Latest issue
All issues / Volume 20 (2026) / Issue 4 (April)
Wen Shyang Chow
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 324-325, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.25
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 324-325, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.25

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Amanda Legnani, André Luis Marcomini, Philipe Augusto Pocidonio Silva, Ricardo Geraldo de Sousa, Anderson Júnior dos Santos, João Paulo Ferreira Santos
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 326-341, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.26
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 326-341, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.26
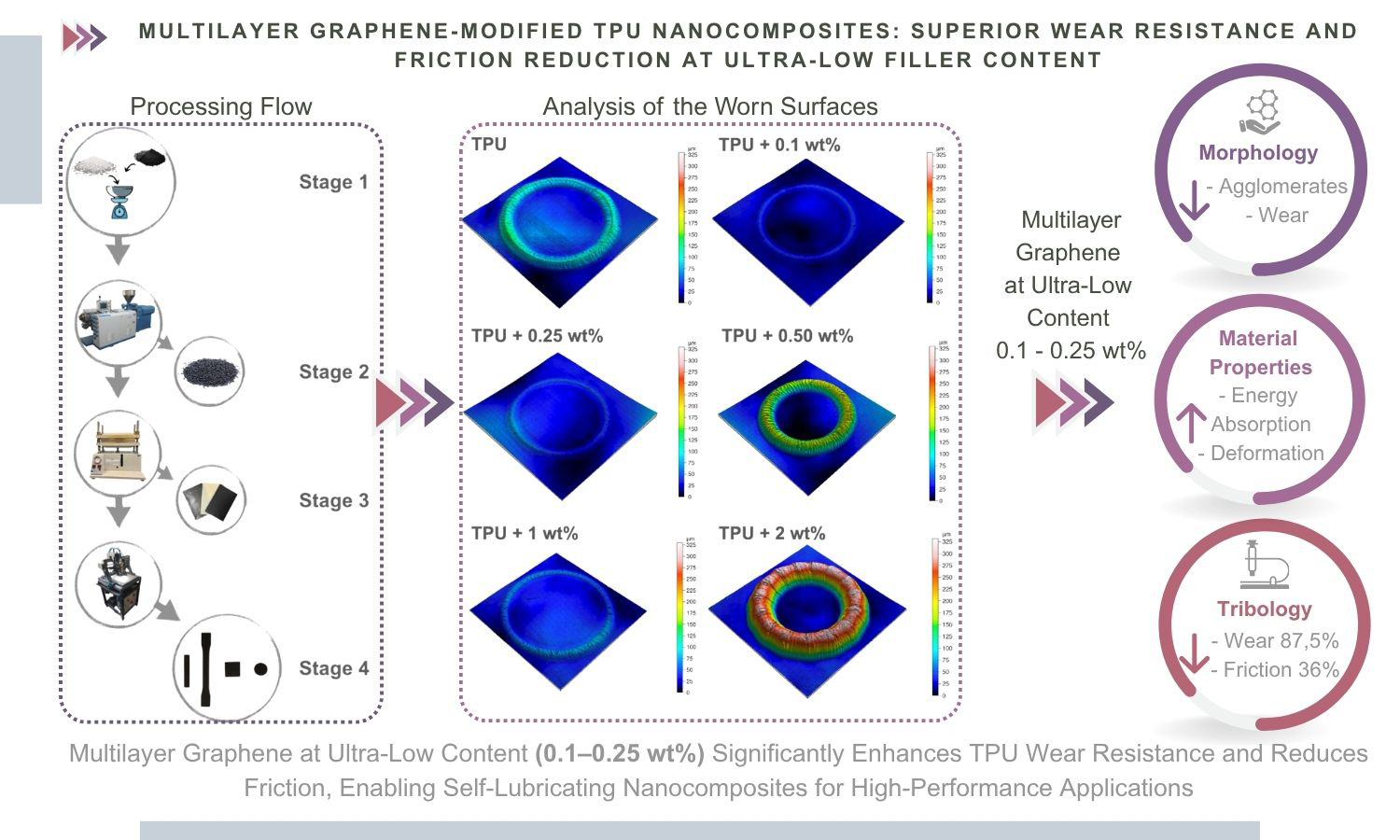
This work presents the development of high-performance thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) nanocomposites reinforced with low contents of multilayer graphene (mG), aiming to improve their tribological behavior. Using twin-screw extrusion followed by hot pressing, nanocomposites containing 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2% mG weight were fabricated and systematically evaluated. Nanocomposites with only 0.1–0.25 wt% mG achieved a 36% reduction in friction coefficient and 87.5% reduction in wear volume compared to neat TPU. Results are rarely reported at such low filler loadings. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis revealed uniform dispersion at these optimal concentrations, while higher mG contents led to agglomeration and performance loss. Rheological studies indicated improved flow behavior, and dynamic-mechanical analysis confirmed increased energy dissipation and thermal response. These results suggest that the concentrations of 0.1% and 0.25% of multilayer graphene used in the study are promising for improving the performance of TPU nanocomposites in applications requiring high wear resistance for advanced applications in automotive, biomedical, and high-load engineering components, where durability and low friction are essential.
