Coordination crosslinks of epoxidized natural rubber with reactive zinc chloride
Vol. 18., No.11., Pages 1149-1163, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.87
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.87
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
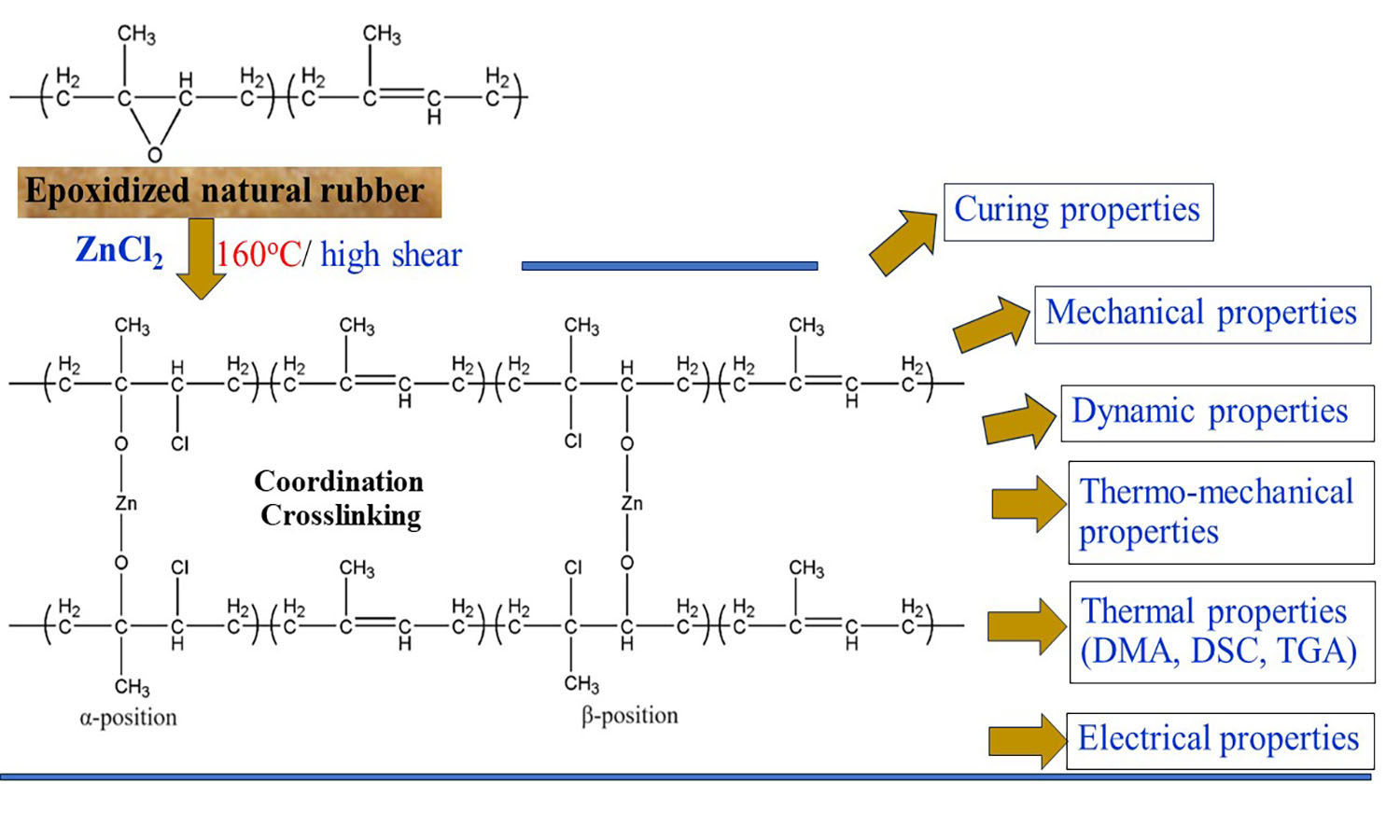
ABSTRACT
Epoxidized natural rubber with 50 mol% epoxide (ENR-50) was compounded with zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and subjected to torque response analysis using a moving die rheometer. It was found that different ZnCl2 concentrations (3, 5, 7, 9, and 12 millimoles (mmol)) mixed in ENR-50 exhibited positive torque responses, prompting further molecular characterization using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The results indicated distinct absorption peaks at wavenumbers of 442 and 809 cm–1, which signify the presence of –O–Zn–O– coordination linkages. The curing characteristics of ENR and ZnCl2 compounds showed that increasing ZnCl2 content resulted in higher minimum and maximum torque values, but also led to a decrease in scorch time and cure rate index (CRI). Moreover, higher ZnCl2 concentrations enhanced the strength properties (tensile strength, moduli, stiffness, toughness, and hardness), crosslink densities, dynamic shear moduli, initial modulus during relaxation experiments, and thermal resistance, as evidenced by temperature scanning stress relaxation (TSSR), thermogravimetric analysis, and dynamic mechanical analysis. However, an increase in ZnCl2 content led to a reduction in elongation at break due to the higher crosslink density within the coordination networks in the ENR matrix, which resulted in the movement constraint of the rubber vulcanizate.
