Polypropylene blends: Impact of long chain-branched polypropylene on crystallization of linear polypropylene
Soňa Zenzingerová , Jana Navratilova
, Jana Navratilova , Lenka Gajzlerová
, Lenka Gajzlerová , Michal Kudláček
, Michal Kudláček , David Jaška
, David Jaška , Lubomir Benicek
, Lubomir Benicek , Roman Čermák
, Roman Čermák
 , Jana Navratilova
, Jana Navratilova , Lenka Gajzlerová
, Lenka Gajzlerová , Michal Kudláček
, Michal Kudláček , David Jaška
, David Jaška , Lubomir Benicek
, Lubomir Benicek , Roman Čermák
, Roman Čermák
Vol. 18., No.9., Pages 921-930, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.69
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.69
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
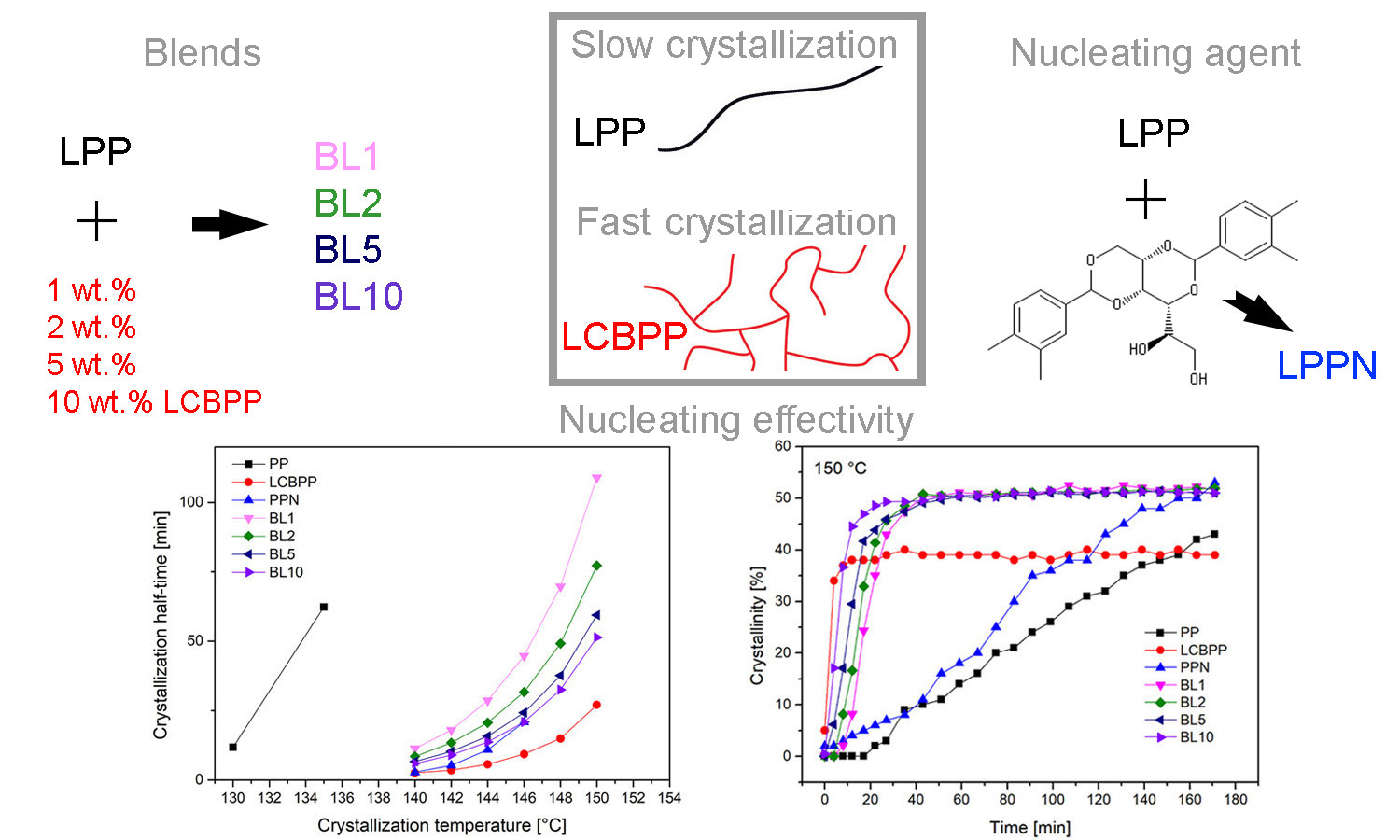
This study compares the efficiency of commercially available sorbitol-based clarifying agent (NA) and varying amounts of long chain-branched polypropylene (LCBPP) acting as a specific α-nucleating agent for linear polypropylene (PP). The sorbitol-based clarifying agent, 1,3;2,4-bis(3,4-dimethyl benzylidene)sorbitol (Millad 3988), in concentration 0.2 wt%, and LCBPP in the concentration of 1, 2, 5 and 10 wt% were mixed into PP. The comparison of the effect of NA and long branches under isothermal conditions on the crystallization process, crystallinity and polymorphic composition was realized by differential scanning calorimetry and wide-angle X-ray scattering. The addition of long chain-branched polypropylene, even at the lowest concentration, performs better at higher crystallization temperatures and has a superior effect on the crystallization process, crystallization rate and overall crystallization than the addition of NA.
