Cyclization of natural rubber (NR) latex: Synthesis, characterization and application in NR compounds and as a compatibilizer in NR/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) blends
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 753-772, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
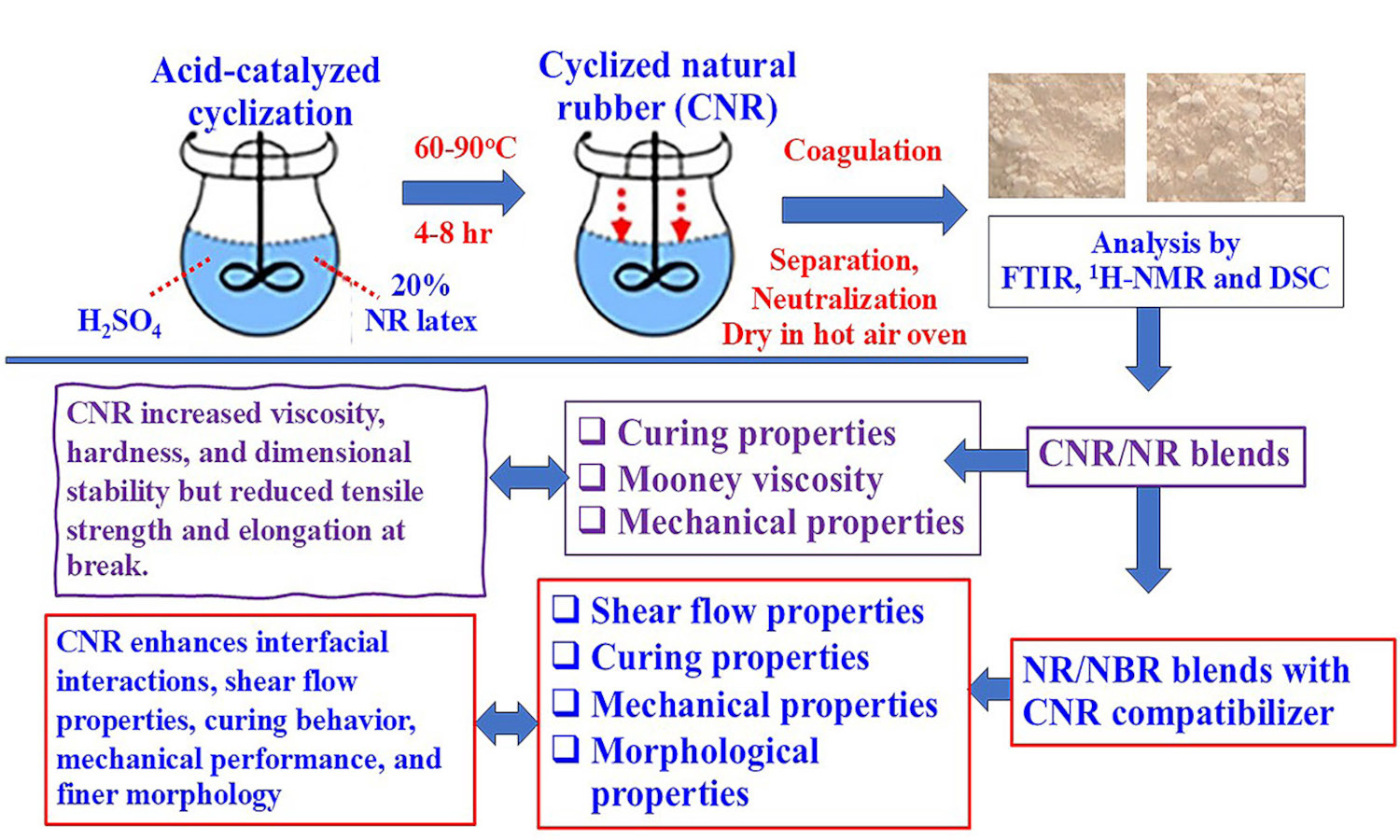
Cyclized natural rubber (CNR) was synthesized through the acid-catalyzed reaction of natural rubber (NR) latex using sulfuric acid as a catalyst and stabilized with a non-ionic surfactant. Cyclization was evaluated by iodine numbers under varying reaction times, temperatures, and NR-to-acid ratios. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR) confirmed the formation of cyclic structures in CNR molecules. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that the glass transition temperature (Tg) of CNR increased with cyclization, indicating greater rigidity and less chain flexibility. CNR was then blended with NR and used as a compatibilizer in NR/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)blends. It increased blend viscosity, hardness, and dimensional stability but reduced tensile strength and elongation due to its rigid cyclic domains. In NR/NBR blends, CNR outperformed a commercial homogenizer in enhancing interfacial interactions, leading to superior shear flow properties, curing behavior, and mechanical performance. This is attributed to the polar groups in CNR, which enhance intermolecular interactions and phase compatibility, resulting in finer phase morphology. This study highlights the potential of CNR as a versatile material for enhancing the performance of rubber compounds, with promising applications in advanced industrial formulations.
