Effect of curing system and blowing agent content on the cellular morphology, mechanical and thermal properties of EPDM foam
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 311-323, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
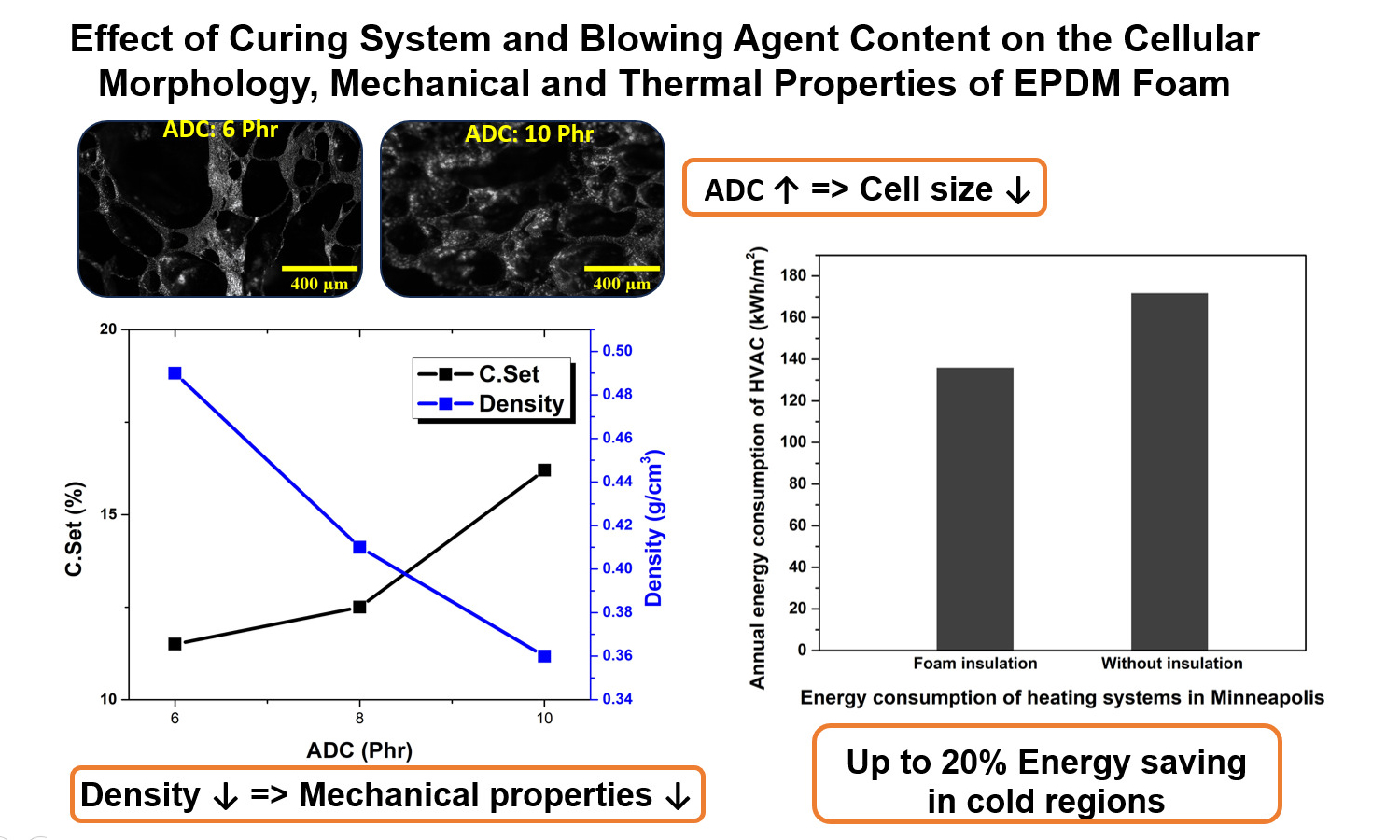
ABSTRACT
In this study, the effect of the amount of blowing agent and the type of sulfur curing system on the cellular structure, thermal, and mechanical properties of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) foam was investigated. Three types of sulfur curing systems including efficient, semi-efficient and conventional and three variable levels of azodicarbonamide (ADC) were considered; as a result, nine EPDM foam formulations were evaluated. Curing process parameters were measured using cure rheometry and cellular structure was examined by optical microscopy images, determining the average cell size and size distribution. For evaluating physical and mechanical properties, density and compression set tests were performed. Thermal conductivity tests were conducted on selected samples. Building energy modeling was performed using DesignBuilder software to evaluate the thermal insulation performance of the foams. The results showed that the type of curing system and the amount of ADC significantly affect cell morphology, density, and mechanical properties. Overall, a decrease in density leads to reduced mechanical properties. The modeling results indicated that using EPDM foams as building thermal insulation can reduce the energy consumption of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems by up to 20%.
