Improvement thermal-mechanical properties of PHBV/hemp MCC biocomposite with ENR grafted silanized MFC as a sustainable additive: Investigation outdoor performance through weathering acceleration
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 423-440, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.31
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.31
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
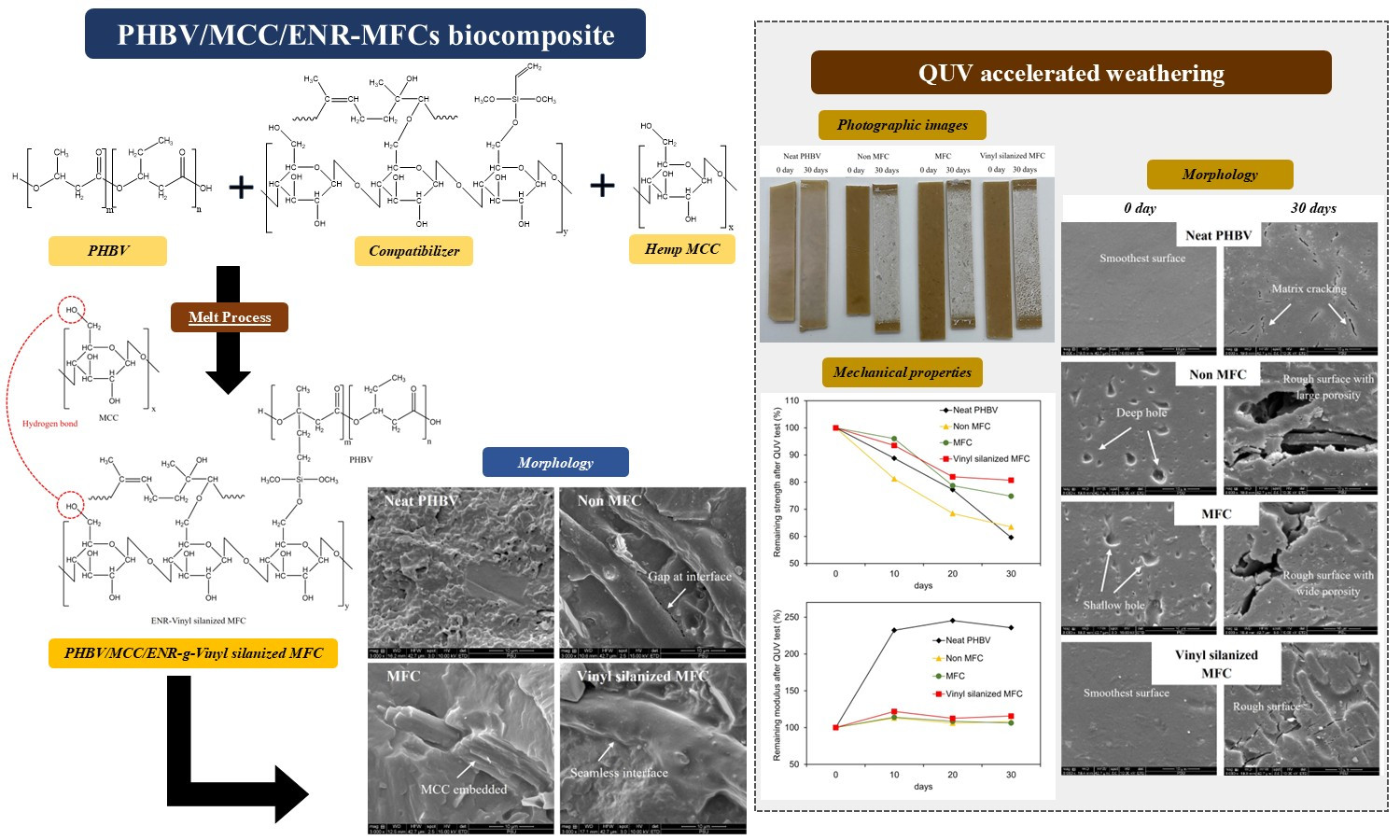
ABSTRACT
This research aimed to enhance the properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) biocomposites by incorporating hemp microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). Additionally, to improve interfacial adhesion between PHBV and MCC phases, a compatibilizer consisting of epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) grafted with microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) modified by vinyltrimethoxysilane (ENR-vinyl silanized MFC) was introduced. The addition of 5 wt% MCC increases the flexural modulus by approximately 65%. The use of ENR-vinyl silanized MFC as a compatibilizer demonstrated improved compatibility, as observed in scanning electron microscope (SEM) images. After 30 days of accelerated weathering (QUV) exposure, the flexural strength of the PHBV-based biocomposite with ENR-vinyl silanized MFC and MCC (vinyl silanized MFC biocomposite) was superior to that of the other samples. The remaining flexural strength can be sequentially categorized as follows: vinyl silanized MFC > MFC > non-MFC > PHBV. The Tg of PHBV-based biocomposites showed no significant change. Interestingly, the crystallinity of the vinyl silanized MFC biocomposite was the highest among all materials and demonstrated higher hydrophobicity. This makes the vinyl silanized MFC biocomposite a suitable material for construction, furniture, and both exterior and interior decoration.
