Role of nanocellulose geometric structures on the properties of green natural rubber composites
Milanta Tom , Sabu Thomas
, Sabu Thomas , Bastien Seantier
, Bastien Seantier , Yves Grohens
, Yves Grohens , Mohamed Pulikaparambil Kochaidrew, Ramakrishnan Subramanian, Tapas Ranjan Mohanty
, Mohamed Pulikaparambil Kochaidrew, Ramakrishnan Subramanian, Tapas Ranjan Mohanty , Henri Vahabi
, Henri Vahabi , Hanna Joseph Maria
, Hanna Joseph Maria , Jibin Keloth Paduvilan, Martin George Thomas
, Jibin Keloth Paduvilan, Martin George Thomas
 , Sabu Thomas
, Sabu Thomas , Bastien Seantier
, Bastien Seantier , Yves Grohens
, Yves Grohens , Mohamed Pulikaparambil Kochaidrew, Ramakrishnan Subramanian, Tapas Ranjan Mohanty
, Mohamed Pulikaparambil Kochaidrew, Ramakrishnan Subramanian, Tapas Ranjan Mohanty , Henri Vahabi
, Henri Vahabi , Hanna Joseph Maria
, Hanna Joseph Maria , Jibin Keloth Paduvilan, Martin George Thomas
, Jibin Keloth Paduvilan, Martin George ThomasVol. 18., No.6., Pages 638-655, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.47
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.47
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

ABSTRACT
The augmented demand for
sustainable nanocomposites has paved the way to explore naturally derived
materials. Nanocellulose, with its bountiful sources and inherent properties,
ranks top in the list of biofillers with a perspective of reducing the carbon
footprint. A systematic study is required to understand the reinforcing effect
of various types of nanocellulose. In the present work, we selected three types
of nanocellulose, i.e.,
cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), cellulose nanofiber (CNF) and microfibrillated
cellulose (MFC), to investigate the effect of geometrical structure on the
properties of unvulcanized natural rubber (NR). Incorporating these fillers
improved the tensile strength and modulus of natural rubber films significantly
through reinforcement via filler network structure. The reinforcing effect of
CNF was found to be higher compared to CNC and MFC, where an increase of 3.85
MPa in tensile strength from the neat sample was obtained. More uniform
dispersion was evident through transmission electron microscopy, atomic force
