Construction of a thermally conductive network to improve the thermal and mechanical performance of silicone rubber foam
Hongjie Xie, Lijuan Zhao, Yanli Chen, Bing Han, Yu Hua, Dongliang Zhang, Zhaoqiang Li, Qibo Deng, Yunfeng Zhao
Vol. 17., No.12., Pages 1182-1199, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.90
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.90
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
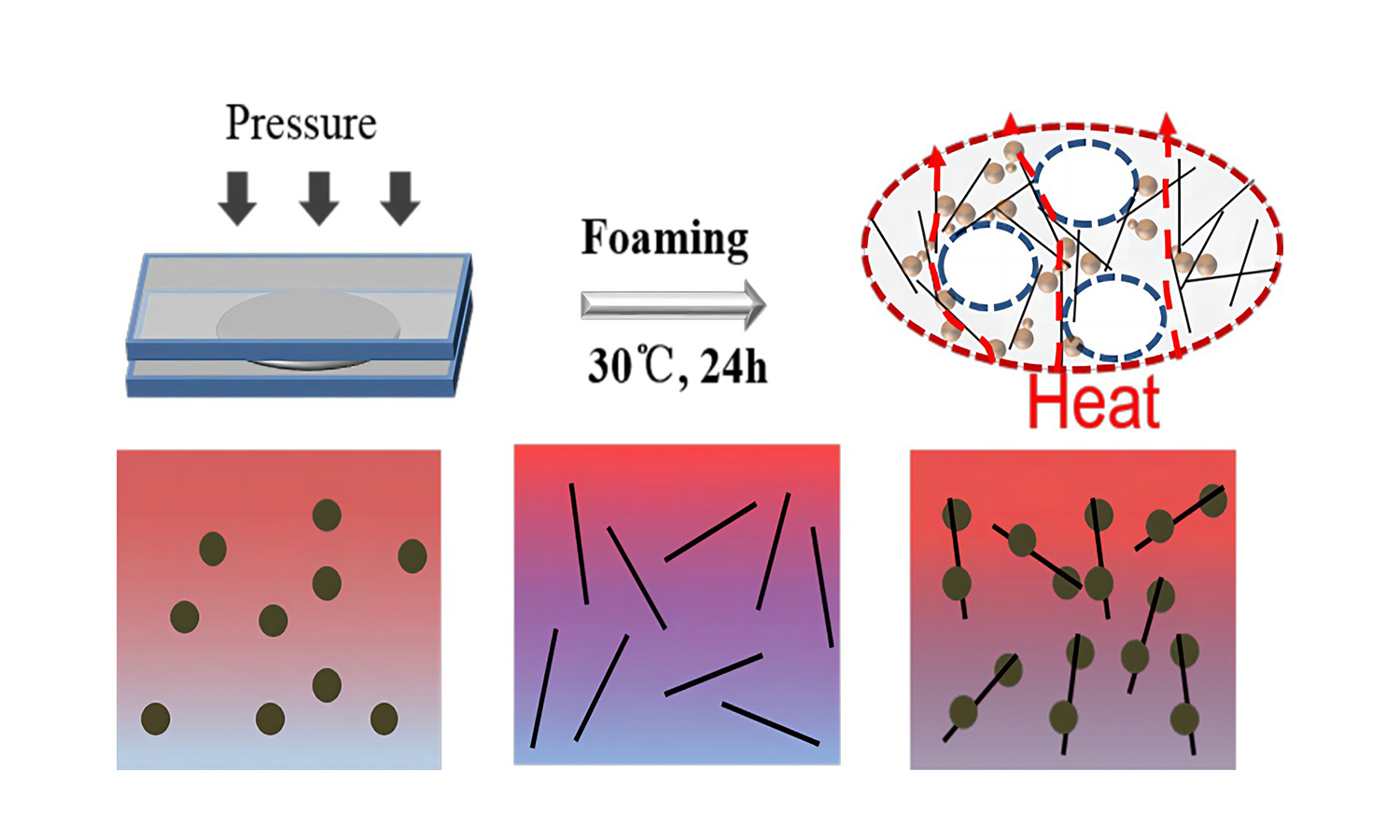
ABSTRACT
Silicone foam (SF) is a porous silicone rubber with a lower density, higher elasticity, and good thermal stability. In this work, we selected aluminum spheres and carbon fiber (CF) as thermally conductive fillers to prepare hybrid SF. After optimization, we found that Al and CF hybrid SF (Al-CF-SF) has a higher thermal conductivity (1.37 W·m–1·K–1) than the single-filler filled SF (CF-SF, 1.2 W·m–1·K–1 or Al-SF, 0.52 W·m–1·K–1) under the same filling amount of 60 wt%. The finite element simulation was used further to explore the thermal conductive mechanism of the hybrid SF. Meanwhile, the compressive and tensile modulus of the material (CF-SF) was increased to 10.8 and 3.3 MPa compared with pure SF, respectively, and the mechanical properties were improved. In addition, infrared thermography further demonstrated that Al-CF-SF has a faster heat transfer rate under relaxation and applied pressure.