RELATED ARTICLES
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
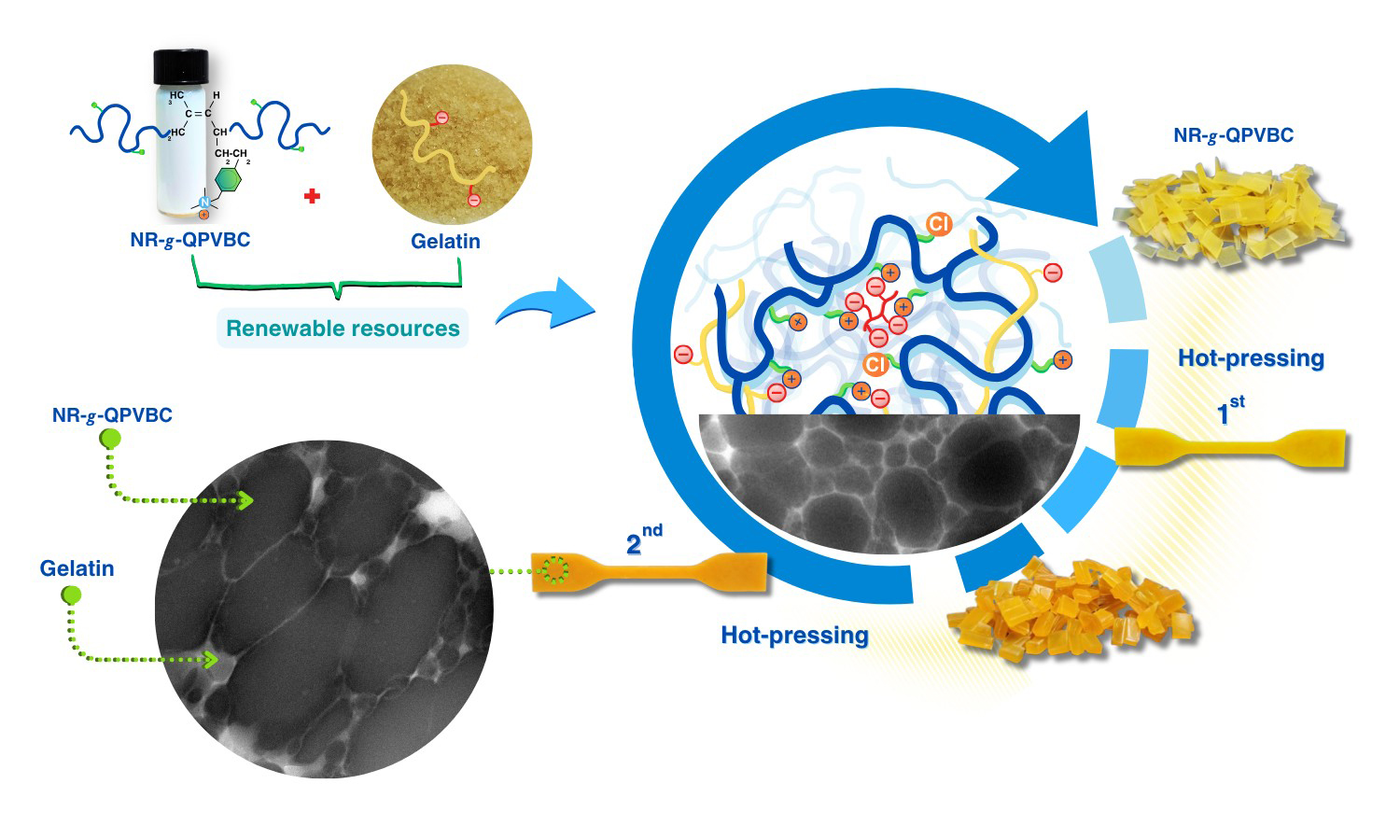
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Kinsuk Naskar
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 977-978, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.73
Vol. 19., No.10., Pages 977-978, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.73

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Azizon Kaesaman, Tassaneeya Khunrang, Charoen Nakason
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 753-772, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 753-772, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
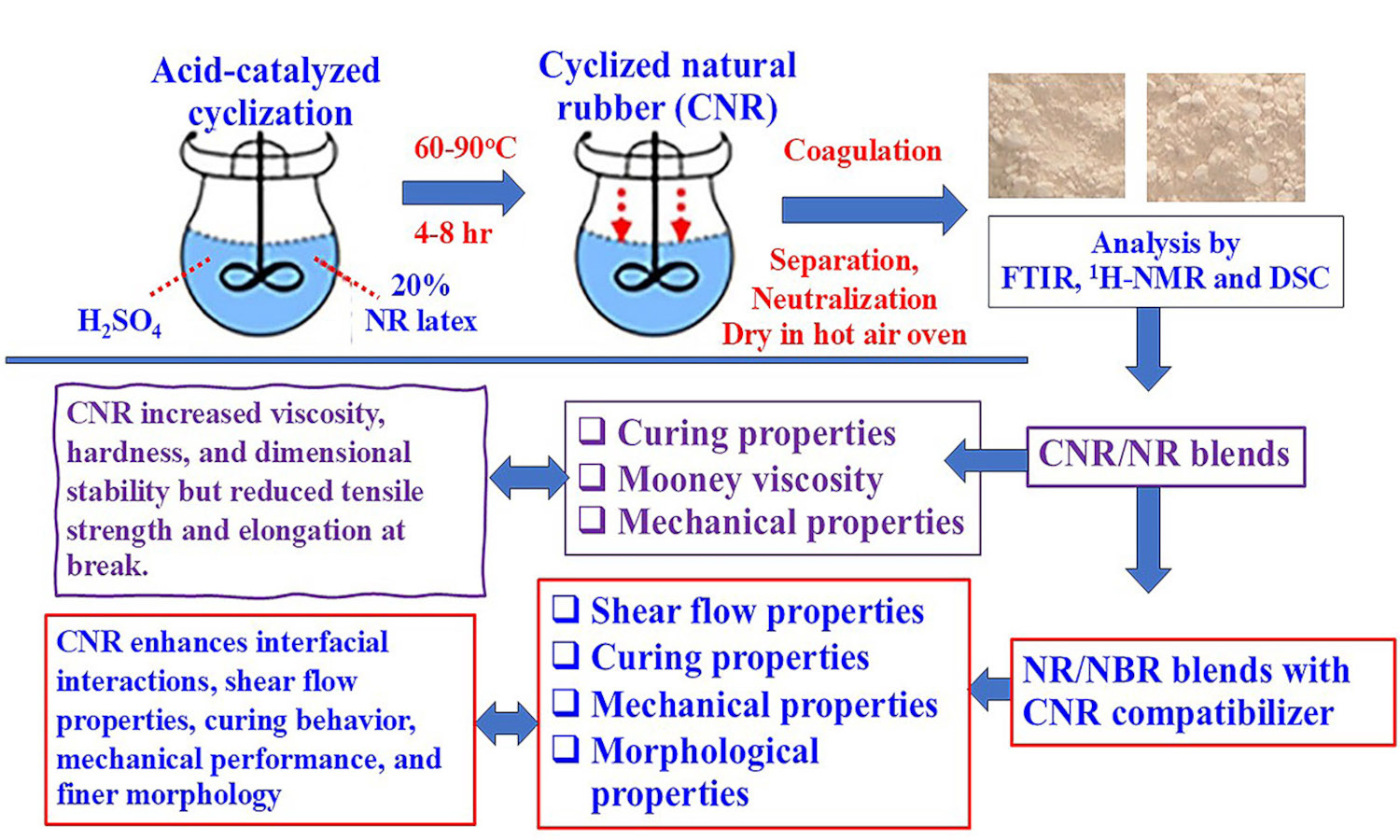
Cyclized natural rubber (CNR) was synthesized through the acid-catalyzed reaction of natural rubber (NR) latex using sulfuric acid as a catalyst and stabilized with a non-ionic surfactant. Cyclization was evaluated by iodine numbers under varying reaction times, temperatures, and NR-to-acid ratios. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR) confirmed the formation of cyclic structures in CNR molecules. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that the glass transition temperature (Tg) of CNR increased with cyclization, indicating greater rigidity and less chain flexibility. CNR was then blended with NR and used as a compatibilizer in NR/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)blends. It increased blend viscosity, hardness, and dimensional stability but reduced tensile strength and elongation due to its rigid cyclic domains. In NR/NBR blends, CNR outperformed a commercial homogenizer in enhancing interfacial interactions, leading to superior