microscopy and Raman imaging for CNF in the rubber matrix. The structural
properties were determined using Raman spectra and X-ray diffraction. The rheological
studies revealed a good interaction between filler and NR. The work presented
comprehensively compares different types of nanocellulose as reinforcing filler
in NR matrix, which will help the researchers select an ideal type for their
specific application and, thus, the proper usage of renewable resources,
leading to sustainability and a circular economy.
RELATED ARTICLES
Reinforcing effect of thermo-oxidative reclaimed rubber on NR/SBR blends for tire tread applications
Yunhui Xu, Zaheer ul Haq, Junrong Li, Hui Tu, Zaixue Wang, Houluo Cong
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 142-153, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.12
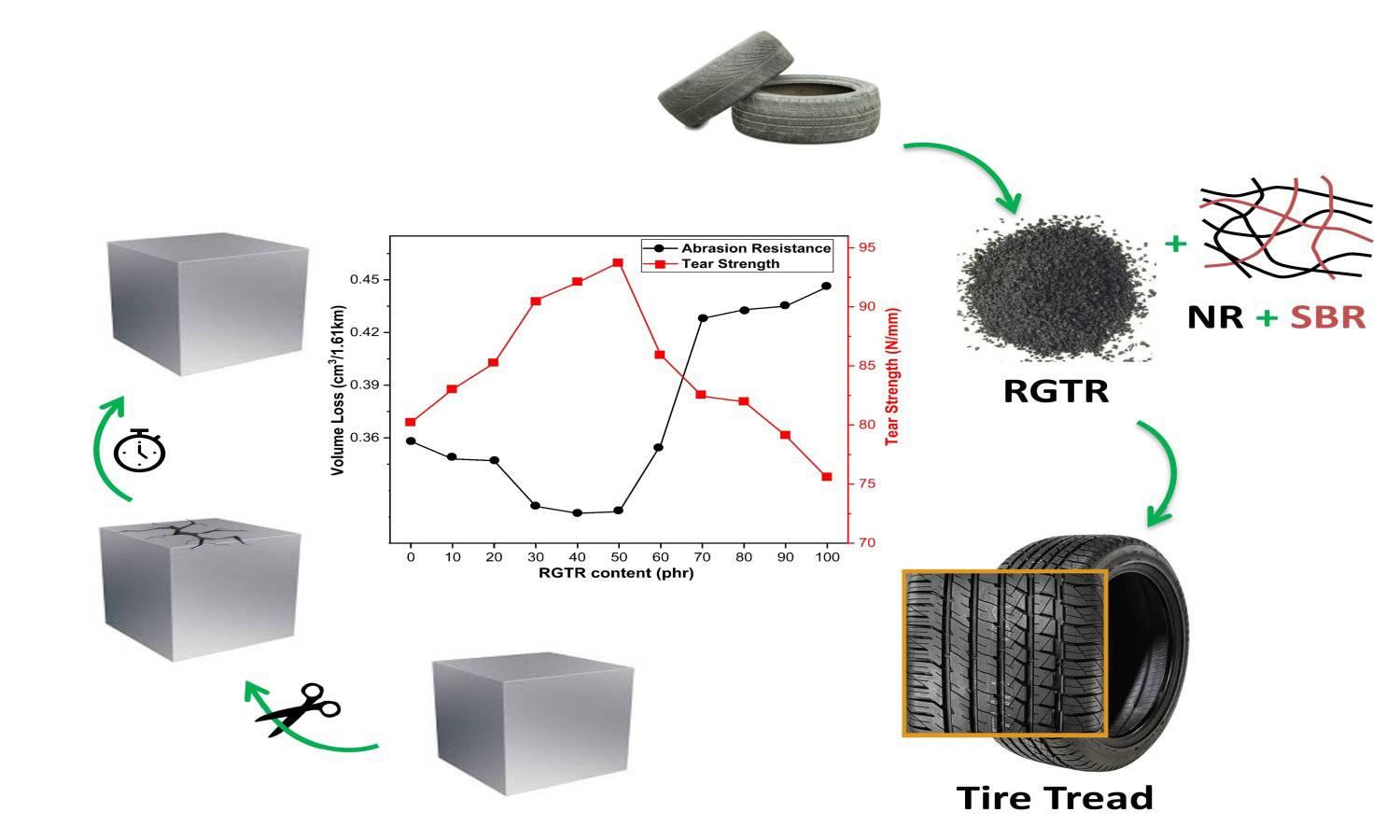
This study explores the application of thermo-oxidative reclaimed ground tire rubber (RGTR) in natural rubber (NR)/styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) composite, focusing on its impact on morphology, mechanical properties, rheological behavior, vulcanization characteristics, aging resistance, tear strength and abrasion resistance. The findings revealed that RGTR enhances the tear strength and abrasion resistance of NR/SBR composites while maintaining comparable tensile strength, elongation at break, and modulus. The incorporation of RGTR reduced Mooney viscosity of the NR/SBR composites and improved flowability. It also shortened the vulcanization time and enhanced vulcanization efficiency. The NR/SBR composites with RGTR loadings below 60 phr exhibited optimal performance, achieved a maximum tear strength of 93.77 N/mm and improved abrasion resistance. However, higher RGTR content led to increased agglomeration, as evidenced by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which showed finer dispersion at lower RGTR contents and larger aggregates at higher loadings. These findings demonstrate the potential of RGTR as a sustainable additive for enhancing specific properties in NR/SBR composites, contributing to both performance optimization and waste tire management.