Benoît Cosson, André Chateau Akue Asseko
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 342-348, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.27
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 342-348, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.27
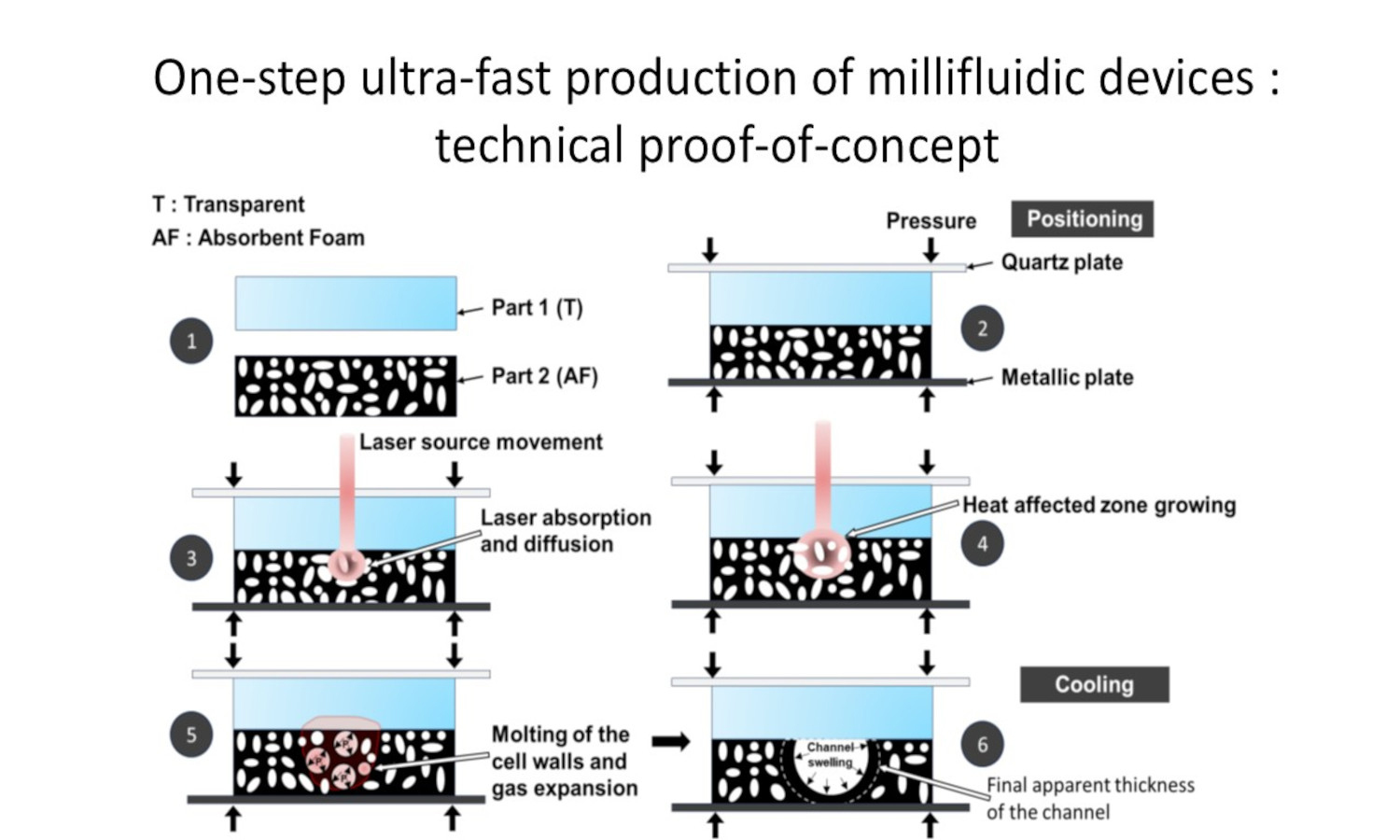
Microfluidic and millifluidic systems are increasingly used for chemical and biological analysis. Thermoplastic polymers offer a practical alternative to glass and silicon. They are inexpensive, easy to shape, and suitable for disposable devices. However, most polymer microfluidic chips are still produced in two steps: machining the channels, then bonding a cover plate. This workflow increases alignment constraints, exposes open channels to contamination, and lengthens production time. This study presents a one-step method based on transmission laser welding (TLW) applied to closed-cell thermoplastic foams. The laser heats and collapses the foam locally, causing the cell walls to fuse and form a channel while welding a transparent cover at the same time. The process creates a sealed microchannel without moving the parts between steps. We examine the feasibility of this method and study how laser output power affects channel