RELATED ARTICLES
Wafa Mustafa Saleh, Esam Bashir Yahya, Mardiana Idayu Ahmad, Abdul Khalil H. P. S.
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 457-469, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.34
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 457-469, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.34
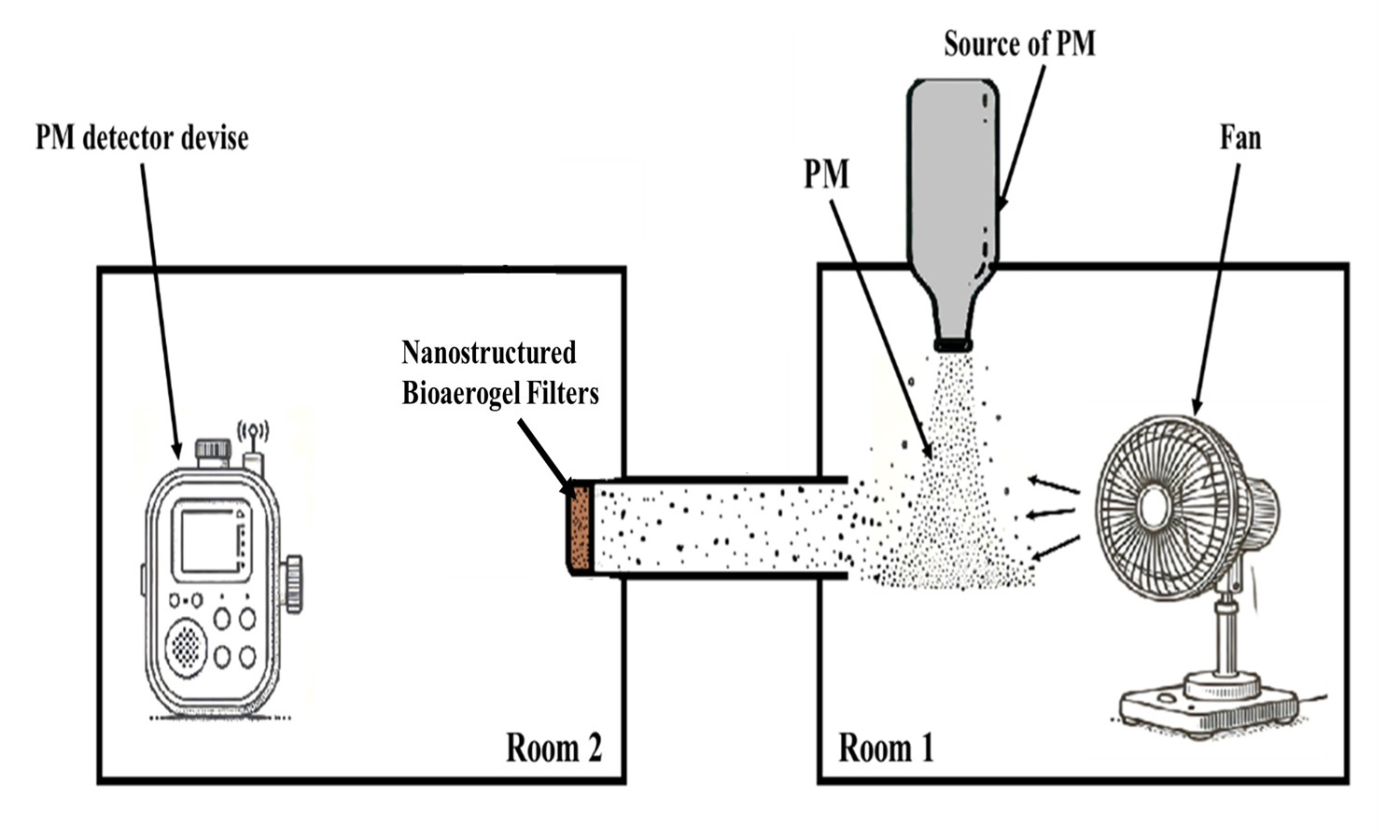
Particulate matter (PM) has been always a significant environmental and public health concern due to its adverse effects on air quality and respiratory health. This study evaluates the efficiency of hydrophobic nanostructured bioaerogels as PM filters under both normal and high-humidity conditions. Bioaerogels were prepared using nanocellulose and chitosan and modified with varying concentrations of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEMS). At normal humidity, the 3% TEMS-modified bioaerogel demonstrated the highest average PM removal efficiency of 91.6%, attributed to its optimized balance of hydrophobicity, porosity, and mechanical strength. Under high-humidity conditions, the unmodified 0% TEMS bioaerogel exhibited a significant decline in performance due to water absorption, reducing its efficiency by over 15% after prolonged exposure. Conversely, the hydrophobic 3% TEMS bioaerogel maintained its efficiency at 91.4%, highlighting its ability to resist water-induced degradation. This study provide valuable insights into the design of bioaerogel-based filters for realworld applications where variable humidity poses a challenge.
