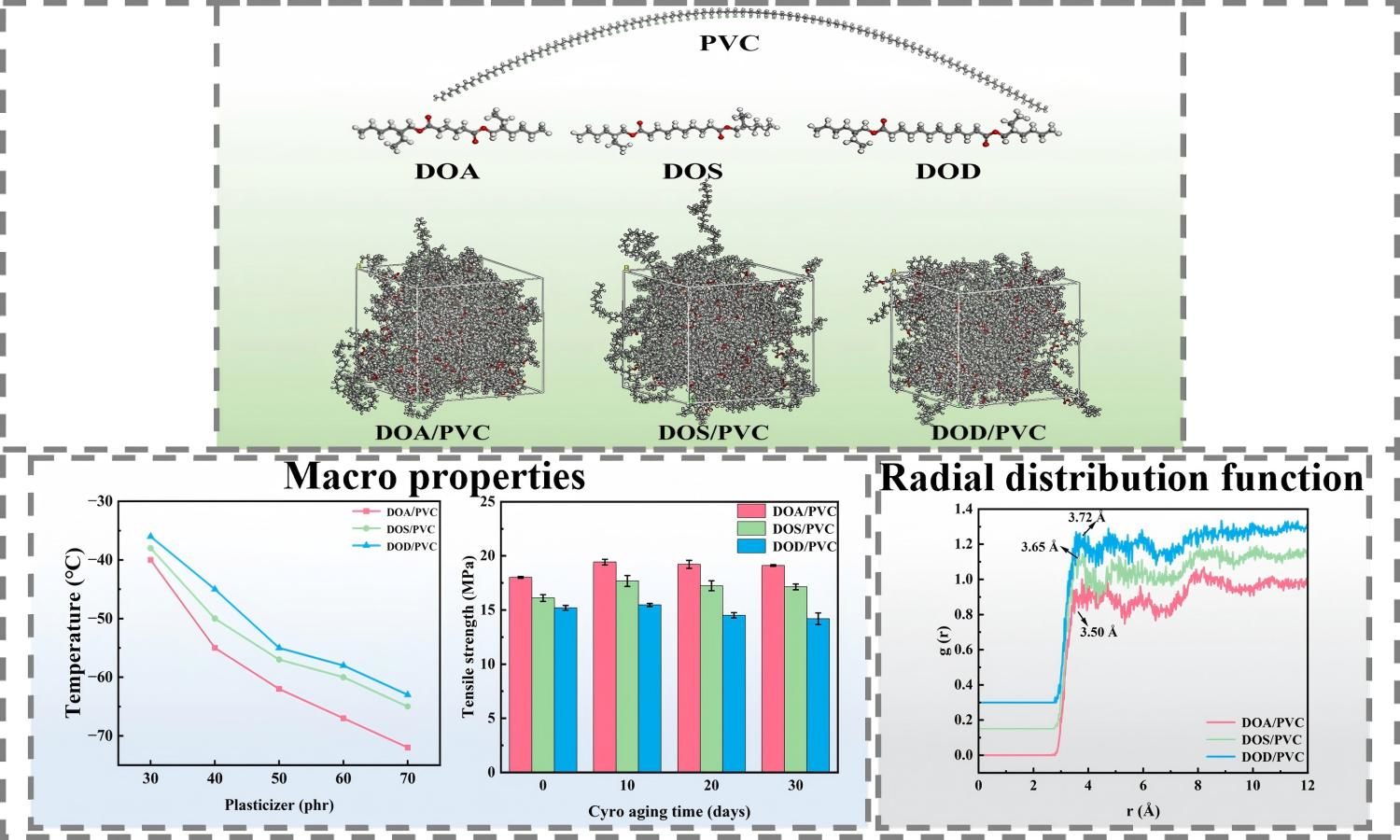
As polyvinyl chloride (PVC) films are hard and brittle in a low-temperature environment, aliphatic dibasic acid ester plasticizers with different acid chain lengths were fabricated, i.e. di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate (DOA), di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate (DOS) and dioctyl dodecanedioate (DOD), and their effects on the cold-resistant properties of PVC were investigated using experiments and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The brittleness temperature and tensile properties of plasticizers/PVC are negatively related to the acid chain length of the aliphatic dibasic acid esters. The brittleness temperatures of the three systems are all below –50 °C. In-situ low-temperature tensile tests and aging tests indicate that DOA/PVC exhibits the best cold resistance and stability. MD simulations further reveal that the best compatibility between DOA and PVC is attributed to its strong binding energy and weak hydrogen bonding interactions, while van der Waals forces are dominant in DOS/PVC and DOD/PVC. This study elucidates the structure-property relationship between aliphatic dibasic acid ester plasticizers and PVC from the perspective of molecular interactions, and provides insights into the design of cold-resistant PVC plasticizers.
Maria Casapu, Ion Fuiorea, Michel Arrigoni
Vol. 18., No.1., Pages 41-60, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.4
Vol. 18., No.1., Pages 41-60, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.4

Composite materials are of increasing interest in aircraft and spacecraft structures, and carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) have emerged as materials meeting quality standards for structural applications in the aircraft industry. Despite their high mechanical properties, CFRPs are associated with high production costs. Building on recent research by the authors, this paper investigates the use of ply-level hybridization to reduce manufacturing costs while maintaining the mechanical performance of the manufactured material. Focusing on the causes of nonlinear response under off-axis tensile loading, the paper involves cyclic load-unload (LU) tensile tests conducted at off-axis angles of 15°, 30°, and 45° to predict mechanical characteristics and damage evolution. Residual strains are directly extracted from load-unload stress-strain responses. Three distinct methods for estimating cycle modulus are employed and compared for damage variable formulation. The research findings reveal dependencies of both the damage variable and residual strains on the off-axis angle. Furthermore, the method used to assess the modulus during cycling loading significantly influences the damage variable estimation. Encouragingly, the hybrid laminates exhibit reduced internal damage and matrix plasticity compared to reference counterparts, indicating a positive effect on the mechanical performances of hybridized CFRPs in addition to the cost reduction.