dimensions. The approach also enables the creation of X and Y junctions by using several fast passes to control melting at the intersections. The channels obtained show smooth internal walls and a near-cylindrical cross-section. Their size can be adjusted through the laser parameters. This method offers a simple and clean way to prototype polymer millifluidic or microfluidic devices.
Yi-jie Yang, Qiang Dou
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 349-370, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.28
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 349-370, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.28
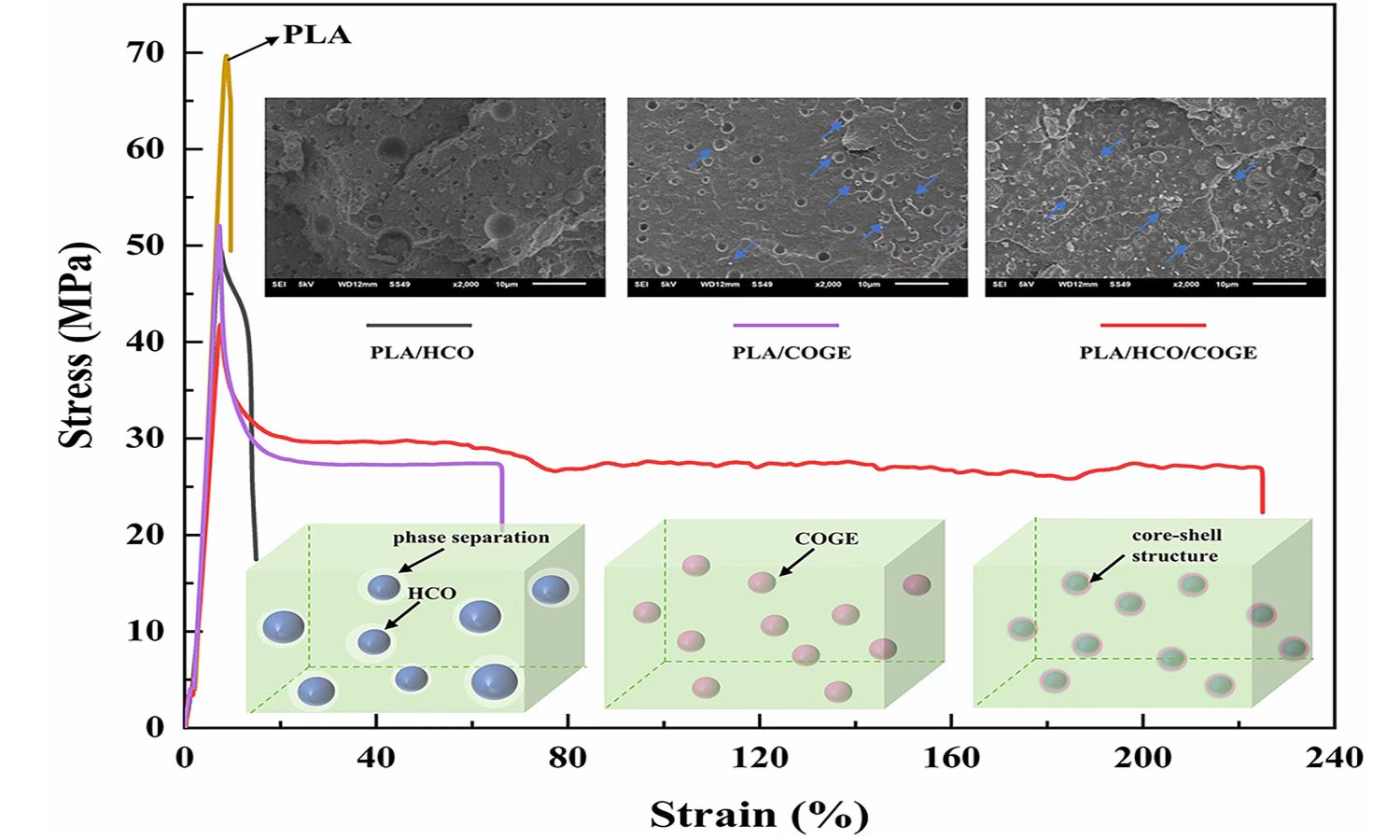
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) has attracted much attention and shows promising applications in numerous fields. In this study, PLA was plasticized using bio-based castor oil derivatives - hydrogenated castor oil (HCO) and castor oil glycidyl ether (COGE). These eco-blends were measured using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, a scanning electron microscope, a contact angle test, rheology, a differential scanning calorimeter, thermogravimetry, polarized optical microscopy, and a tensile test, respectively. The findings