Recent advances in the applications of nanocellulose for sustainable development
Mohammad Mehdi Alighanbari, Firoozeh Danafar, Araam Namjoo, Asma Saeed
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 15-46, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
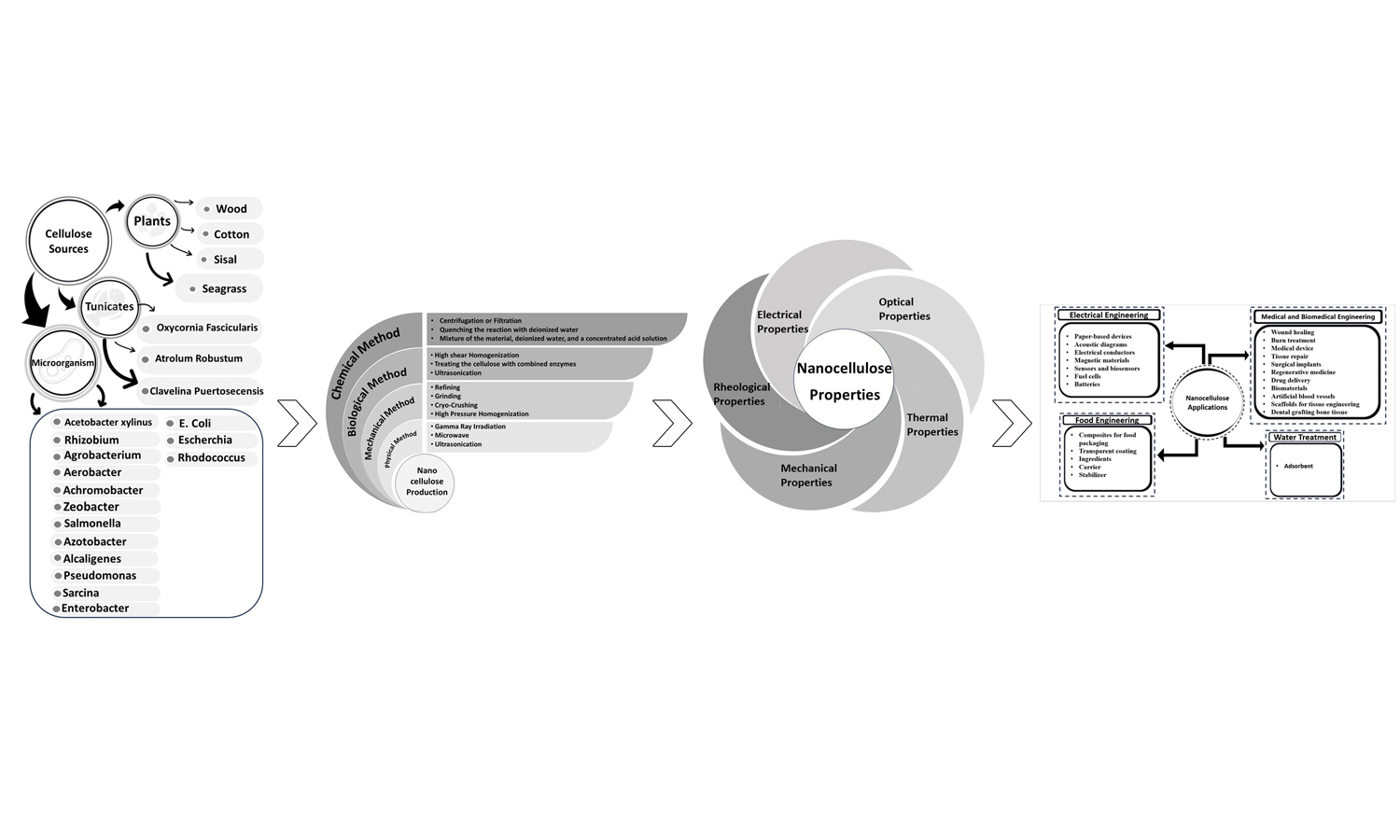
The environmental and ecological concerns drive researchers to synthesize functional materials using components from natural resources. Nanocellulose (NC), derived from plants, marine animals, or microorganisms, is a green material attracting attention due to its abundance, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. NC’s interstice properties enable the synthesis of functional nanocomposites in forms like aerogels, foams, paper, sheets, or hollow filaments. This review briefly describes NC classification and production while comprehensively presenting its mechanical, rheological, optical, and electrical properties, offering foundational knowledge for future research. Additionally, it highlights recent developments in NC-based products across fields such as papermaking, water treatment, civil engineering, electronics, cosmetics, food, and medicine. For the first time, this paper explores recent advances in NC molecular simulation, providing insights into structure, arrangement, and interactions through molecular dynamic simulation. Finally, future prospects for NC-based applications are discussed to encourage studies addressing current challenges.