RELATED ARTICLES
Jana Navratilova
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 112-113, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.9
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 112-113, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.9

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Sandra Paszkiewicz, Kamila Sałasińska, Zaida Ortega, Mateusz Barczewski, Jacek Andrzejewski, Konrad Walkowiak, Izabela Irska, Magdalena Jurczyk Kowalska, Anna Boczkowska, Marcin Borowicz, Joanna Paciorek-Sadowska, Elżbieta Piesowicz, Katarzyna Pokwicka-Croucher
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1286-1309, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.95
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1286-1309, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.95

Two series of polymer blends based on post-consumer polypropylene (rPP) and tire rubber crumbs (Trc) under the trademark ECOPLASTOMER® PP70 with a mutual ratio of components 70/30 wt%, containing 10, 20, and 30 wt% of flame retardants, have been prepared using a twin-screw extruder. The influence of commercially available silane-treated alumina trihydrate (ATH-sil) with the eco-friendly system based on melamine phosphate (MP), aluminum hydroxide (AC), and peanut shells (PS), used as flame retardant agents, on the mechanical, thermal, and flammability properties of polymer blends was assessed – the incorporation of ATH-sil results in the appearance of peaks related to OH groups in the Fouriertransform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra. Similar observations are made for the MP/AC/PS system. differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis revealed that using the selected flame retardants did not impact the melting and crystallization temperatures of the polymer. Tensile strength experienced a minor decrease, particularly in compositions containing more than 20 wt% of the flame retardants, while hardness remained unaffected by their share. Both flame