RELATED ARTICLES
Reinforcing effect of thermo-oxidative reclaimed rubber on NR/SBR blends for tire tread applications
Yunhui Xu, Zaheer ul Haq, Junrong Li, Hui Tu, Zaixue Wang, Houluo Cong
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
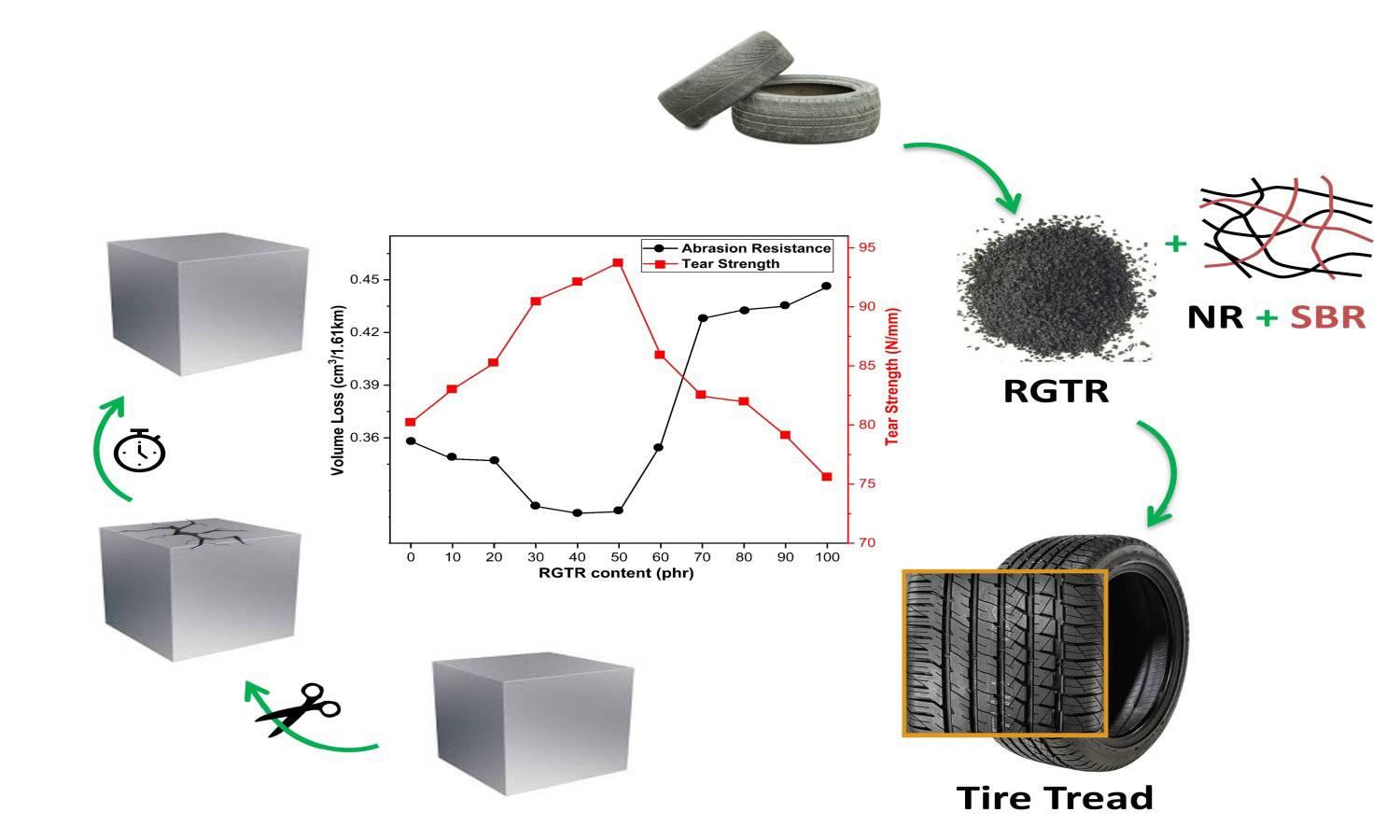
This study explores the application of thermo-oxidative reclaimed ground tire rubber (RGTR) in natural rubber (NR)/styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) composite, focusing on its impact on morphology, mechanical properties, rheological behavior, vulcanization characteristics, aging resistance, tear strength and abrasion resistance. The findings revealed that RGTR enhances the tear strength and abrasion resistance of NR/SBR composites while maintaining comparable tensile strength, elongation at break, and modulus. The incorporation of RGTR reduced Mooney viscosity of the NR/SBR composites and improved flowability. It also shortened the vulcanization time and enhanced vulcanization efficiency. The NR/SBR composites with RGTR loadings below 60 phr exhibited optimal performance, achieved a maximum tear strength of 93.77 N/mm and improved abrasion resistance. However, higher RGTR content led