show that a core-shell morphology of COGE-HCO encapsulation is formed in PLA matrix, and the hydrogen bonding interaction and ring-opening chemical reaction among functional groups of the components greatly improve the compatibility, ductility, cold crystallization ability, and thermostability of the eco-blends, but the melt crystallization ability is hindered. The incorporation of HCO improves the hydrophobicity and oleophobicity of the eco-blends. Due to the combined effect of HCO and COGE, the melt viscosity reduces, and the Newtonian behavior enhances; the nucleation density and spherulitic growth of PLA increase. The strain at break of the PLA/HCO/COGE (90/7.5/2.5) blend reached 221%, which is 22.6 times higher than that of the neat PLA. These eco-blends present appropriate rheological, thermal, and mechanical properties, showing application scenarios in biodegradable packaging and disposable appliances.
Xuecheng Lu, Ke Feng, Zhiqiang Zhang, Xuyan Lü, Yujie Xiao, Haijun Wang
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 371-382, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.29
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 371-382, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.29
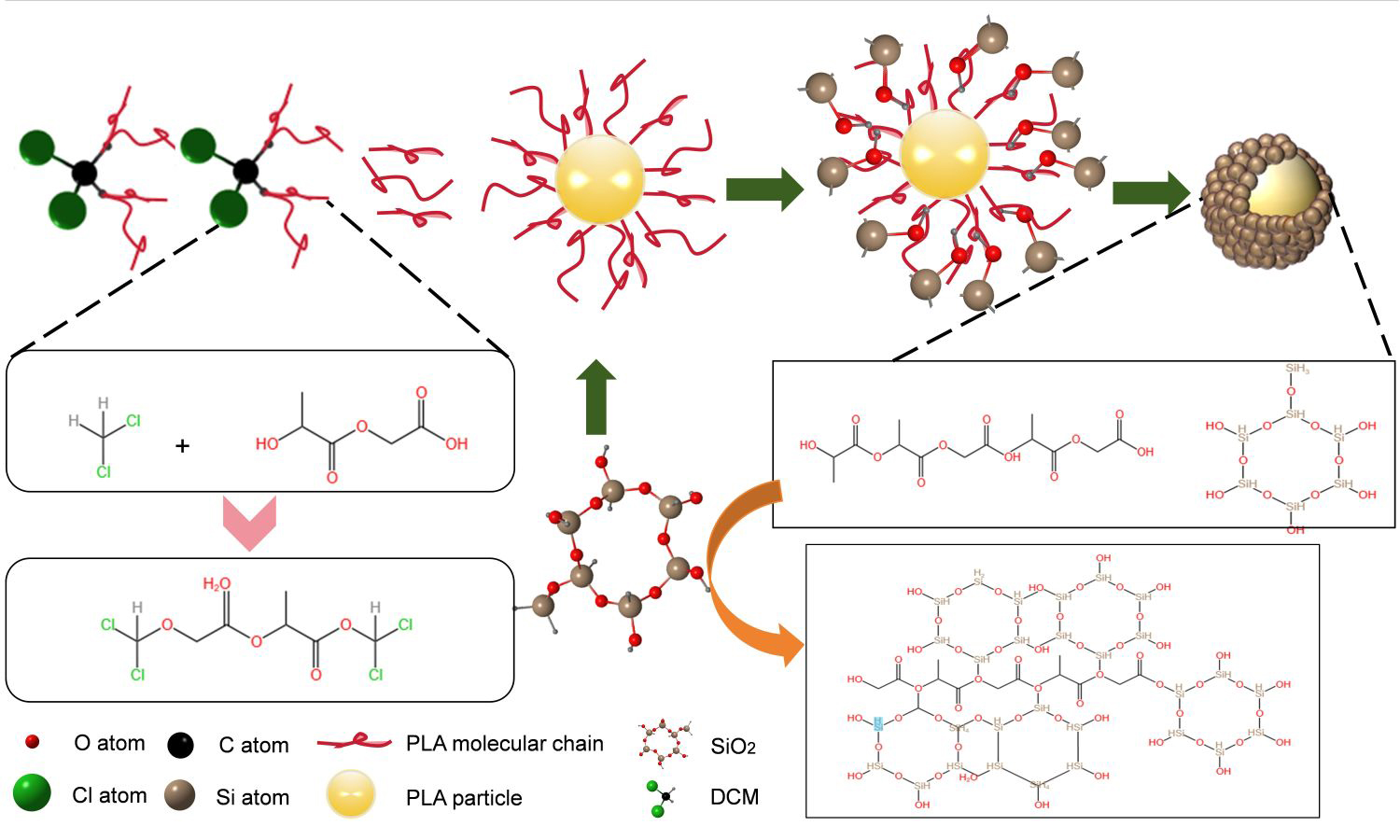
To improve the toughness, thermal stability, and melt processability of polylactic acid (PLA), this study introduced chlorinated polyethylene-polyethylene glycol (CPE-PEG, 10 wt%) into the PLA matrix and investigated the effect of the content of nano-SiO2 surface-modified with the silane coupling agent KH570 (K-SiO2) on the composite properties. Composite filaments were prepared via single-screw extrusion, and standard specimens were printed using fused deposition modeling (FDM) technology. Comprehensive characterization indicated that the composite achieved optimal mechanical properties at a K-SiO2 content of 1.5 wt%; simultaneously, the material’s thermal stability and crystallization behavior were optimized. Rheological behavior demonstrated that K-SiO2 could regulate the melt viscoelasticity, broadening the FDM processing window. This study provides an effective strategy for developing high-performance PLA composites for FDM printing.
Khmais Zdiri, Aurélie Cayla, Christine Campagne
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 383-394, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.30
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 383-394, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.30