retardants reduced the flammability of the modified polypropylene/rubber powder blends, and the most favorable outcomes were achieved with ATH-sil; however, only when employed at a minimum of 30 wt%. The formulated MP/AC/PS system proved more adept at reducing flammability and smoke emissions at lower flame retardant levels (up to 20 wt%).
Abdulaziz Al-Shehri, John Sweeney, Paul Spencer, Phil Coates, Fin Caton-Rose, Ajay Taraiya
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1238-1255, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.92
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1238-1255, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.92
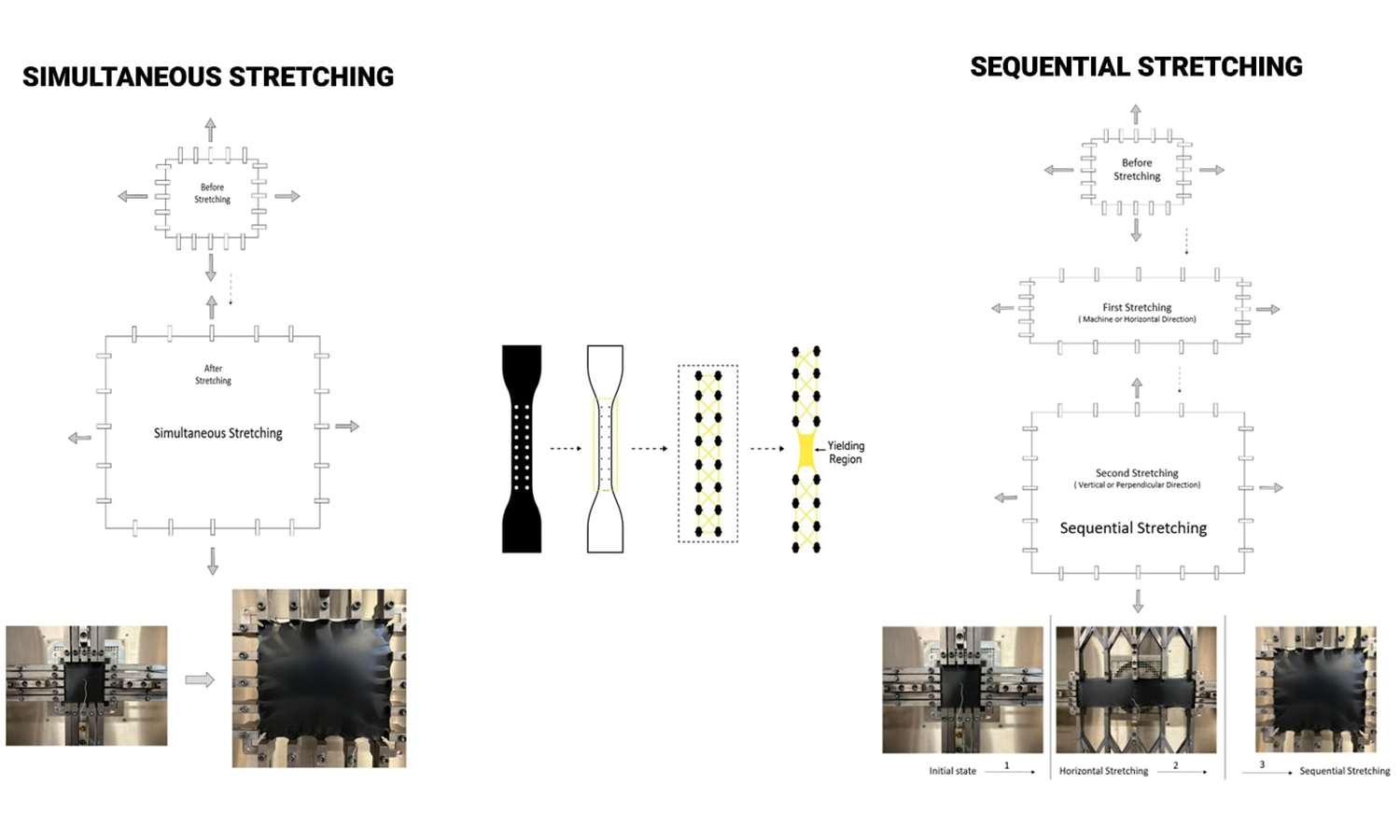
This study examines the combined effects of molecular modalities (unimodal, bimodal, trimodal) and biaxial stretching modes (sequential and simultaneous) on the yielding, stiffness, and necking behaviour of stretched high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Yield strength and stiffness were examined in relation to oriented material produced by drawing at linear strain rates 5.4·10–3, 2.2·10–2, and 8.6·10–2 s–1 under both stretching modes. Simultaneous stretching outperformed sequential stretching, with yield strength increasing with draw rate. Unimodal HDPE showed higher yield strength and stiffness than bimodal and trimodal grades, while trimodal HDPE had the lowest necking tendency from greater flexibility and uniformity. The highest necking tendency was observed in unimodal HDPE in strain localization analysis using the maximum strain/average strain ratio, while trimodal HDPE deformed more uniformly due to improved molecular weight distribution and strain hardening. Increasing the draw rate reduced strain localization, improving mechanical performance. Insights for optimising polyethylene materials in industry are provided by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and mechanical analyses, establishing the correlation between HDPE structure, processing, and properties.
