Graphene-filled natural rubber nanocomposites: Influence of the composition on curing, morphological, mechanical, and electrical properties
Vol. 17., No.8., Pages 819-836, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.61
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.61
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
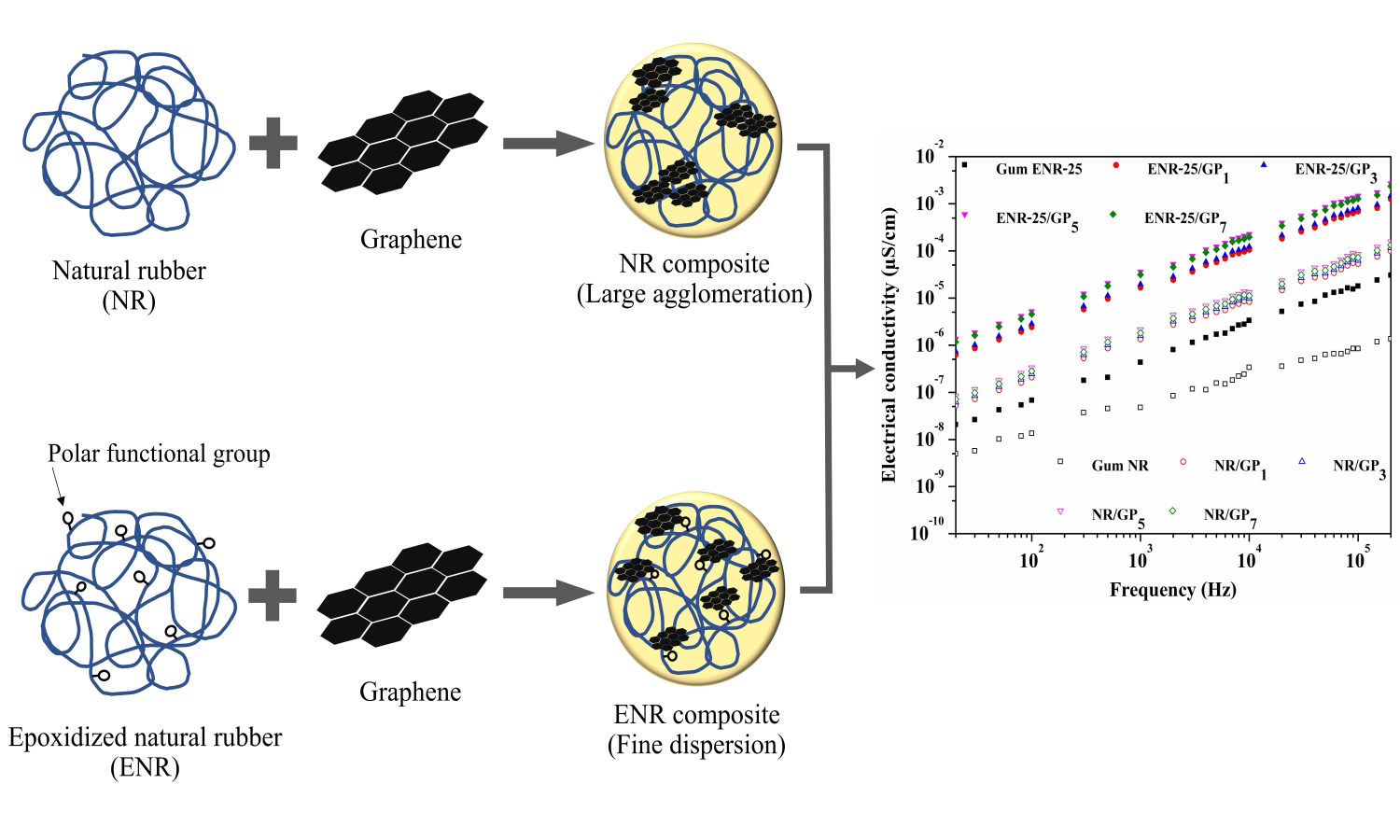
ABSTRACT
The properties of graphene (GP) filled rubber nanocomposites were investigated in functions of rubber type (unmodified natural rubber (NR) and epoxidized natural rubber with 25 mol% epoxides (ENR-25)) and filler content. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectrum indicated that GP surfaces contain polar hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups. The ENR-25/GP compound exhibited higher maximum torque, torque difference, storage modulus, initial relaxation modulus, bound rubber, and degree of reinforcement with smaller GP aggregates dispersed in the rubber matrix than the NR/GP composites. Additionally, an increasing trend of tensile strength was observed in the ENR-25/GP composite, but the contrary trend was obviously seen in the NR/GP composites due to the interaction between polar functional groups in ENR-25 and GP surfaces. Furthermore, a higher Payne effect (filler-filler interaction) was found in the NR/GP composites, corresponding to larger GP agglomerates and voids dispersed in the NR matrix. Moreover, the ENR-25/GP composite had higher electrical conductivity and dielectric constant than the NR/GP composite due to the higher polarity of the ENR with the dipoles, leading to increasing orientation polarization and interfacial polarization.