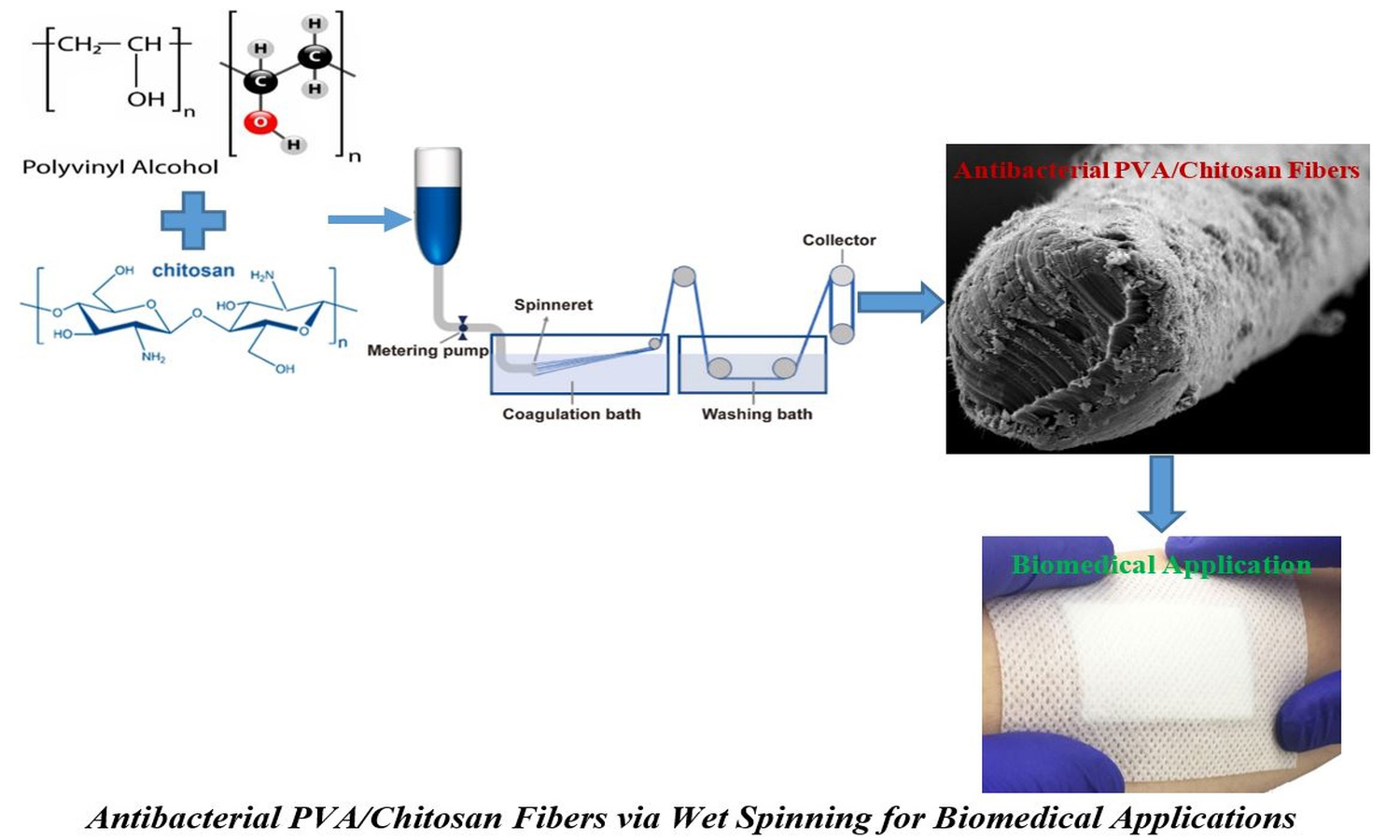
Growing interest in natural and eco-friendly materials has driven the search for sustainable alternatives to synthetic antimicrobial agents. This study aims to develop antibacterial fibers based on poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) reinforced with chitosan (CTS) using an environmentally friendly wet-spinning process. Morphological analysis revealed surface irregularities that increased with CTS content, confirming its effect on fiber microstructure. Thermal analyses by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) showed that CTS incorporation decreased the melting temperature while improving thermal stability. Mechanical testing demonstrated enhanced tensile strength (σs) and Young’s modulus (E) due to strong intermolecular interactions between CTS and the PVA matrix. The highest σs (1045 MPa) was obtained at 3 wt% CTS, while E reached 7.1 GPa at 5 wt%. Antibacterial tests against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli confirmed strong activity attributed to –NH2 groups of CTS disrupting bacterial membranes. These results highlight the potential of PVA/CTS fibers for biomedical applications such as wound dressing and antibacterial materials.