Fatma Nur Parın, Hatice Dinç, Uğur Parın, Elife Kıldalı, Gökçe Taner
Vol. 18., No.3., Pages 282-295, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.20
Vol. 18., No.3., Pages 282-295, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.20
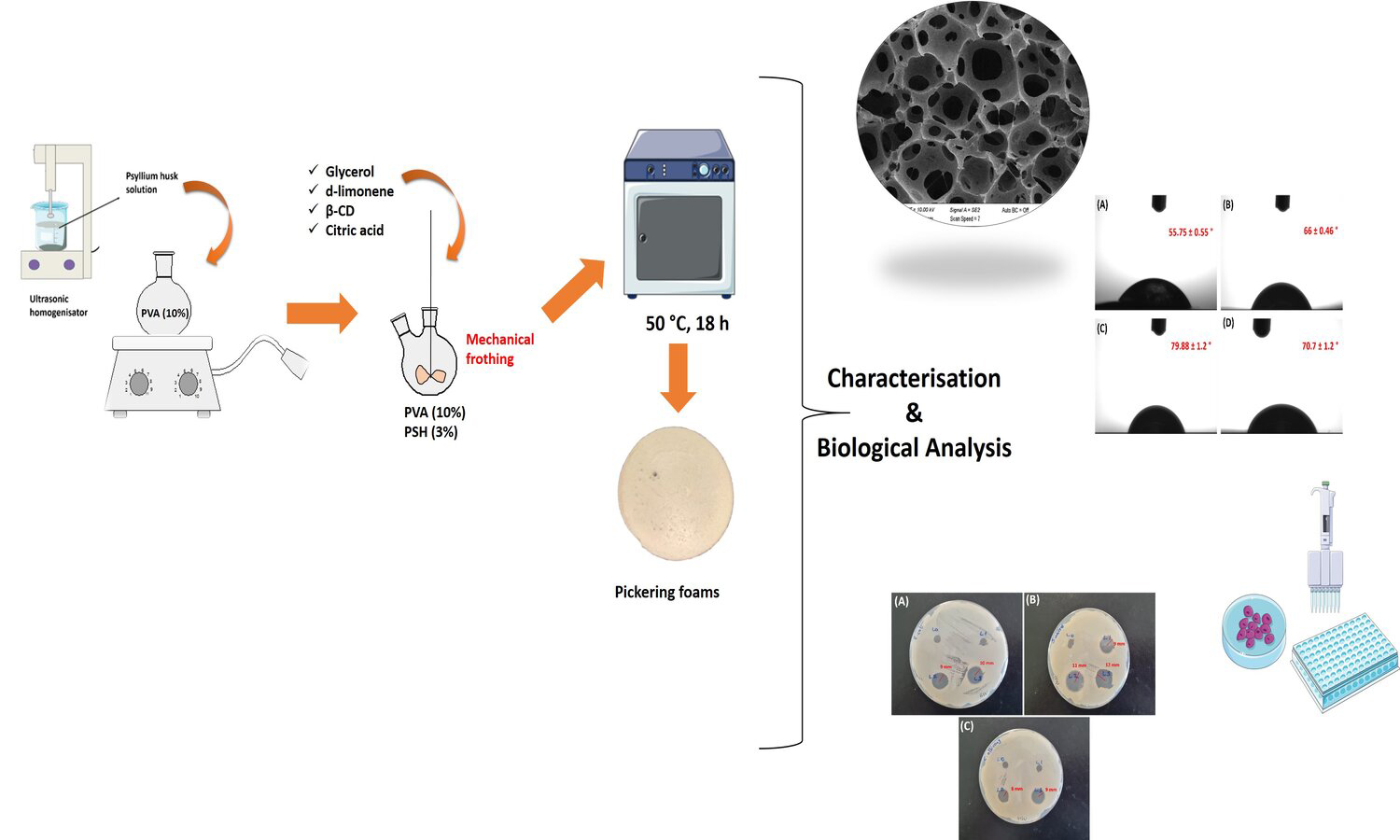
In this study, Pickering foamed emulsions have been prepared using β-cyclodextrin (β-CD), and d-limonene as a surfactant and an oil phase, respectively. The incorporation of β-CD/d-limonene inclusion complexes (ICs) in specific proportions (1:1, 1:3, and 1:5) to water phase, which is a polymer matrix composed of a mixture of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and psyllium husk (PSH) by mechanical frothing at high speed, and air bubbles have been formed in oil in water (o/w) emulsions. Ecofriendly bio-based foams have been developed in this method. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis showed PVA/PSH Pickering foams usually open porous morphologies and the addition of d-limonene increases the amount of porosity from 43 to 49%. Although the resulting foams indicated similar thermal degradation profile, the presence of d-limonene in foams increased thermal stability. The surfaces of foams have a hydrophilic property with contact angles values lower than 80°. The tensile strength of foams decreased from 170 to 100 kPa due to the increased porosity. All foams indicated antibacterial activity to Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) with 9–12 mm zone inhibition. The incorporation of d-limonene into foams surprisingly decreased the cell viability. In brief, our findings show that the Pickering foams can be beneficial for wound healing applications.