Dibyendu Dey, Sharmistha Dhar, Barkat Aziz, Sambhu Bhadra, Sujith Nair, Kinsuk Naskar
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 127-141, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.11
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 127-141, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.11
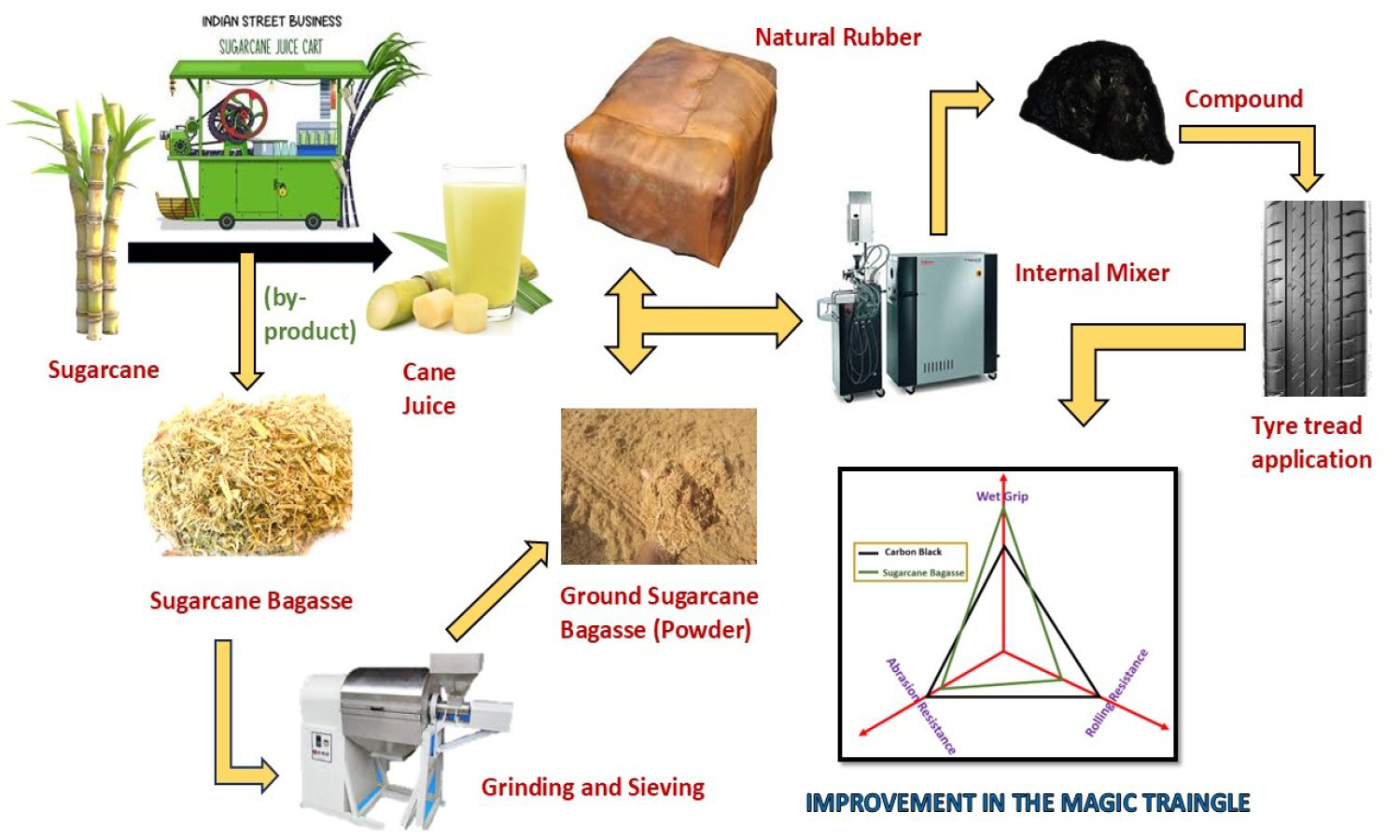
Ground sugarcane bagasse (GSB), an agro-waste rich in lignocellulosic components, was studied as a sustainable bio-filler in natural rubber (NR) tread compounds to lessen reliance on petroleum-derived carbon black (CB). A control formulation with 45 phr CB was compared to hybrid formulations with 40, 35, and 30 phr CB mixed with 5, 10, and 15 phr GSB. Tensile strength 13.1 MPa, elongation at break 700%, and hardness 67 Shore A were all optimally balanced by the compound containing 10 phr GSB (S2), while also exhibiting good cure behavior and thermal stability. Improved tire performance characteristics were confirmed by a dynamic mechanical study, which showed that tan δ at 60 °C decreased by 8.0% (resulting in lower rolling resistance) and increased by 3.9% (improving wet traction) at 0°C. The Payne effect showed improved filler dispersion as a result of GSB partially replacing CB. The results show that appropriately dispersed GSB can partially reinforce NR, enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. However, larger GSB loadings decrease modulus, tear strength, and abrasion resistance due to lower interfacial adhesion and the presence of micro-voids. According to this study, pulverized sugarcane bagasse shows promise as an environmentally friendly filler for green tire applications, promoting the circular economy and lowering the carbon footprint of rubber compounding.