RELATED ARTICLES
Cláudia Andréa Batista dos Santos, Bartłomiej Kryszak, Rafał Malinowski, Aleksandra Ujćič, Konrad Szustakiewicz
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
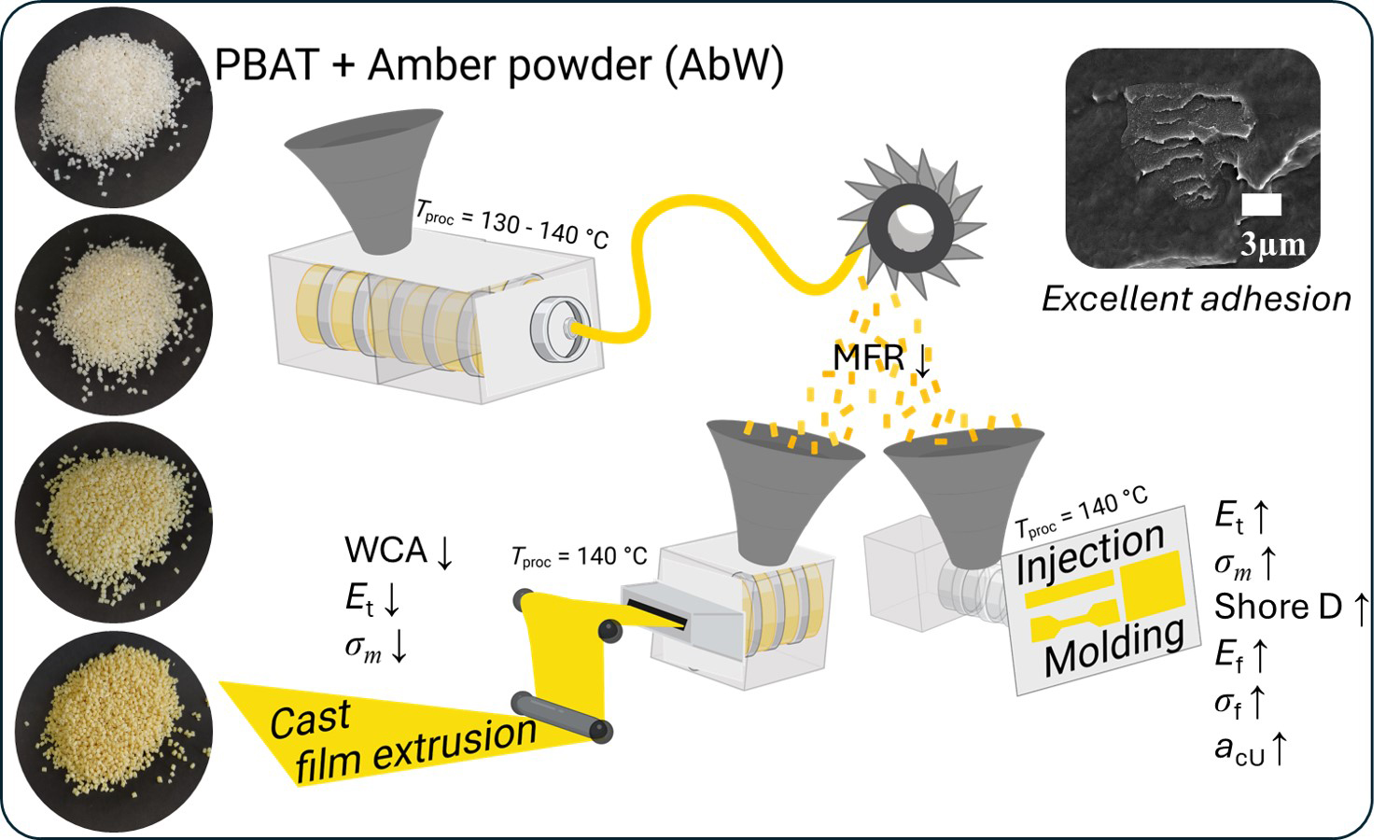
This study investigates the interaction between poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and amber powdered waste (AbW) from jewelry at different filler concentrations (0, 1, 2.5, and 5 wt%) obtained via melt mixing in a corotating twin screw extruder. The resulting materials were pelletized and processed using two techniques: 1) cast film extrusion and 2) injection molding. The shaped specimens exhibited excellent interfacial adhesion. Thermal behavior, as assessed by Vicat softening temperature (VST), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), showed minimal variation among the composites. Despite similar melt flow rate (MFR) values among the samples, the incorporation of AbW affected the behavior of the polymer during cast film extrusion. Consequently, the composite films exhibited lower tensile mechanical parameters (tensile strength, Young’s modulus, stress and strain at break) compared to the neat PBAT film. In turn, the injection molded composites showed improved tensile, flexural, and impact parameters compared to their neat counterpart. Additionally, a slight decrease in water contact angle (WCA) suggested increased surface hydrophilicity of the extruded films. These findings demonstrate the potential of AbW as an additive for biopolymer composites with enhanced mechanical performance. The increased surface hydrophilicity is particularly relevant for applications targeting biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Effect of natural cinnamon extract on the stabilizing properties of biodegradable packaging polymers