Çiçek Özes, Tuba Alpyildiz, Hasan Onur Sağir, Serhat Göz
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 395-413, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.31
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 395-413, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.31
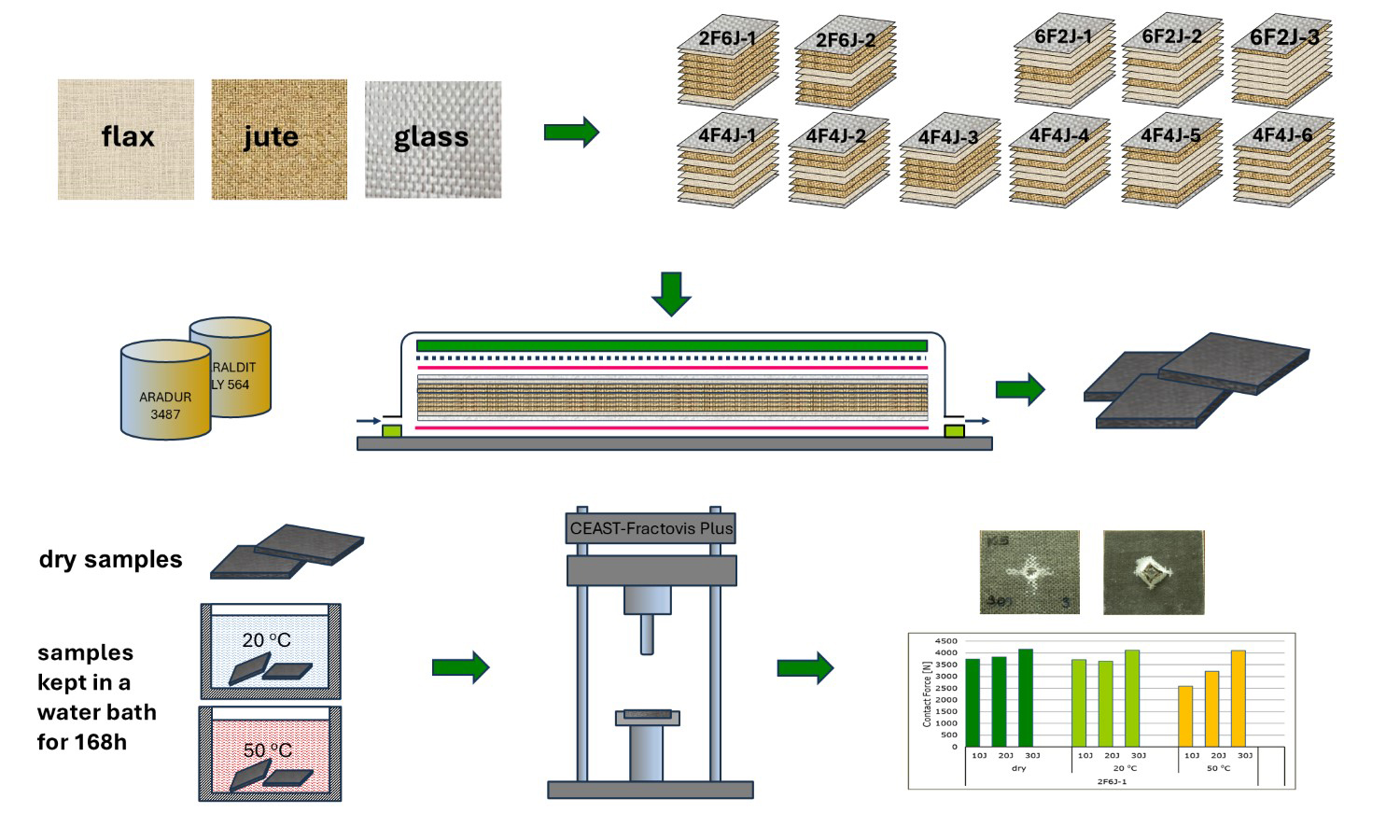
Natural fiber-reinforced composites, whose use is increasing daily in the building, automotive, and aerospace industries, are subjected to low-velocity impact loads in indoor applications. In most impact-exposed applications, increasing impact resistance through the hybrid use of different natural fibers is a frequently used solution. In this study, the impact resistance of hybrid composites reinforced with flax and jute fabrics was investigated in dry and water-absorbed conditions. The stacking layouts, the number of jute and flax fabric layers, and the type of fabric on the impact surface have been observed to affect the impact resistance of dry composites. Increasing the number of flax fabric layers increased water absorption. Although water absorption reduces the impact resistance of composites, it was also observed that impact damage is reduced at 20 J impact energy in some stacking layouts. The study results show that natural fiber-reinforced hybrid composites, produced with appropriate reinforcement elements and stacking layouts to enhance impact resistance, have the potential to increase their applicability in automotive and building sectors, where lightness and cost are key considerations.