shear flow properties, curing behavior, and mechanical performance. This is attributed to the polar groups in CNR, which enhance intermolecular interactions and phase compatibility, resulting in finer phase morphology. This study highlights the potential of CNR as a versatile material for enhancing the performance of rubber compounds, with promising applications in advanced industrial formulations.
Liu Yang, Xuan Zhao, Sun Xinyu, Shuai Yuan, Lei Zhu
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60

Waste tire rubber poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and complex crosslinkedvstructure. In this sense, this study aims to examine the utilization of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) in the desulfurizationvprocess of ground tire rubber (GTR). A range of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs), including ethylene glycol, malonic acid,vimidazole, toluene sulfonic acid, and urea, were combined with choline chloride, which serves as a hydrogen bond acceptorv(HBA), to synthesize deep eutectic solvents. Subsequently, these DESs are used in the modification of rubber devulcanizationvprocesses. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Horikx analysis werevused to confirm the occurrence of devulcanization. The studies confirmed that the devulcanization process was selective invnature, effectively reducing random chain scission while maintaining the integrity of the polymer. Furthermore, the vulcanizatesvobtained post-treatment demonstrated enhanced properties, including increased tensile strength, modulus, tear strength, hardness, and durability, with ethylene glycol-based DES (DES-E) exhibiting the most pronounced enhancements.
Abdulhakim Masa, Nureeyah Jehsoh, Sawitree Dueramae, Nabil Hayeemasae
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 653-669, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.50
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 653-669, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.50

An antibacterial natural rubber (NR) latex film was successfully prepared in this study. This was done by coating silver (Ag) nanoparticles onto the surface of the NR latex film. The Ag nanoparticles were synthesized using green tea (GT) extract as a bio-reducing agent. The corresponding Ag nanoparticles were then deposited onto the NR latex film. Before synthesis, the phenolic compounds were identified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The Ag nanoparticles were found to be smaller than 25 nm in size. Subsequently, an experimental evaluation was conducted to determine the influence of deposition time, namely 1 to 20 min, on the film’s overall performance. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) confirmed that the Ag content was higher over the deposition time. The surface roughness of the samples was also screened by atomic force microscopy (AFM), where the films became rougher over the deposition time, confirming that Ag nanoparticles dispersed over the surface. As for the antibacterial activities, both qualitative and quantitative tests showed significant outputs. The clear zones of S. aureus and E. coli increased over the deposition time, and a shorter contact time was used to kill the bacteria. This study offers a scientific foundation that supports the development of future rubber products utilizing these findings.