to increased agglomeration, as evidenced by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which showed finer dispersion at lower RGTR contents and larger aggregates at higher loadings. These findings demonstrate the potential of RGTR as a sustainable additive for enhancing specific properties in NR/SBR composites, contributing to both performance optimization and waste tire management.
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
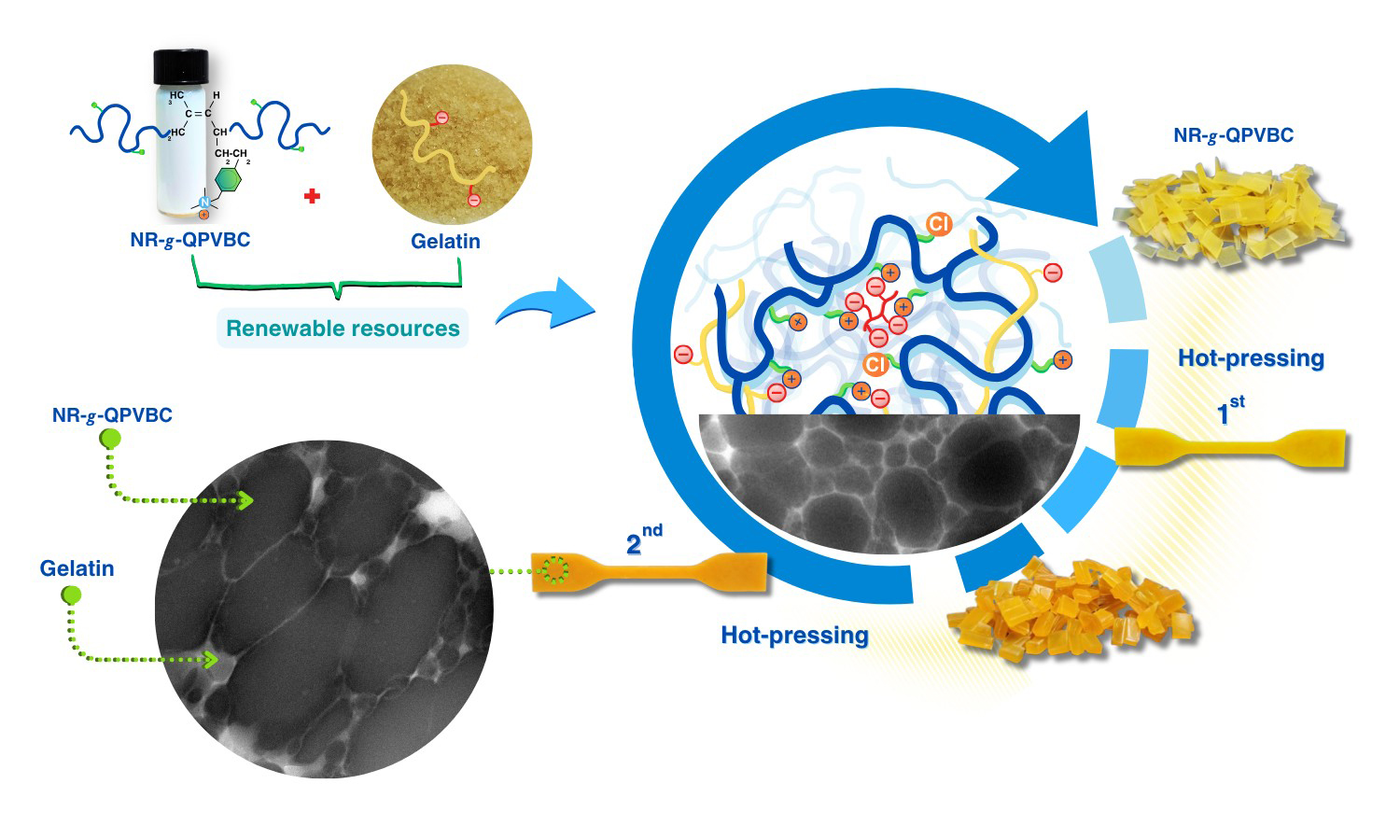
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Zeshang Jiang, Jiacheng Yu, Wuchao Cheng, Zhenxiang Xin, Jieting Geng, Lin Xia
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 372-385, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.28
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 372-385, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.28
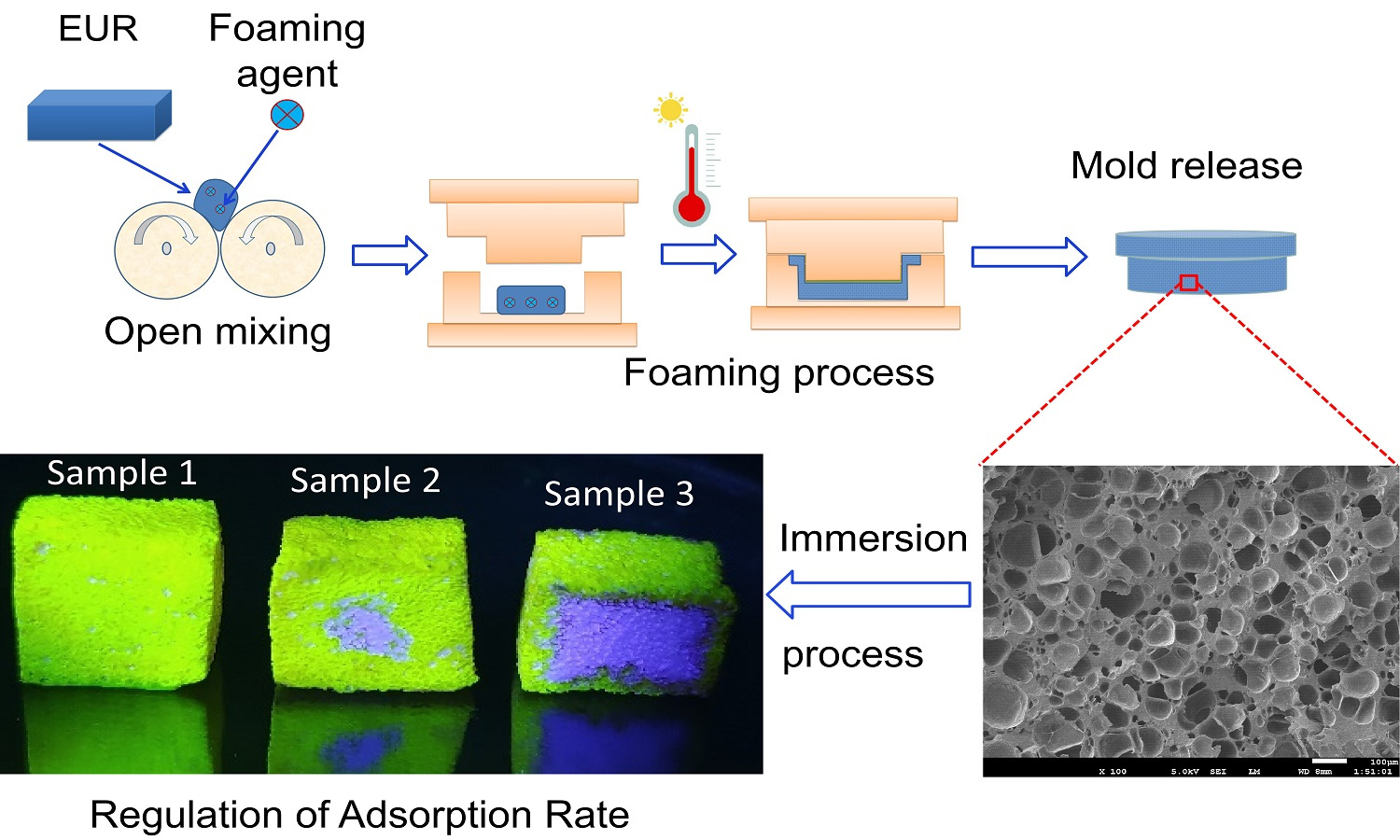
Inspired by the micro structure of loofah sponge in nature, this article successfully employs a biomimetic approach to develop a novel series of natural Eucommia rubber foamed materials with excellent shape memory properties. This article explores the characteristic features of natural Eucommia ulmoides