RELATED ARTICLES
Jose James, George Vazhathara Thomas, Sisanth Krishnageham Sidharathan, Mohammad Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 697-705, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.53
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 697-705, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.53
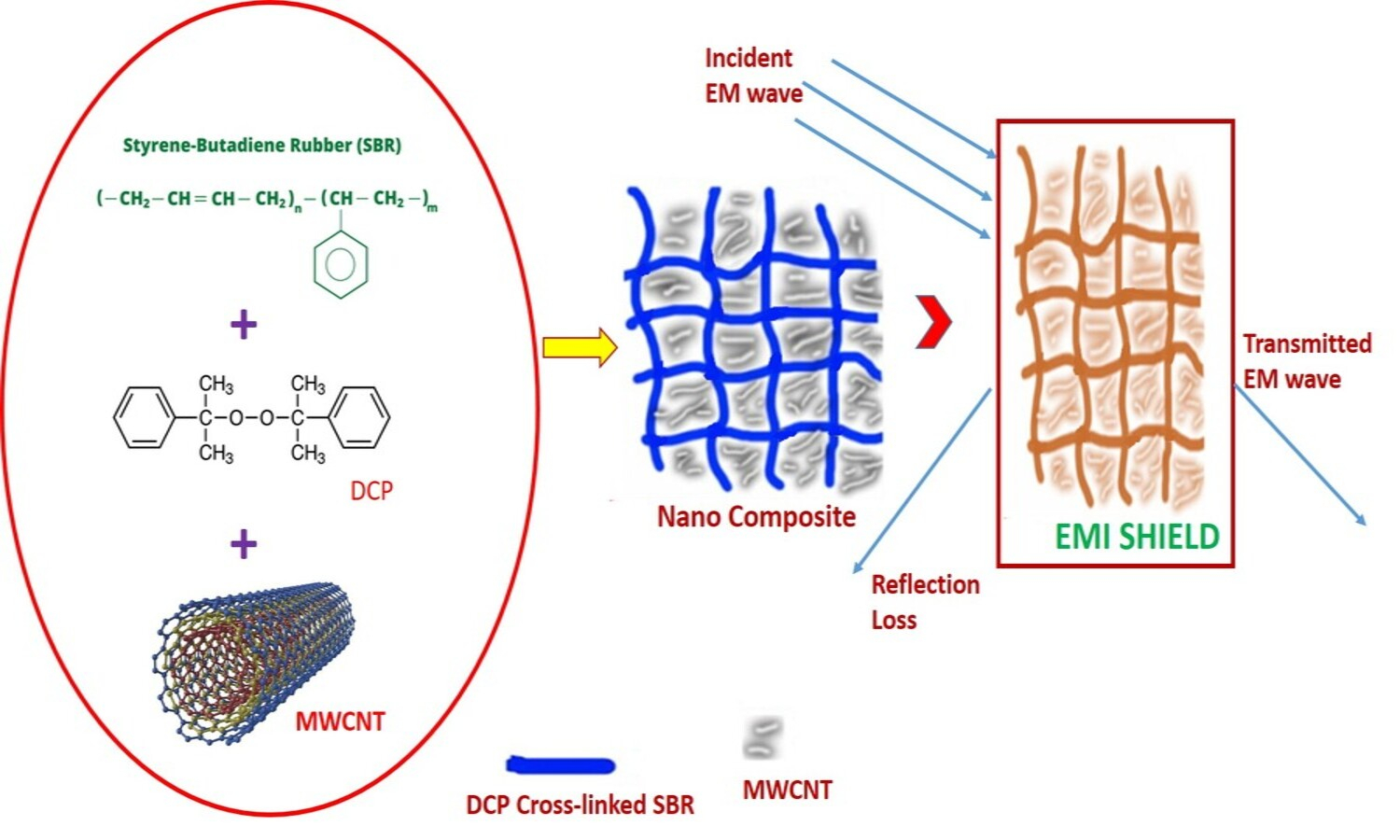
A nanocomposite of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) was fabricated using an internal melt mixer. Systematically investigated the role of MWCNT loading on the mechanical, dielectric, electrical and Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding characteristics of developed nanocomposites. The fine dispersion of MWCNTs in the SBR matrix was clearly observed from high-resolution transmission electron microscope images. The nanocomposites exhibited outstanding electrical, dielectric and EMI shielding behaviours (~45 dB at 20 phr of MWCNT). A high conductivity of 0.92 S/cm was attained in the nanocomposites and is attributable to the establishment of percolation networks of MWCNT in the SBR matrix. These composites displayed