Maja Csapó, József Gábor Kovács
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 414-434, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.32
Vol. 20., No.4., Pages 414-434, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.32
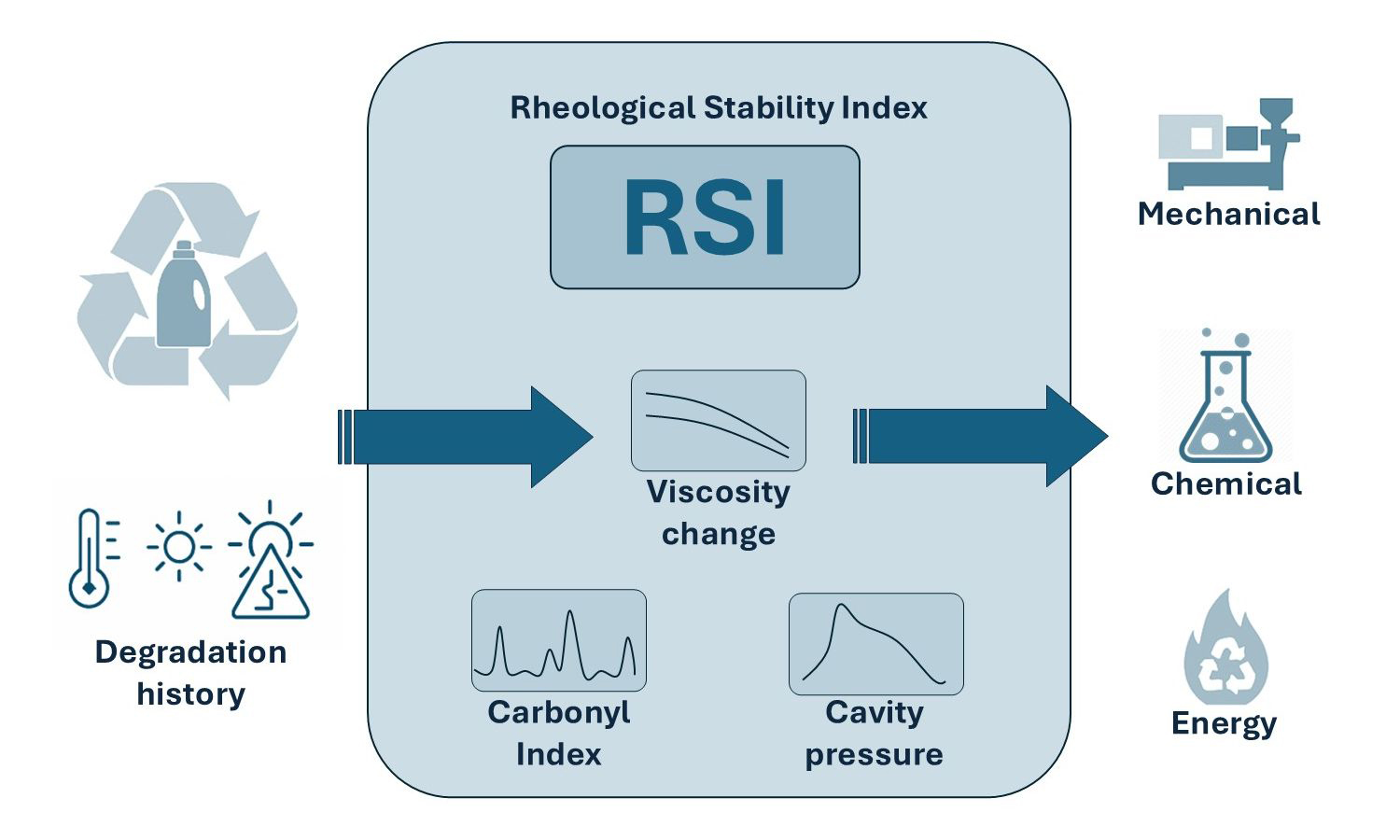
The greatest obstacle to recycling post-consumer high-density polyethylene (PCR-HDPE) is typically the degradation of properties caused by impurities and heterogeneity. However, a critical analysis of the literature reveals that the real bottleneck is not the material composition, but rather rheological stability, which simultaneously determines the degradation history of the waste stream, melt behavior, and processability at the cycle level. This review proposes a new perspective: the decision among mechanical, chemical, and energetic recycling is better made based on a unified rheological stability index (RSI), which integrates carbonyl index, viscosity change after multiple instances of melting, melt flow index (MFI) instability, in-mold pressure fluctuation, and the degree of polymer incompatibility. RSI enables the prediction of the processability of PCR-HDPE and identifies which recycling path a fraction is most suitable for. The study demonstrates how an RSI-based approach can reduce quality risk, improve cycle stability, and support circular decision-making in an industrial environment.


