Molecular design of cyanate ester resin using amino-POSS and C60 to create high-performance thermostable polycyanurate nanocomposites
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 504-518, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.37
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.37
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
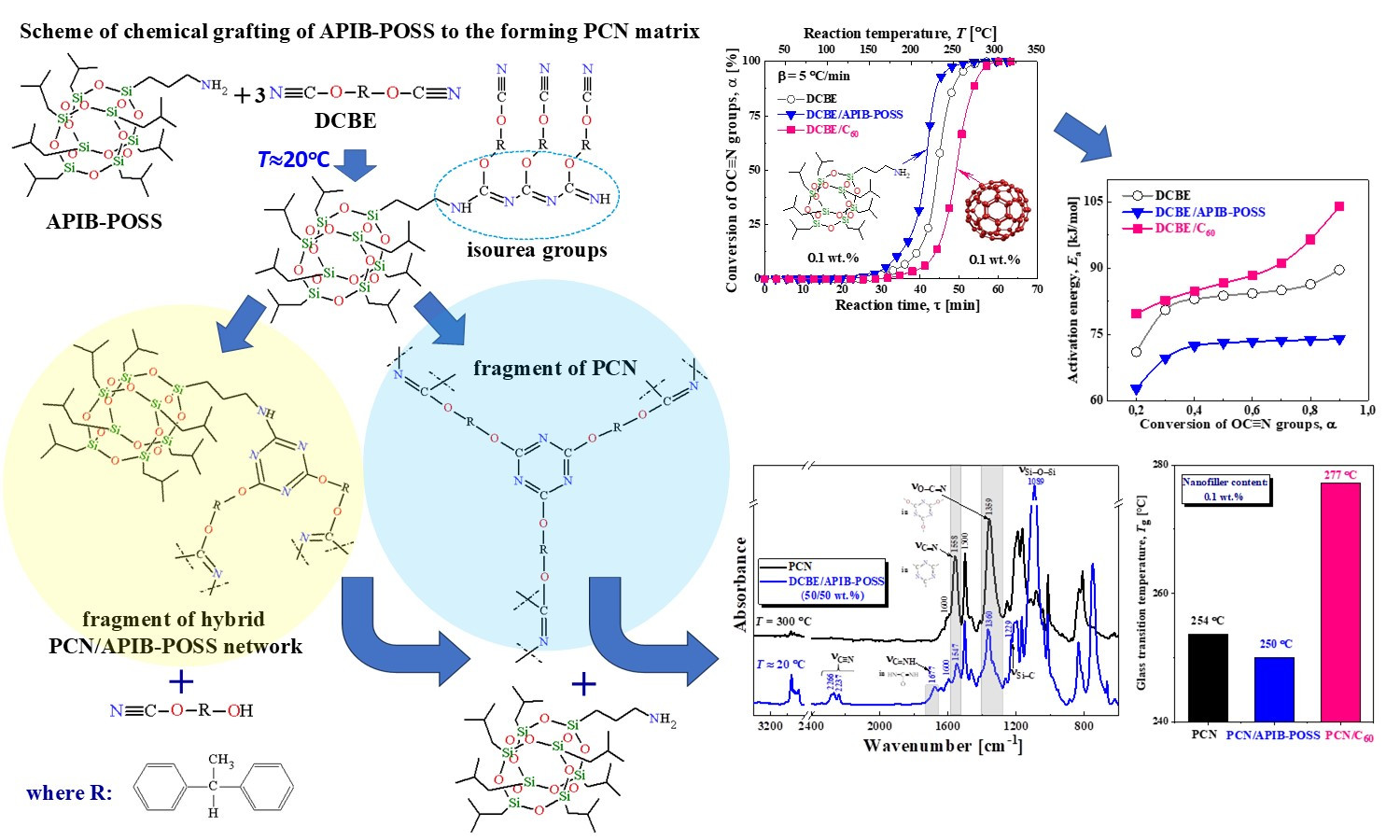
ABSTRACT
The kinetics of polycyclotrimerization of cyanate ester resin (CER), viz. dicyanate ester of bisphenol E (DCBE), was studied by DSC method during its molecular design at ultra-low content (0.1 wt%) of two types of nanofillers: reactive aminopropylisobutyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (APIB-POSS) or inert fullerene C60 having inorganic closed cage structure of nanomolecules. The polycyclotrimerization of DCBE was significantly accelerated in the presence of APIBPOSS, and its nanoparticles were covalently incorporated into the structure of the growing polycyanurate (PCN) matrix to form a hybrid organic-inorganic PCN/APIB-POSS network. Using FTIR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopy for the DCBE/APIB-POSS (50/50 wt%) reactive blend the chemical interaction between the NH2 groups of APIB-POSS and the –OC≡N groups of DCBE was confirmed even from the beginning of mixing of the components at T ≈20°C. In contrast, the distribution of inert C60 nanoparticles in DCBE slowed down its polycyclotrimerization, but, unexpectedly, this led to the formation of a PCN/C60 nanocomposite with increased glass transition temperature (Tg) reaching 277°C, which is 24°C higher than the Tg of unfilled PCN. The nanocomposites developed are characterized by high thermal stability (Тd5% > 440°C).