reasonably good mechanical properties because of the reinforcing effect of MWCNT. The economically viable and easy fabrication protocol of this nanocomposite can act as a platform for the synthesis of low-cost and highly effective composite for EMI shielding applications.
Cristian Valdés, Valentina Guzmán, Camila Ponce, Maribel Mamani, Juan Guevara, Claudia Vergara, Rodrigo Andler
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
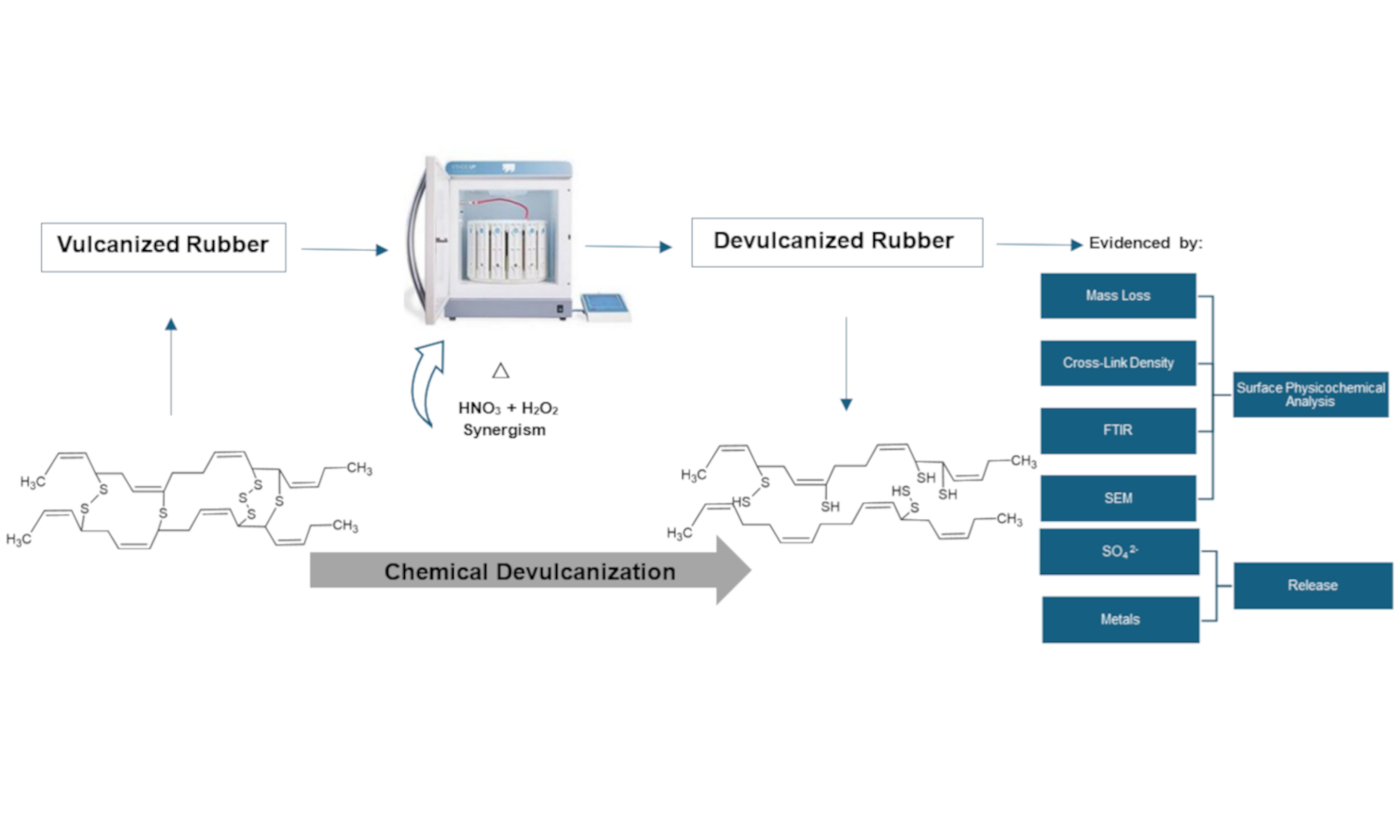
Waste rubber disposal causes considerable negative environmental impacts due to its increase worldwide, mainly in the automotive industry. Therefore, the search for technological solutions for rubber waste is a priority, and the first step in this material degradation is devulcanization due to its difficult degradation. This study evaluated rubber devulcanization using a closed vessel microwave digestion system with nitric acid (HNO3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) through chemical characterization, aiming at verifying the synergistic effect between these oxidizing agents. Microwave irradiation was applied as a heating method to facilitate