Felipe Oliveira Campos Bernardo, Sebastião Vicente Canevarolo
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 636-650, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.48
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 636-650, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.48
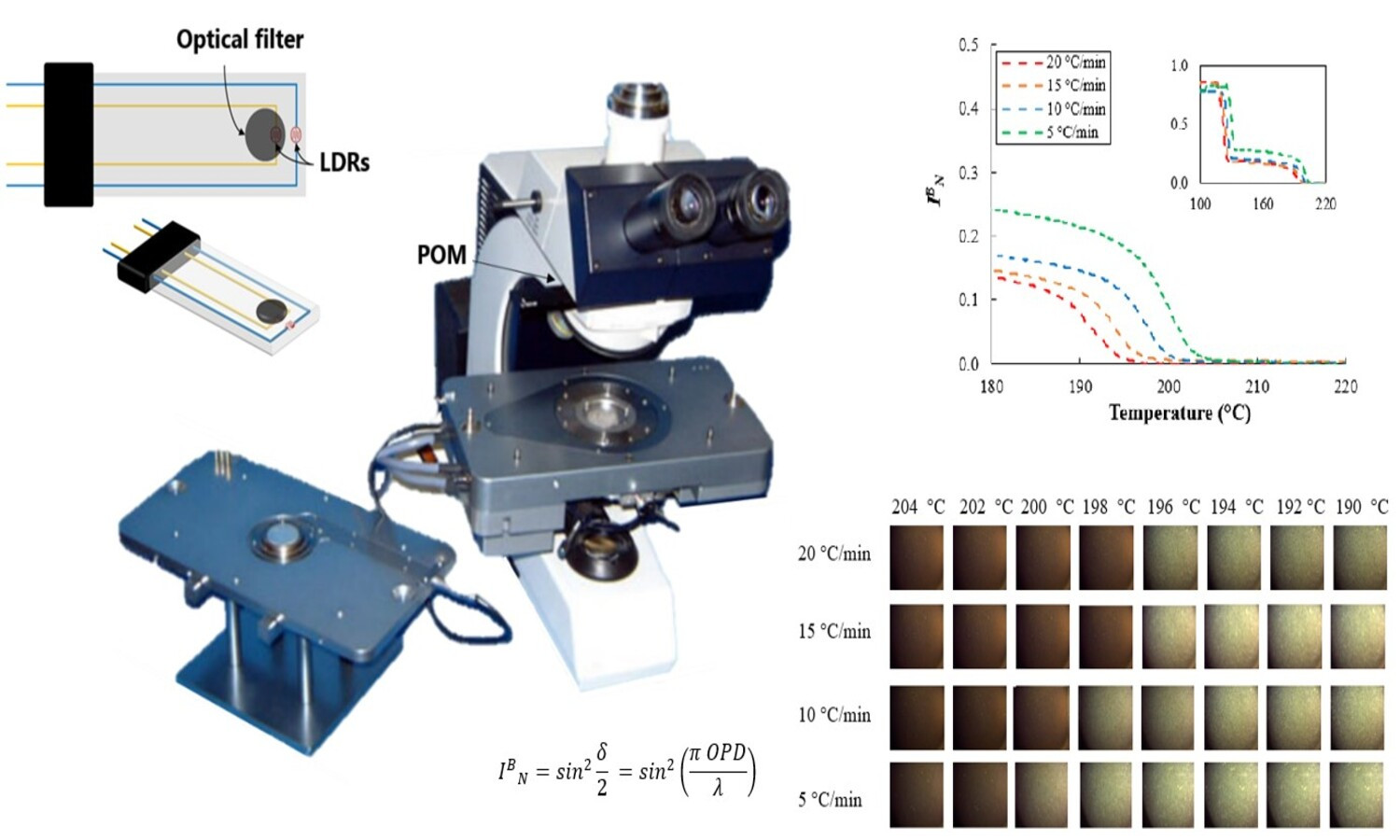
The use of rheo-optical techniques to evaluate crystallization in polymer processing has many advantages; however, it is still little seen. Shear-induced crystallization of polyamide 6 (PA6) was here proposed and studied with these techniques. Mixtures of PA6 in a polypropylene (PP) matrix were also studied. A polarized light optical microscope, with an AxioVision system attached to its top allowing the acquisition of photos at any time during the measurement and a Linkam hot stage device to control shear and temperature, was modified to receive a specially built quantitative rheo-optical detector. Temperature was variable, characterizing non-isothermal analysis. The experiments consisted of varying the shear rate on the polymer system while collecting the respective cross-polarized transmitted light intensity response by LabVIEW software. Shear rates of 1, 10, 100 and 180 s–1 were applied to all samples. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis was also performed to predict crystallization behavior. PA6’s crystallization increased with the increase of shear rate; however, for the PP/PA6 mixtures under the highest rates, crystallization intensity falls from a specific temperature in which the polymer’s viscosity is not enough to maintain the structural integrity. Data related to PP/PA6 mixtures showed that shear increases crystallization if the polymer has time to organize itself.