Anna Kosmalska-Olańska, Anna Masek
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5

The growing focus on sustainability, eco-friendly technologies, decarbonization, and reducing carbon footprints shapes current industry challenges. This article reviews the potential of cinnamon as a bio-additive for polymer stabilization in packaging. Samples were prepared from ethylene-norbornene copolymer (Topas), a cyclic olefin copolymer known for purity, transparency, and low gas permeability, and poly(lactic acid) (PLA), a bio-based alternative to petroleum plastics. Cinnamon powder was added in 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 wt%. After solar and thermo-oxidative aging, hydrophobicity, chemical composition, mechanical, and color properties were analyzed. Results showed higher hydrophobicity and resistance to hydrolytic degradation due to reduced water penetration. PLA, normally brittle, became more flexible, with 0.5 wt% cinnamon showing optimal performance after 100 h of solar aging, similar to Topas composites. Overall, PLA and cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) films with cinnamon improved durability, extended food shelf life, and acted as natural color indicators of material aging.
Elumalai Vengadesan, Swaminathan Muralidharan, Dhanjit Das, Thirugnanasambandam Arunkumar
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 822-842, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.63
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 822-842, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.63
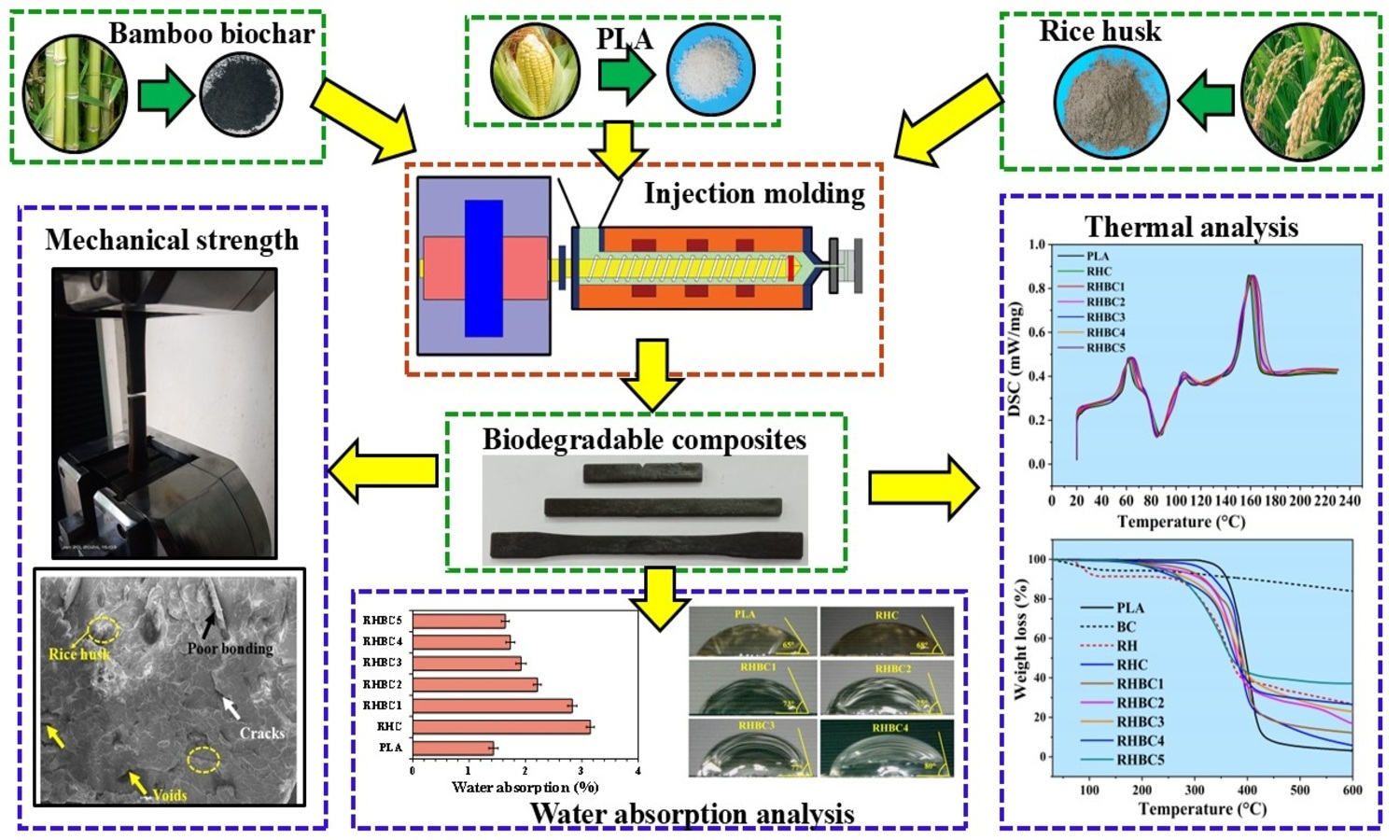
The growing need for sustainable materials has stimulated research into eco-friendly composites, with biochar emerging as an important reinforcement in polymer matrices. Biochar is a carbon-rich material produced by pyrolyzing organic biomass, offering various benefits over traditional fillers, including sustainability, waste reduction, and carbon sequestration. This study explores the effects of bamboo biochar as a hybrid reinforcement on the properties of polylactic acid (PLA)-rice husk composites. The present hybrid composites are prepared by varying the bamboo biochar from 5–25% and have better mechanical properties than PLA and its composite reinforced with a rice husk filler. The tensile, flexural, and compressive strengths of 51.5, 166.0, and 77.5 MPa are measured for the biochar percentage of 10%, representing increases of 73.1, 150.0, and 58.2% compared to PLA, and 158.2, 98.6, and 31% compared to the PLA composite with rice husk. Higher tensile and flexural moduli of 1.46 and 7.34 GPa are observed for 10 and 15%, respectively. However, the impact strength decreases with higher biochar content due to increased rigidity. The material’s hardness increases at higher biochar content due to enhanced stiffness. Thermal transition and degradation points rise due to increased crystallinity from the biochar reinforcement’s nucleation effect. Additionally, the hydrophobic biochar reinforcement reduces water absorption of PLA composite from 3.2 to 1.6%.