the chemical reactions, focusing on the synergism between HNO3 and H2O2. Results showed that 5 M H2O2 in combination with 1% HNO3, presented better results. A greater decrease in cross-link density was demonstrated as the concentration of H2O2 increased (3.96·10–5±1.99·10–6 mol/cm3), likewise, higher sulfates released (926.8±53.4 mg/L), increased mass loss (12.184±1.06%), rubber surface fragmentation, and important variations in the C–S, C=O bands, showing better results when devulcanization is carried out in synergism between HNO3 and H2O2.
Timothy K. Mulenga, Sanjay Mavinkere Rangappa, Suchart Siengchin
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 470-493, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.35
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 470-493, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.35
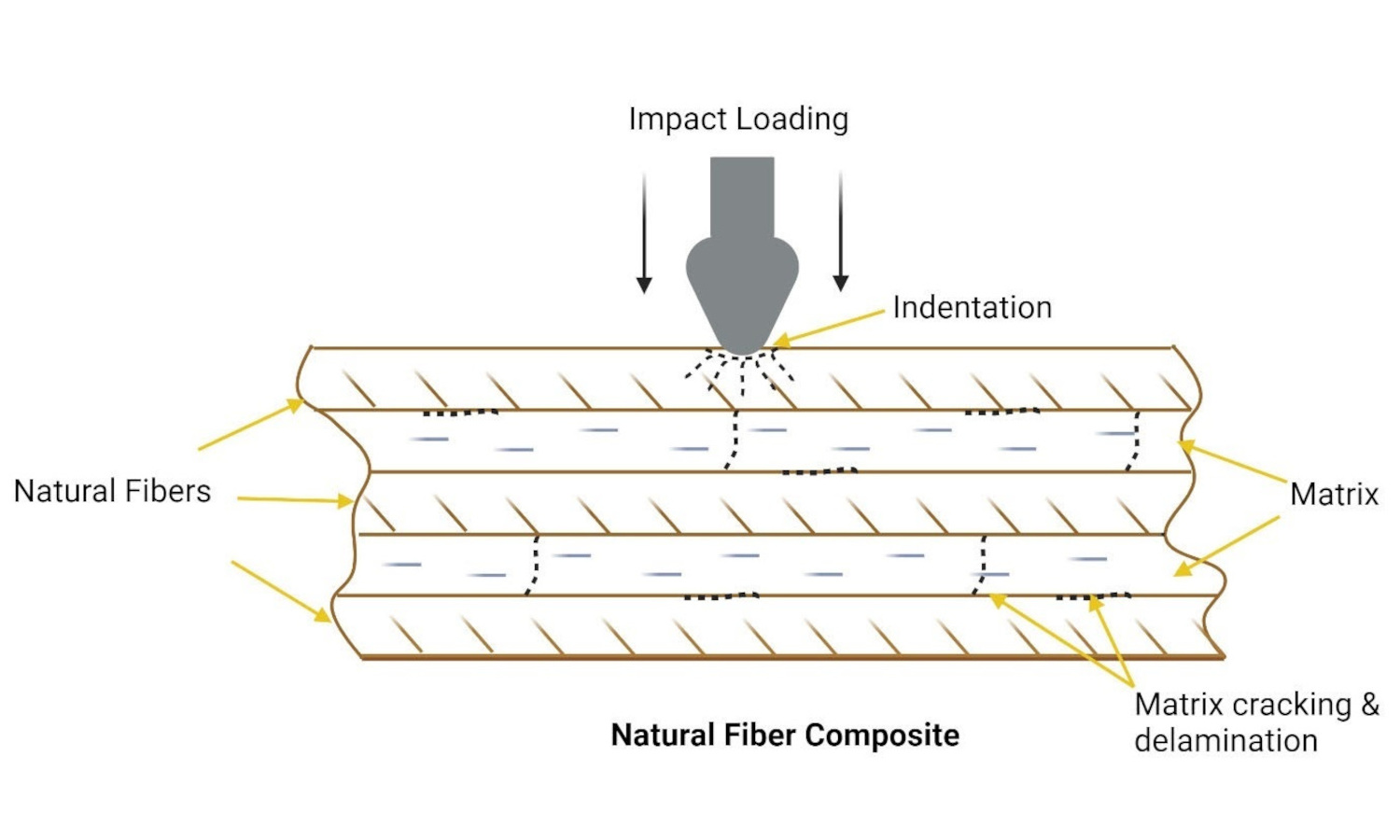
Natural fiber composites (NFC) have emerged as promising sustainable alternatives to conventional synthetic materials due to the increasing environmental concerns and unsustainable reliance on depleting petroleum resources. NFCs offer various advantages, such as reduced costs, low density, biodegradability, and good specific mechanical properties. However, their impact resistance remains a crucial factor that greatly influences their suitability for sectors like automotive, construction, and aerospace, where impact loading is prevalent. This review comprehensively analyzes the impact resistance of NFCs, aiming to elucidate the factors governing their behavior under varying impact loading conditions. The study delves into the influence of key parameters such as fiber type, matrix properties, and fiber-matrix adhesion on the impact response of NFCs. Different impact loading methods, including low-velocity impact and high-velocity impact, are examined, highlighting their distinct effects on NFC failure mechanisms. Furthermore, the review investigates the effectiveness of various methods employed to enhance the impact strength of NFCs. Finally, it identifies current challenges and limitations associated with impact-resistant NFCs and outlines potential future research directions to overcome these obstacles and unlock the full potential of these sustainable materials.
