Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable–electroactive polymer–Au nanocomposite materials for H2S sensing
Aamna Bibi , Ying-Hsuan Li, Hsi-Wei Jia, Hsien-po Kuo, Nadaraj Sathishkumar, Hsin-Tsung Chen, Karen S. Santiago, Jui-Ming Yeh
, Ying-Hsuan Li, Hsi-Wei Jia, Hsien-po Kuo, Nadaraj Sathishkumar, Hsin-Tsung Chen, Karen S. Santiago, Jui-Ming Yeh
 , Ying-Hsuan Li, Hsi-Wei Jia, Hsien-po Kuo, Nadaraj Sathishkumar, Hsin-Tsung Chen, Karen S. Santiago, Jui-Ming Yeh
, Ying-Hsuan Li, Hsi-Wei Jia, Hsien-po Kuo, Nadaraj Sathishkumar, Hsin-Tsung Chen, Karen S. Santiago, Jui-Ming YehVol. 16., No.10., Pages 1022-1037, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.75
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.75
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
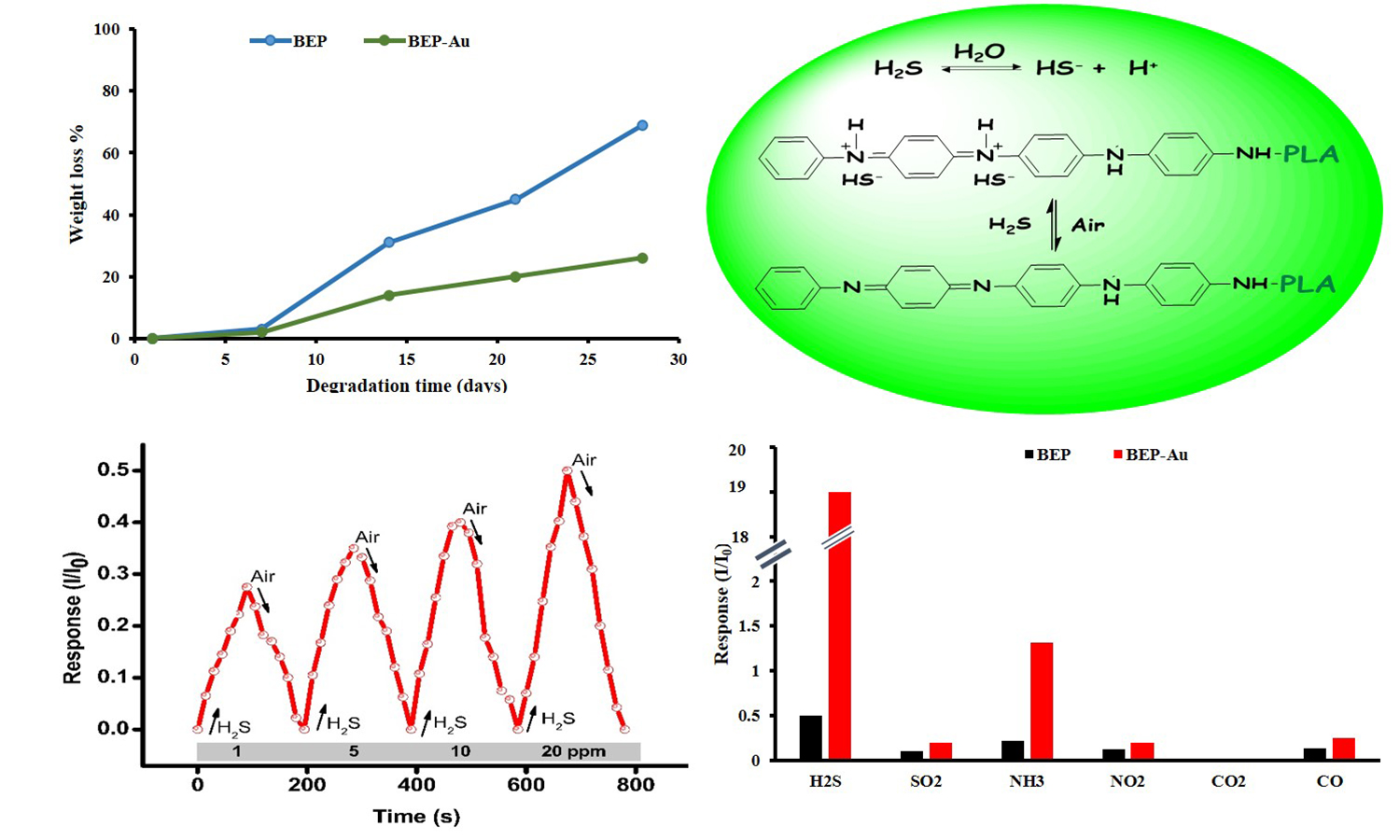
ABSTRACT
In this paper, a series of biodegradable-electroactive polymers (BEP) and its composite with gold nanoparticles (BEPAu) were prepared and used in the detection of H2S gas. First, the starting materials which included the electroactive aniline tetramer (ACAT) and biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA) were synthesized and characterized. The BEP was then prepared by reacting tri-isocyanate (N-3300) with the synthesized ACAT and PLA at a specific feeding ratio. In this case, ACAT served as a pendant group. The BEP-Au composite was subsequently prepared by immersing a specific amount of BEP in a certain concentration of HAuCl4·3H2O solution for 6 h, followed by characterization. The gas sensing performances of as-prepared sensors were tested. Results revealed that the BEP sensor has a good sensitivity of 0.0114 ppm–1 towards increasing concentrations of H2S gas (1–20 ppm), which was observed to have increased up to 0.907 ppm–1 after the addition of gold nanoparticles, i.e., BEP-Au. Furthermore, the said sensors also showed rapid response and recovery rates, good repeatability, and high selectivity. To fully evaluate the feasibility of BEP and BEP-Au for the detection of H2S gas, the adsorption was further investigated via the ab initio density functional. theory (DFT). The DFT calculations complemented the experimental gas sensing results.