Lilla Bubenkó, Násfa Németh, Sára Frey, Tamás Molnár, Károly Belina, Orsolya Viktória Semperger
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
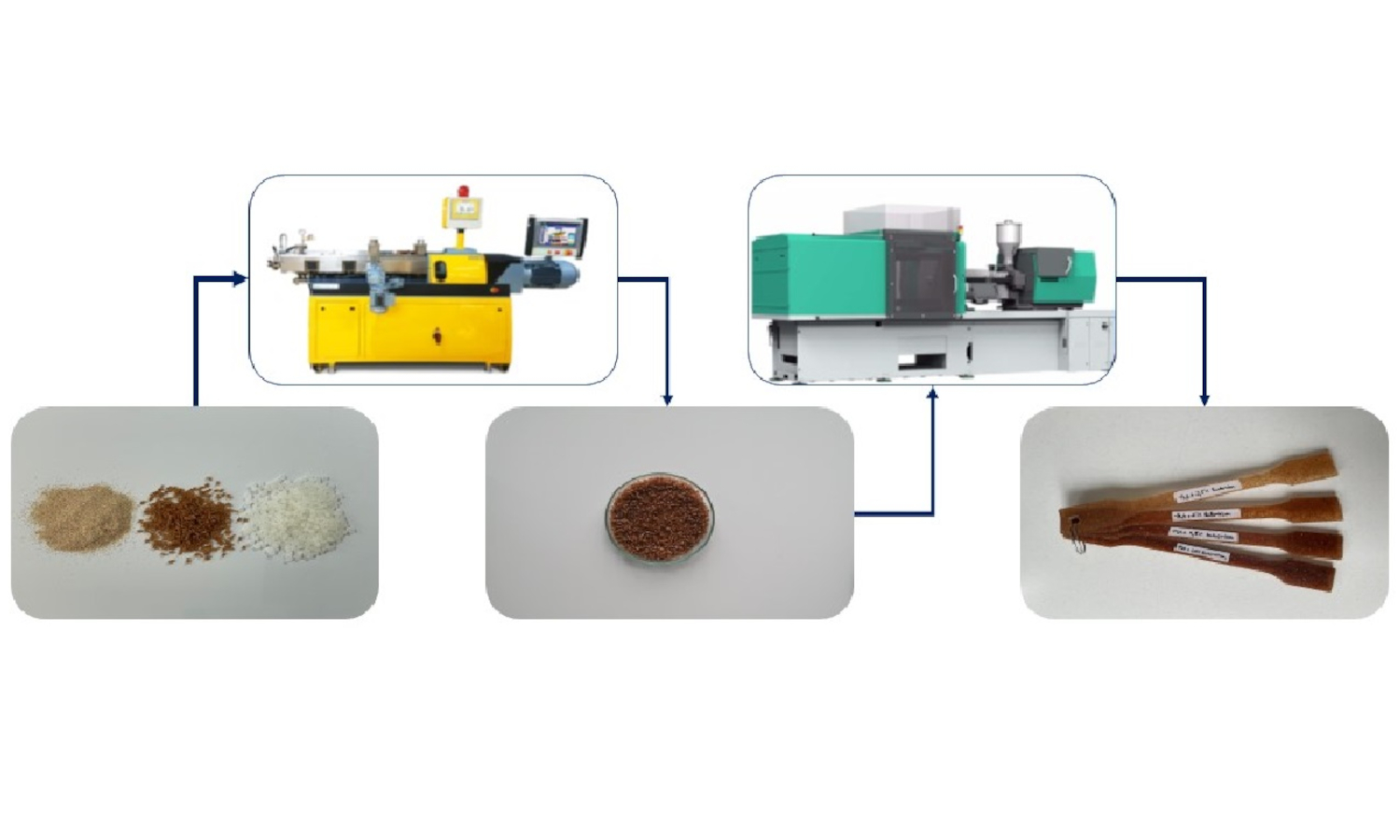
Biocomposites have recently received more attention because of raising environmental awareness and the drive toward sustainable technologies. The most common biodegradable polymer is poly(lactic acid) (PLA), which has an excellent balance of physical and rheological properties, but there is some limit to its usage. PLA properties can be improved by adding different types of fibers or fillers that come from agricultural waste. In this study, corn cob and lavender stem were used to reinforce PLA without any coupling agent, and the properties of the composites were investigated. The melt flow rate (MFR) values decreased with the corn cob content and increased with the addition of lavender stem. Mechanical tests showed that the tensile and flexural modulus of the composites increased and the strengths decreased with the reinforcement material content. The rigidness of PLA slightly decreased with the addition of fillers. There was no significant effect on the thermal properties. The unremarkable improvement of the reinforcement was due to the lack of appropriate adhesion of the two phases. The structure of the compounds was found to be homogenous on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs. The incorporation of corn cob and lavender stem can reduce the production cost of materials.
