Thermally expandable microspheres with excellent high-temperature expansion property
Jing Zhang, Tinghui Yan, Hongli Zhang, Ye Fang, Yuzhong Huang, Jijun Tang, Mingyang He
Vol. 16., No.7., Pages 760-771, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.55
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.55
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
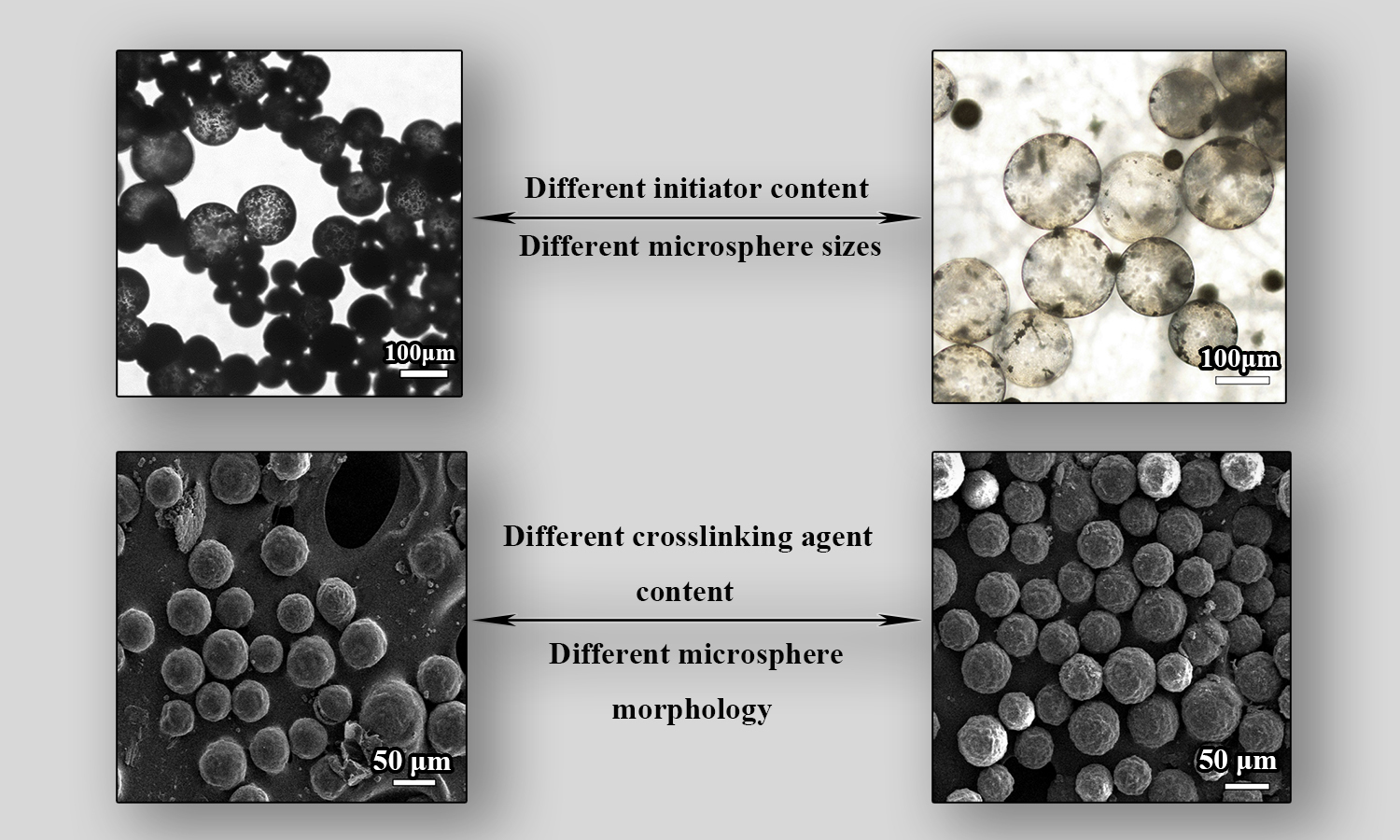
Core-shell thermally expandable microspheres (TEMs) were prepared via Pickering suspension polymerization. Acrylonitrile (AN), methacrylic acid (MAA) and N,N-dimethylacrylamide (DMAA) were used as the comonomers, the 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) was used as the initiator and the ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) was used as the crosslinker. The effects of initiator concentration, cross-linking agent concentration and modified monomer type on the morphology, thermal properties and encapsulation content of TEMs were investigated. The results show that the small change in initiator concentration had a significant effect on the properties of TEMs. When the initiator concentration was 0.55%, the microspheres showed core-shell structure and the maximum expansion ratio was 3.06 times. According to the scanning electron microscope (SEM) image, the heat resistance of the microspheres increased with the increase of the content of crosslinking agent. The lower the water solubility of the modified monomer, the more stable the foaming of the TEMs. When methyl acrylate (MA) was used as a modified monomer, the initial expansion temperature of the microspheres was 163.2°C, the maximum expansion temperature was 223.5 °C, and the encapsulation content of the blowing agent was 14.70%.