RELATED ARTICLES
Xavier Colom, Scott Martínez, Fernando Carrillo-Naverrete, Javier Cañavate
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 114-126, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.10
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 114-126, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.10
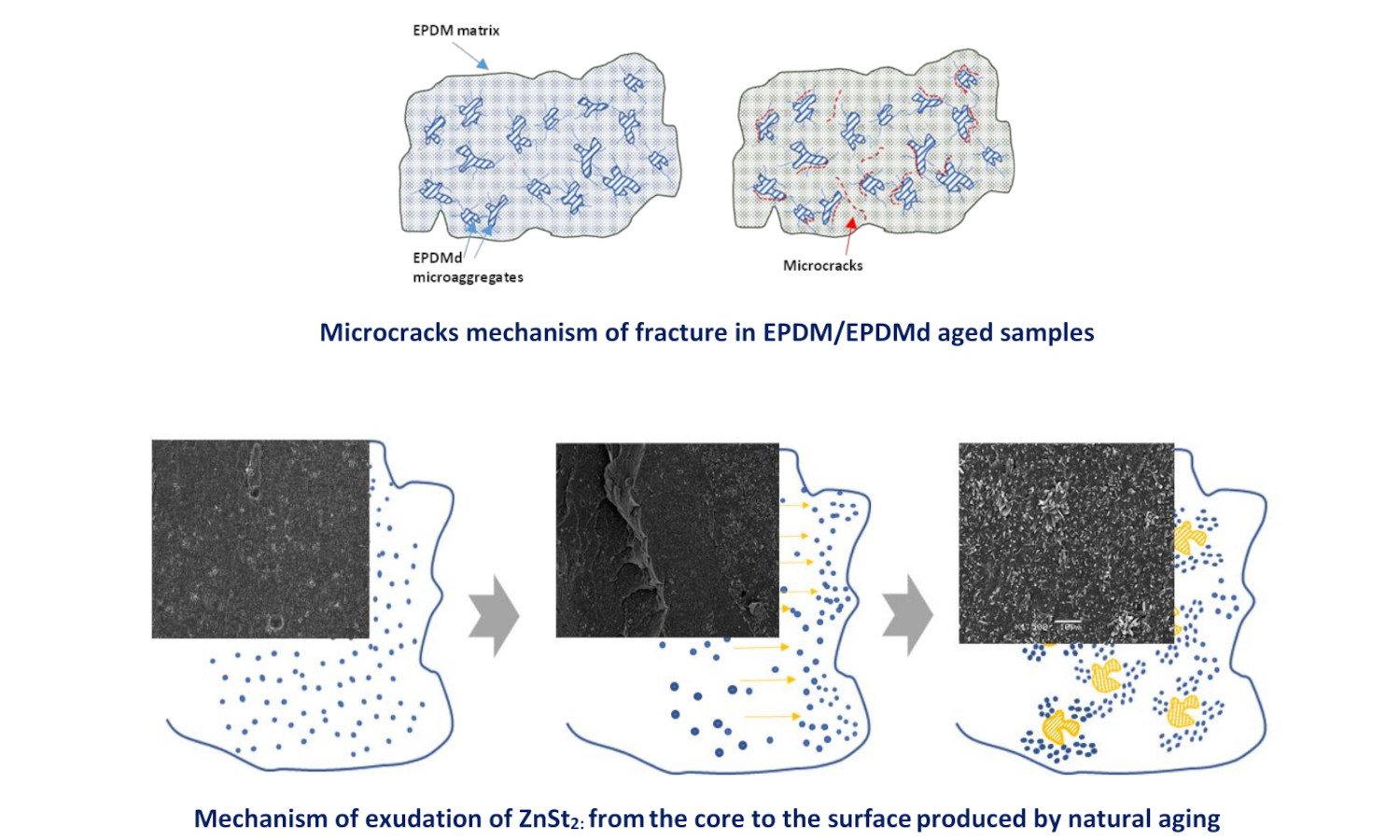
The need to recycle elastomeric waste requires studying its viability in industrial applications. This study investigates the feasibility of recycling elastomeric waste by analyzing whether virgin ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) can be replaced by blends of virgin EPDM and thermomechanically and microwave devulcanized EPDM (EPDMd) in industrial applications from the perspective of environmental degradation. Two types of samples were examined: conventional EPDM used to roof membranes, and EPDM blended with different amounts (20, 40, and 50 phr) of EPDMd. Samples were subjected to natural aging in coastal and mountainous environments. Results show that mechanical properties