Dazhi Zhu, Junhao Wang, Yongheng Sun, Jianqiang Chu, Zhaobo Wang
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 361-371, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.27
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 361-371, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.27
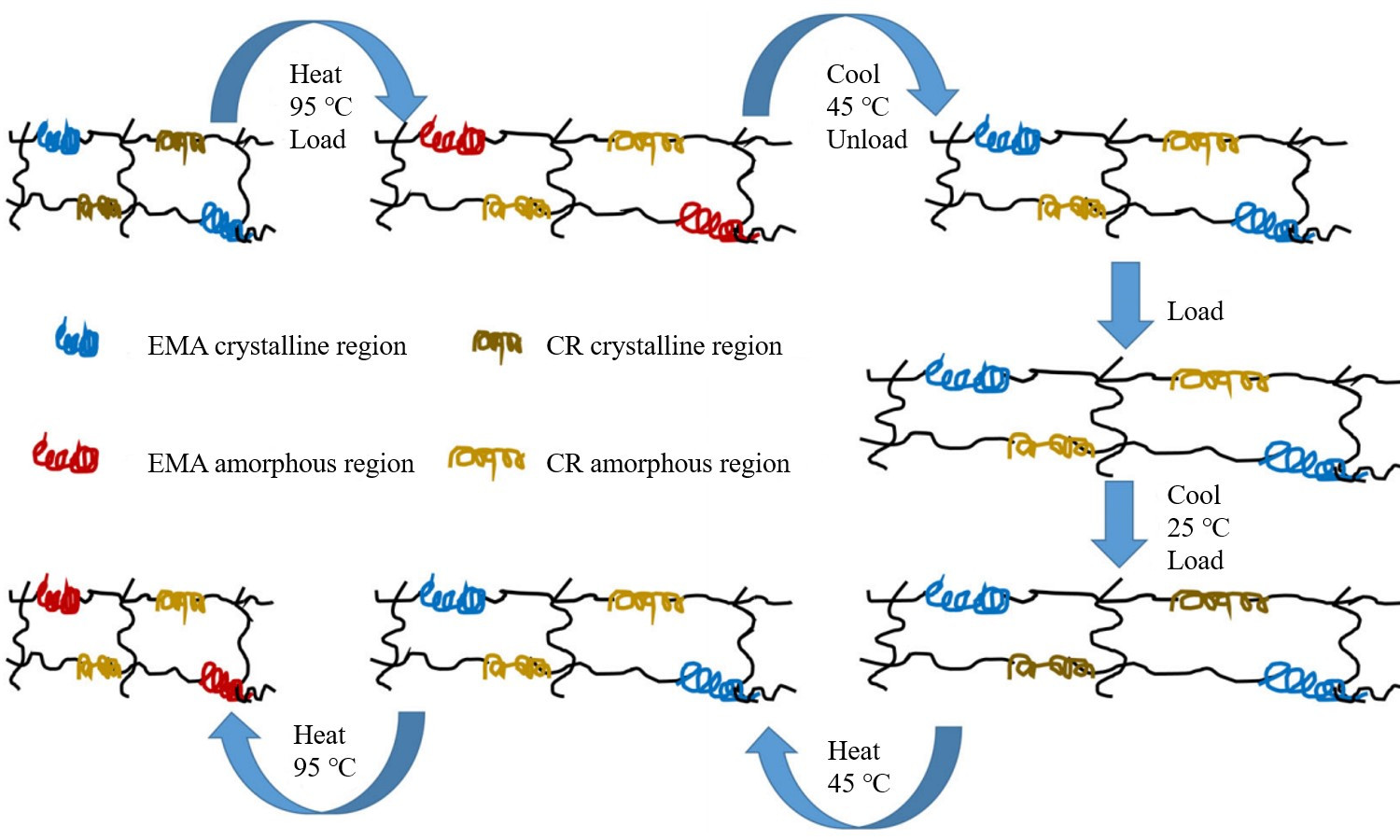
In this research, heat-triggered triple-shape memory polymers (TSMPs) based on the ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer (EMA)/chloroprene rubber (CR) thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPVs) were prepared by dynamic vulcanization successfully; meanwhile, an effective and facile triple-shape memory strategy was designed to realize the efficient and stable shape fixity and recovery of two temporary shapes. The field-emission scanning electron microscope images showed that EMA/CR TPV surface was a sea-island structure with the CR particle size ranging from 3 to 6 μm. Differential scanning calorimeters and X-ray diffraction were used to investigate the crystallization behavior of both EMA and CR. These served as a significant basis for the two temporary shapes: fixity and recovery. The results of triple-shape memory tests showed that the EMA/CR TPV had excellent triple-shape memory properties, where the first shape fixity ratio was higher than 89% and both the first shape recovery ratio and second shape recovery ratio could be higher than 95%. It can be observed that the EMA/CR TPV exhibited rapid shape recovery speed with the first shape recovery time of 10 s and the second shape recovery time of 20 s, respectively. This research presents a novel approach to extending the application of TPV in the field of smart devices, endowing them with excellent mechanical and triple-shape memory properties.