rubber foamed materials, including the foaming process, mechanical properties, shape memory performance, and adsorption properties. This paper introduces the innovative use of natural Eucommia ulmoides rubber’s shape memory properties to create a temperature-responsive foam adsorbent material. The foamed material’s unique ability to modify its pore structure through simple compression and heating processes offers tailored adsorption speed and capacity for varied practical applications. The adjustable adsorption properties of this foamed material present novel opportunities for its utilization in adsorption applications.
Kriengsak Damampai, Kanoknan Boonpan, Yeampon Nakaramontri
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 409-422, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.30
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 409-422, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.30

This study investigated the properties of the natural rubber (NR) foam filled with azodicarbonamide (ADC) blowing agents by combination to various ratios of epoxidized NR (ENR) for flexible foam applications. Compound operation was prepared with an open two-roll mill and the production was fabricated by compression molding. The study elucidated properties related to crosslinking behaviors, mechanical and dynamic properties, elasticity, abrasion, weathering resistance, and sound absorption efficiency. The ENR and ADC concentrations affected the tensile testing and also the durability properties of the NR/ENR. The NR and ENR foam of 60/40 filled with 10 phr of ADC demonstrated good properties across various parameters, showing acceptable tensile properties, abrasion resistance, and QVA light resistance. Additionally, the presence of a closed-cell structure in the blends reduced crack propagation in the NR matrix during aging, improving weathering resistance. The absorption coefficient increased with higher ADC content, being optimal at 15 phr, due to the lower density and higher porosity of the opened-cell material, which enhances its ability to interact more effectively with incoming energy at 1600 and 6400 Hz. The findings encourage the use of ENR for blending in NR for improved ENR and ADC concentrations since dipole-dipole interaction from ENR-ADC caused ADC dispersability, providing complexed foam structures for force expansion and aslo sound wave absorption.