Quentin Watel, Aurélie Cayla, Fabien Salaün, François Boussu
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 494-503, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.36
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 494-503, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.36
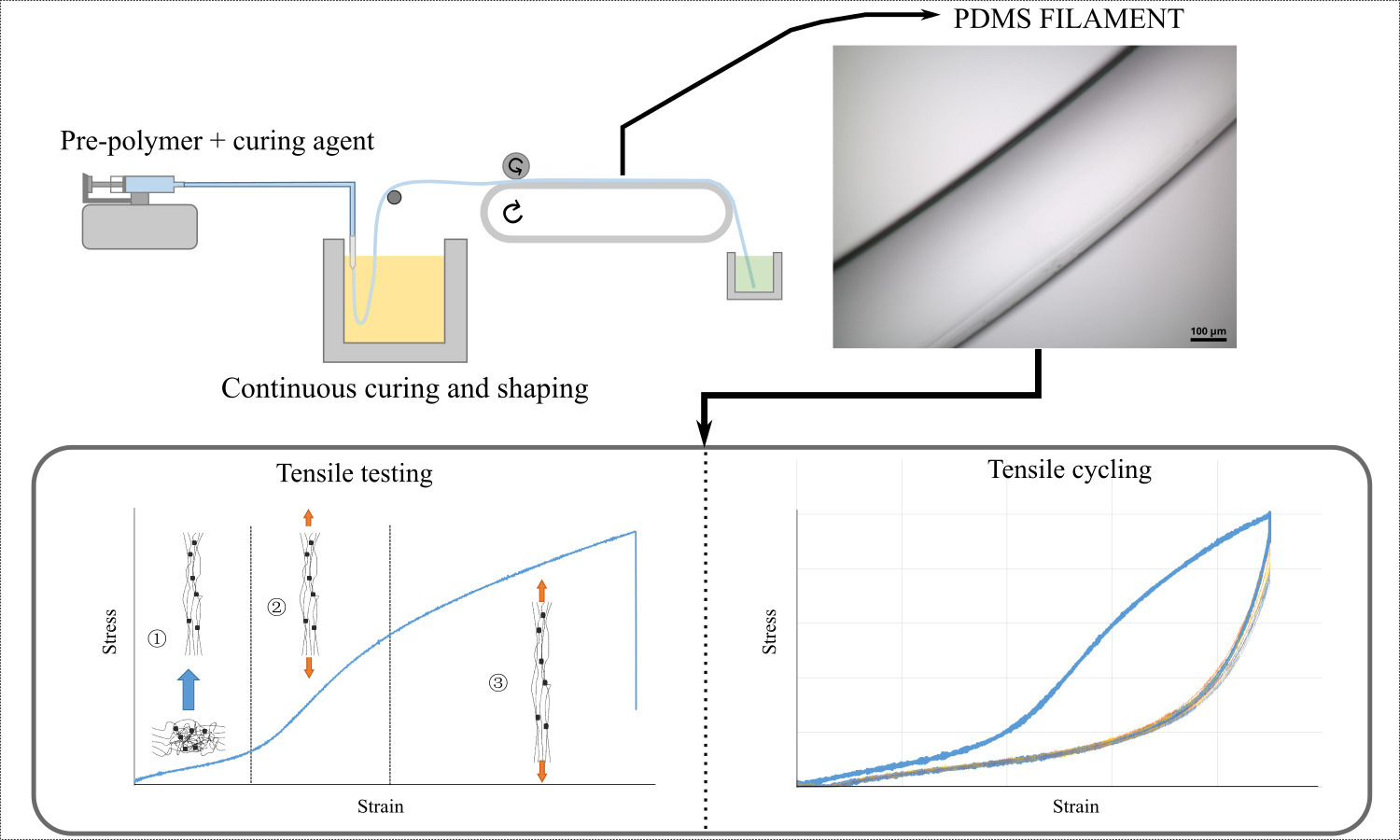
In this work, a PDMS spinning technique is developed and enables the continuous production of a filament with a circular cross-section (~500 μm diameter). The production of continuous silicone polymer filaments can be useful in the textile field to provide new properties in applications such as weaving, knitting or composite reinforcement. The method involves injecting the pre-polymer and curing agent mixture into a heated oil bath (202–215 °C) to simultaneously shape and cure the PDMS. The morphological and mechanical properties of the filament are studied regarding the production parameters (formulation, needle diameter, bath temperature, conveyor belt speed). The most homogeneous filament is produced at the highest temperature (215°C) and conveyor belt speed (13.6 m∙min–1). When subjected to cyclic mechanical stress, the PDMS filament produced exhibits stable mechanical behavior, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Katalin Litauszki, Tamás Tábi, László Mészáros
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 455-456, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 455-456, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.