decline with higher EPDMd content and, to a lesser degree, with prolonged outdoor exposure. The coastal climate proved more aggressive than the mountainous one when EPDMd content exceeded 40 phr. Zinc stearate (ZnSt2), a byproduct of vulcanization, was found to influence the evolution of the mechanical behavior. The combined analysis of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), abrasion tests, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) provided insights into the degradation processes of these elastomeric blends.
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
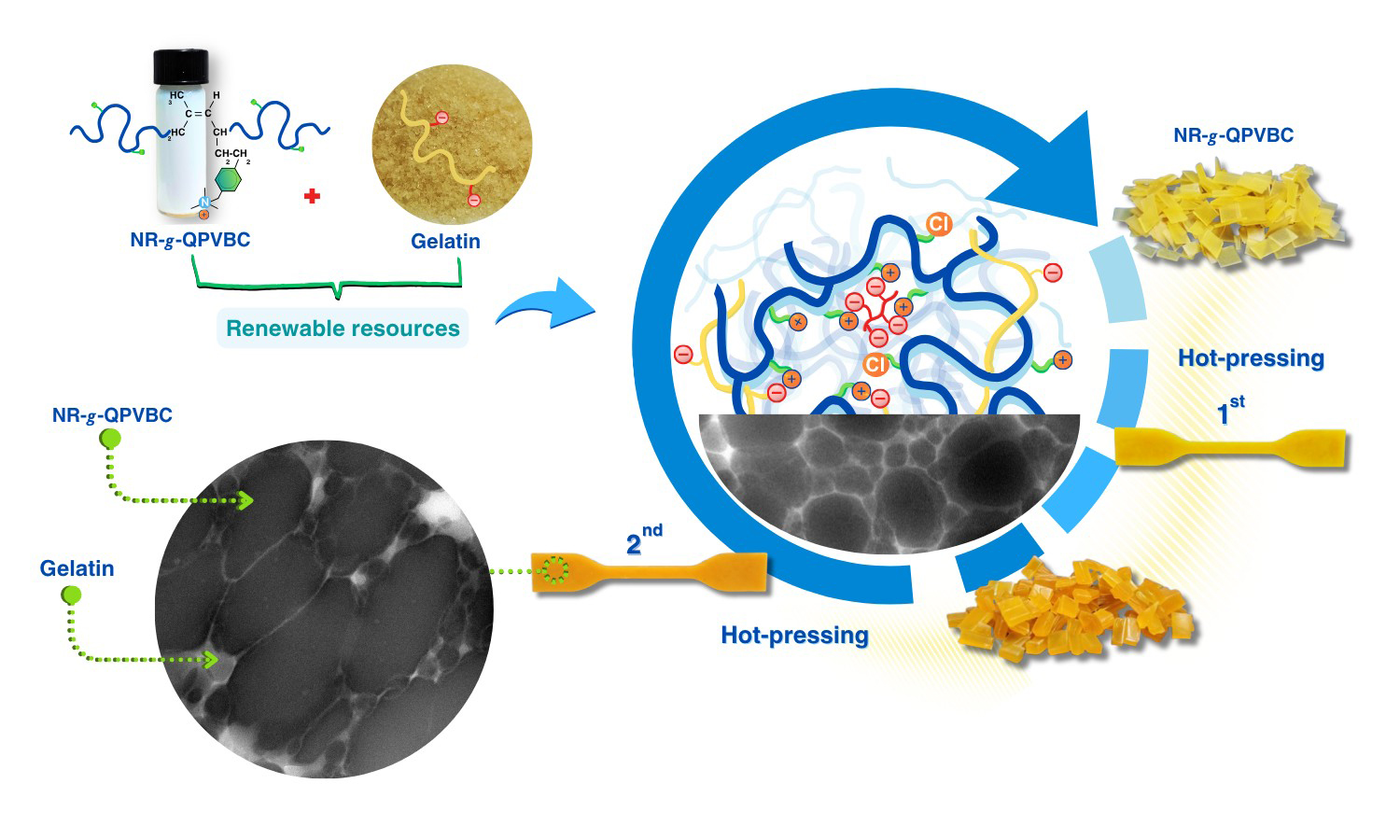
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Hatay Cöcen, Nilgün Kızılcan
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 82-96, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.7
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 82-96, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.7
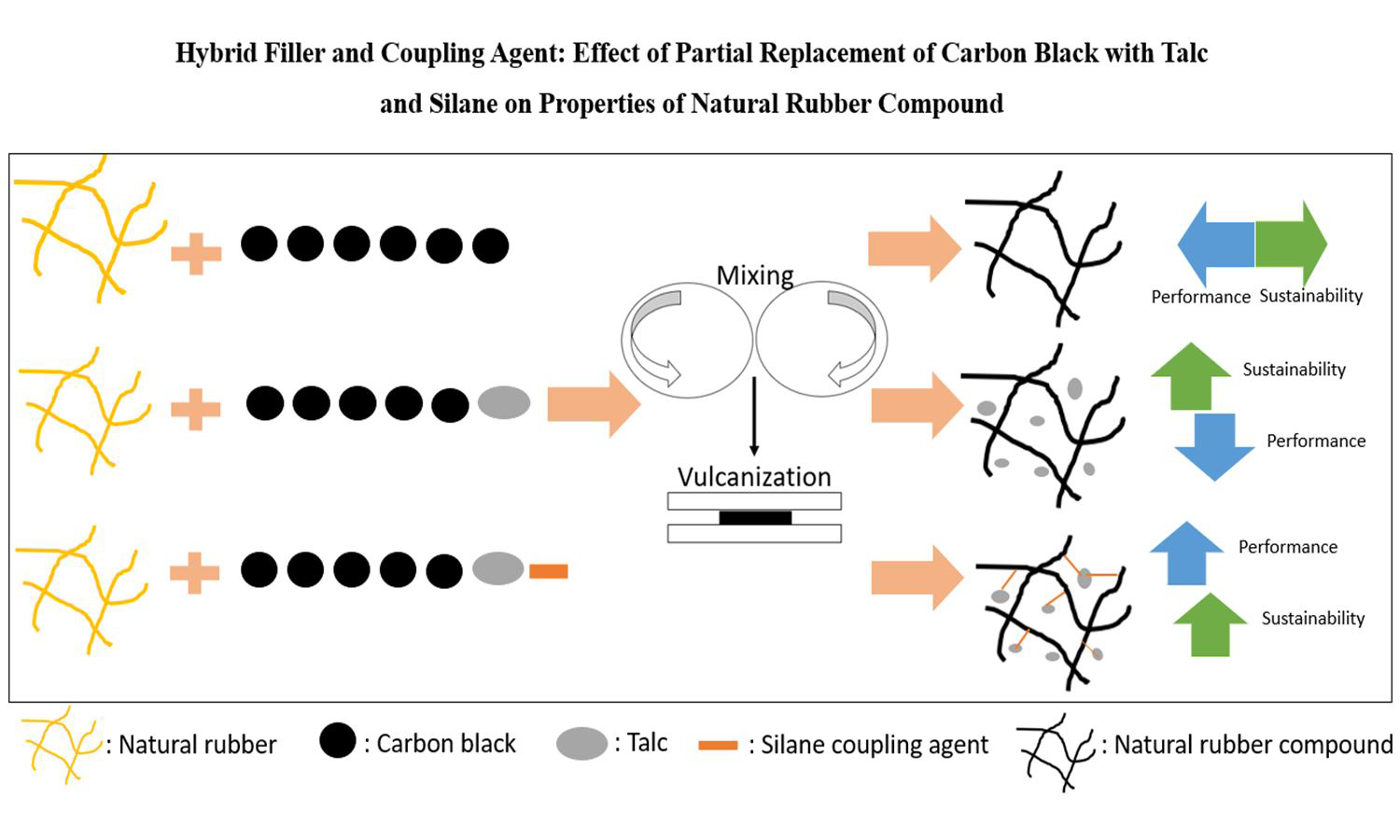