Marek Pöschl, Radek Stoček, Petr Zádrapa, Martin Stěnička, Gert Heinrich
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1178-1190, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.90
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1178-1190, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.90
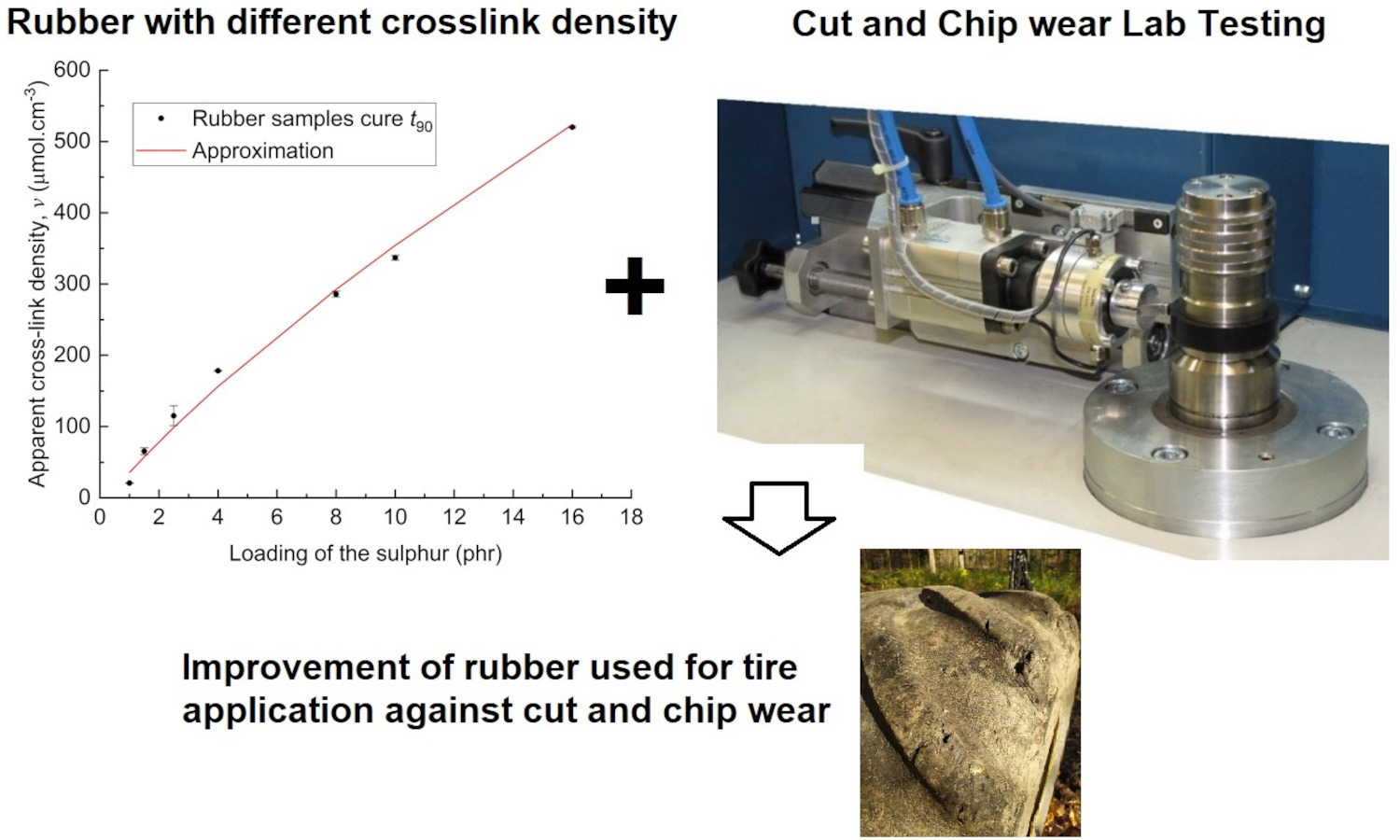
This paper extends previous studies by the authors that aimed to describe the effect of apparent cross-link density (CLD) of the rubber polymer networks on the fracture mechanism caused by cut and chip (CC) wear of natural rubber (NR), demonstrating the positive effect of conventional vulcanization (CV). This work is focused on the determination of the effect of CLD while keeping constant the accelerator-to-sulfur ratio A/S = 0.2, typical for CV systems. For this ratio, different sulfur quantities were chosen, and the concentration of the accelerator N-tert-butyl-benzothiazole sulphonamide (TBBS) was calculated to achieve CLDs in a range from 35 to 524 μmol・cm–3. Standard analyses such as tensile tests, hardness, rebound resilience and DIN abrasion were performed. From these analyses, the optimum physical properties of the NR-based rubber were estimated to be in the CLD range of approximately 60 to 160 μmol・cm–3. A CC wear analysis was performed with an Instrumented cut and chip analyzer (ICCA) and it was found that the highest CC wear resistance of the NR is in the CLD range of 35 to 100 μmol・cm–3. Furthermore, the effect of straininduced crystallization (SIC) of NR on CC wear and its dependence on the CLD region was discussed. For the first time, we determine a CLD range for a CV system in which the material achieves both optimal mechanical properties and CC wear resistance.