Konrad Stefaniak, Anna Masek
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
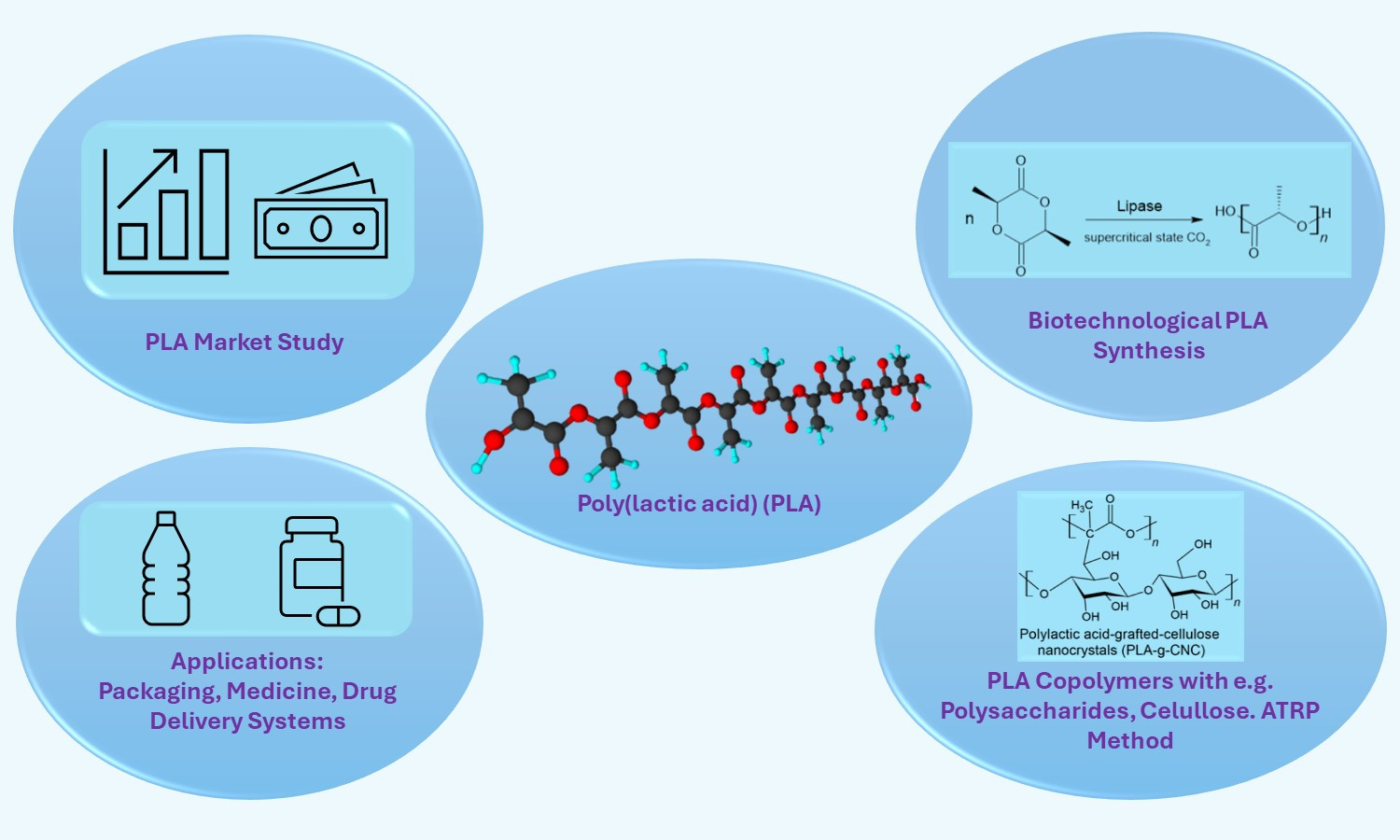
This review is focused on recent achievements in poly(lactic acid) (PLA) synthesis and copolymerization with special regard to biotechnological routes of PLA synthesis, which use bacteria/enzymes (e.g., enzymatic ring opening polymerization (eROP)). Besides PLA, also lactic acid (LA) synthesis is described and an emphasis is put on the biotechnological methods. Having regard to PLA copolymerization, this paper attempts to describe different types of PLA copolymers (such as block copolymers, PLA copolymers with polysaccharides, PLA-cellulose copolymer composites, and PLA polymer brushes). A detailed overview of the recent accomplishments in the field of PLA copolymers is presented. Various enhanced properties and applications of presented PLA copolymers are discussed. The attention is placed mainly on applications in the field of tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and the packaging sector. Furthermore, a PLA market study and its economic forecast are presented. Eventually possible directions for future research in the field of PLA synthesis and copolymerization are indicated.