This study investigates a sustainable hybrid-filler strategy for natural rubber (NR) compound by partially replacing petroleum-based carbon black (CB) with talc and introducing a silane coupling agent to mitigate interfacial incompatibility. Compounds containing CB, CB+talc and CB+talc+increasing silane were produced via two-stage mixing and characterized for morphology (dispersion/mapping), curing and flow behavior (differential scanning calorimetry DSC/moving die rheometer, MDR/Mooney), crosslink density (Flory–Rehner), physical–mechanical properties, dynamic performance (Payne effect/heat build-up/tension–fatigue), and thermal stability (aging/thermogravimetric analysis,TGA). Talc reduced the compound viscosity, offering processing benefits. The swelling test indicated that talc decreased crosslink density, but silane recovered it, forming covalent linkages. Tensile strength and elongation at break were improved without altering hardness. Dynamically, talc increased heat build-up, whereas silane inverted the trend and reduced the temperature rise gradually from 41.5 to 29.4°C at 2 phr. Fatigue life was improved with talc (~10%), and further with silane (up to 36% at 2 phr), highlighting a favorable stiffness–fatigue balance with compatibilization. Overall, partial CB replacement by talc, in combination with silane, delivers meaningful sustainability gains with improved dynamic performance while preserving key mechanical properties of NR compounds.
Jutatip Makmanee Treitler, Diew Saijun, Kritsada Phatcharasit, Suwat Rattanapan
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1310-1319, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.96
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1310-1319, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.96
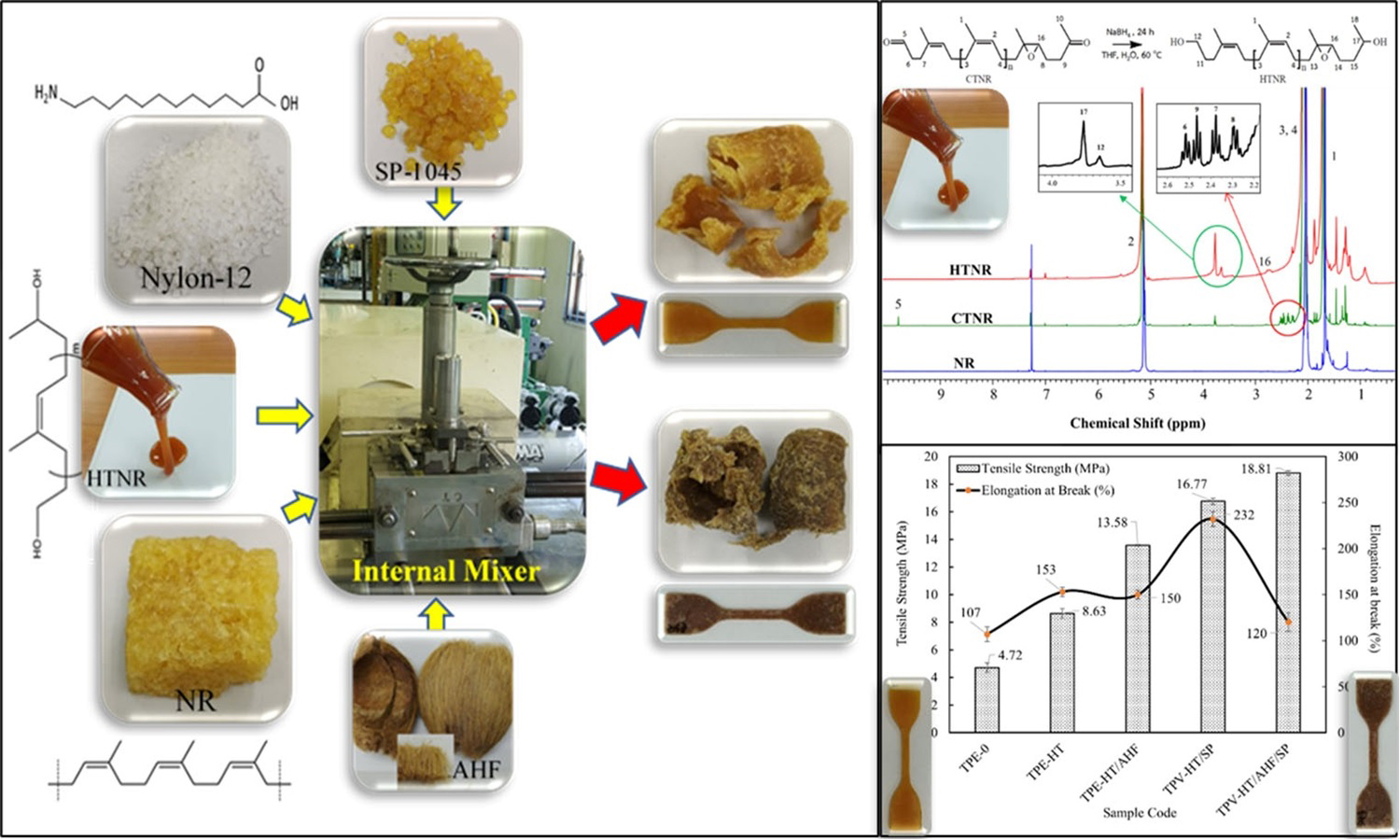
This work introduces an innovative method to enhance the compatibility of nylon-12/natural rubber thermoplastic elastomers by utilizing hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber as a reactive compatibilizer and natural fibers as reinforcement. Hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber was synthesized from natural rubber via oxidative cleavage to carbonyl telechelic natural rubber, followed by reduction with sodium borohydride. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) verified the structure. Incorporating hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber into nylon-12/natural rubber (40/60 wt%) blends significantly enhanced interfacial adhesion, improving tensile strength and elongation at break compared to the uncompatibilized mix. Dynamic vulcanization using phenolic resin achieved an optimal balance of strength and ductility. The incorporation of areca husk fiber enhanced tensile strength, hardness, and solvent resistance, with a slight decrease in ductility and tear strength. Rheological analysis indicated that hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber increased melt viscosity due to improved phase interactions, while dynamic vulcanization reduced the melt flow index through network formation. Solvent uptake experiments confirmed that hydroxyl telechelic natural rubber, areca husk fiber, and SP-1045 vulcanizing agent minimized swelling in isooctane, toluene, and diesel oil.
Torfan Srisuwanno, Jobish Johns, Christopher Bascucci, Frank Clemens, Yeampon Nakaramontri
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1053-1072, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.79
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 1053-1072, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.79
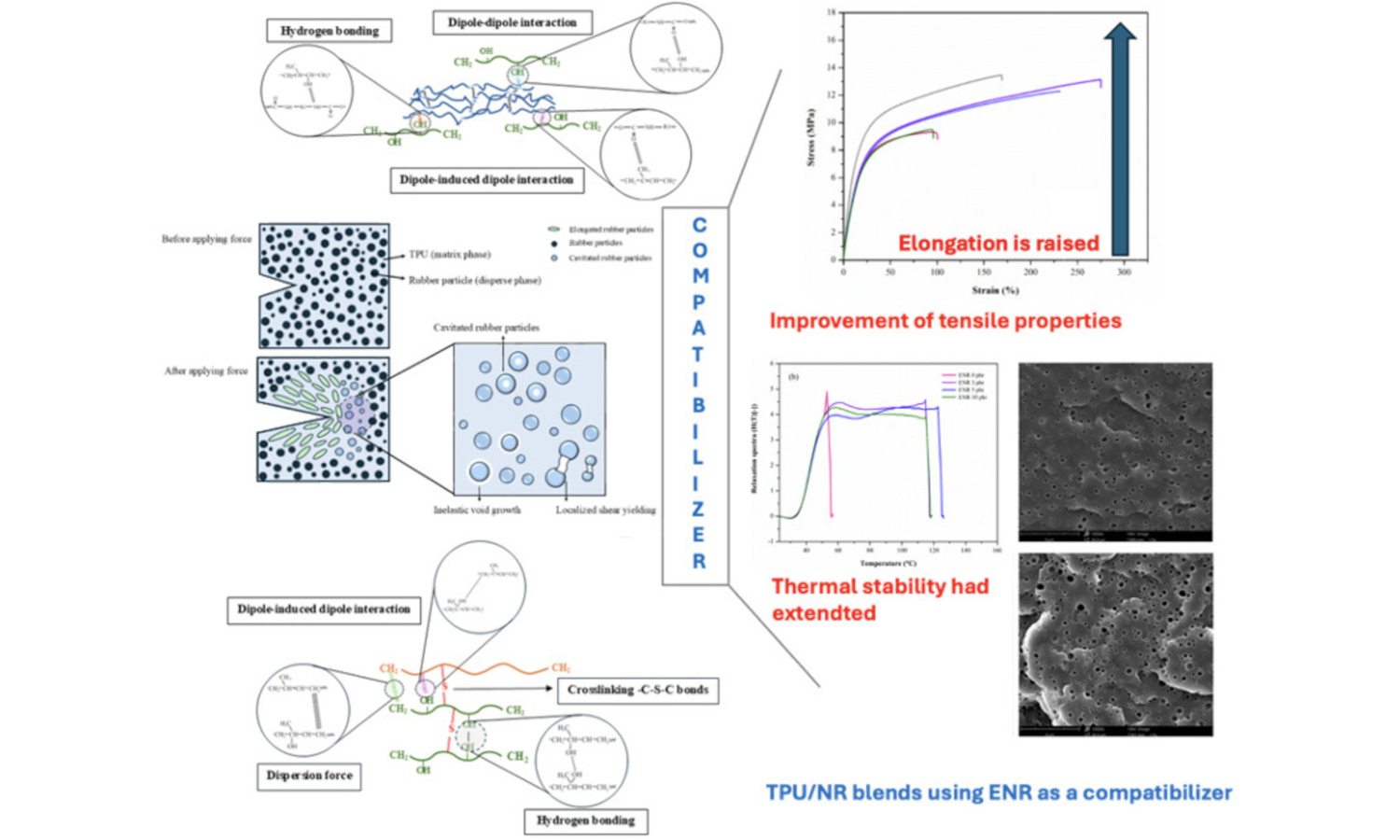
Thermoplastic natural rubber (TPNR) is widely used across industries due to its unique blend of elasticity and processability. Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) based on thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) offer excellent mechanical properties and flexibility, yet often require enhanced elasticity and durability. Blending TPU with natural rubber (NR) is promising; however, phase incompatibility reduces mechanical strength and thermal stability. To address this, epoxidized NR (ENR) was employed as a compatibilizer in TPU/NR blends. ENR’s hydrocarbon backbone interacts with crosslinked NR, while epoxy groups enhance adhesion with TPU. Incorporating 3 phr of ENR significantly improved crosslinking, increased tensile strength by 41.1%, enhanced stress relaxation, and lowered the glass transition temperatures of both TPU and NR phases in the TPU/NR blends. These effects are attributed to improved chemical bridging between TPU and NR. However, excess ENR disrupts phase compatibility, causing polymer entanglement and reduced strength. Optimizing ENR content is essential for developing high-performance TPU/NR blends. Printability was demonstrated using the material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEx-AM) fused deposition modeling (FDM), showing potential for flexible applications like splints and medical devices.