Xavier Colom, Scott Martínez, Fernando Carrillo-Naverrete, Javier Cañavate
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 114-126, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.10
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 114-126, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.10
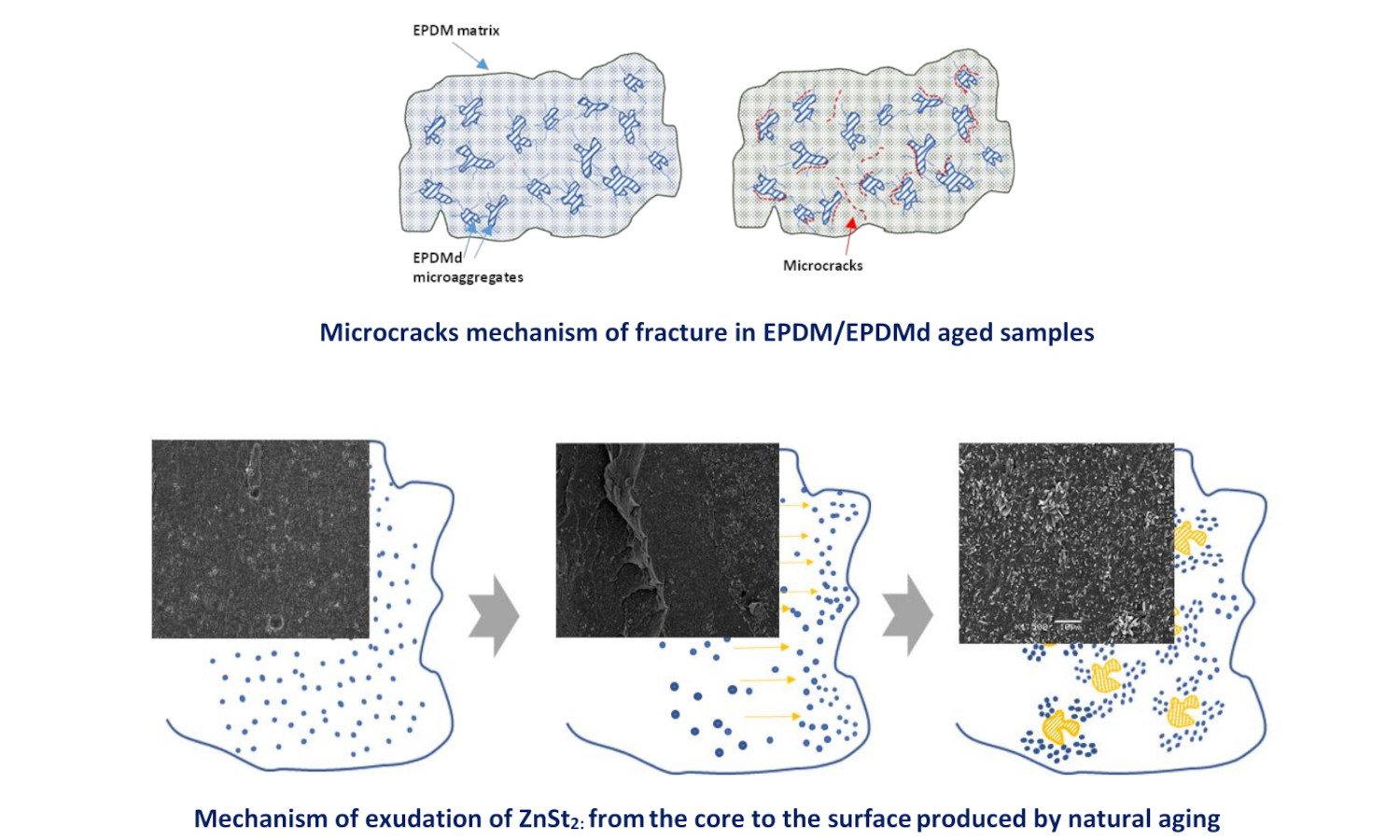
The need to recycle elastomeric waste requires studying its viability in industrial applications. This study investigates the feasibility of recycling elastomeric waste by analyzing whether virgin ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) can be replaced by blends of virgin EPDM and thermomechanically and microwave devulcanized EPDM (EPDMd) in industrial applications from the perspective of environmental degradation. Two types of samples were examined: conventional EPDM used to roof membranes, and EPDM blended with different amounts (20, 40, and 50 phr) of EPDMd. Samples were subjected to natural aging in coastal and mountainous environments. Results show that mechanical properties decline with higher EPDMd content and, to a lesser degree, with prolonged outdoor exposure. The coastal climate proved more aggressive than the mountainous one when EPDMd content exceeded 40 phr. Zinc stearate (ZnSt2), a byproduct of vulcanization, was found to influence the evolution of the mechanical behavior. The combined analysis of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), abrasion tests, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) provided insights into the degradation processes of these elastomeric blends.
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Phakawat Tongnuanchan, Subhan Salaeh, Jutharat Intapun, Abdulhakim Masa, Natinee Lopattananon
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 18-35, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.3
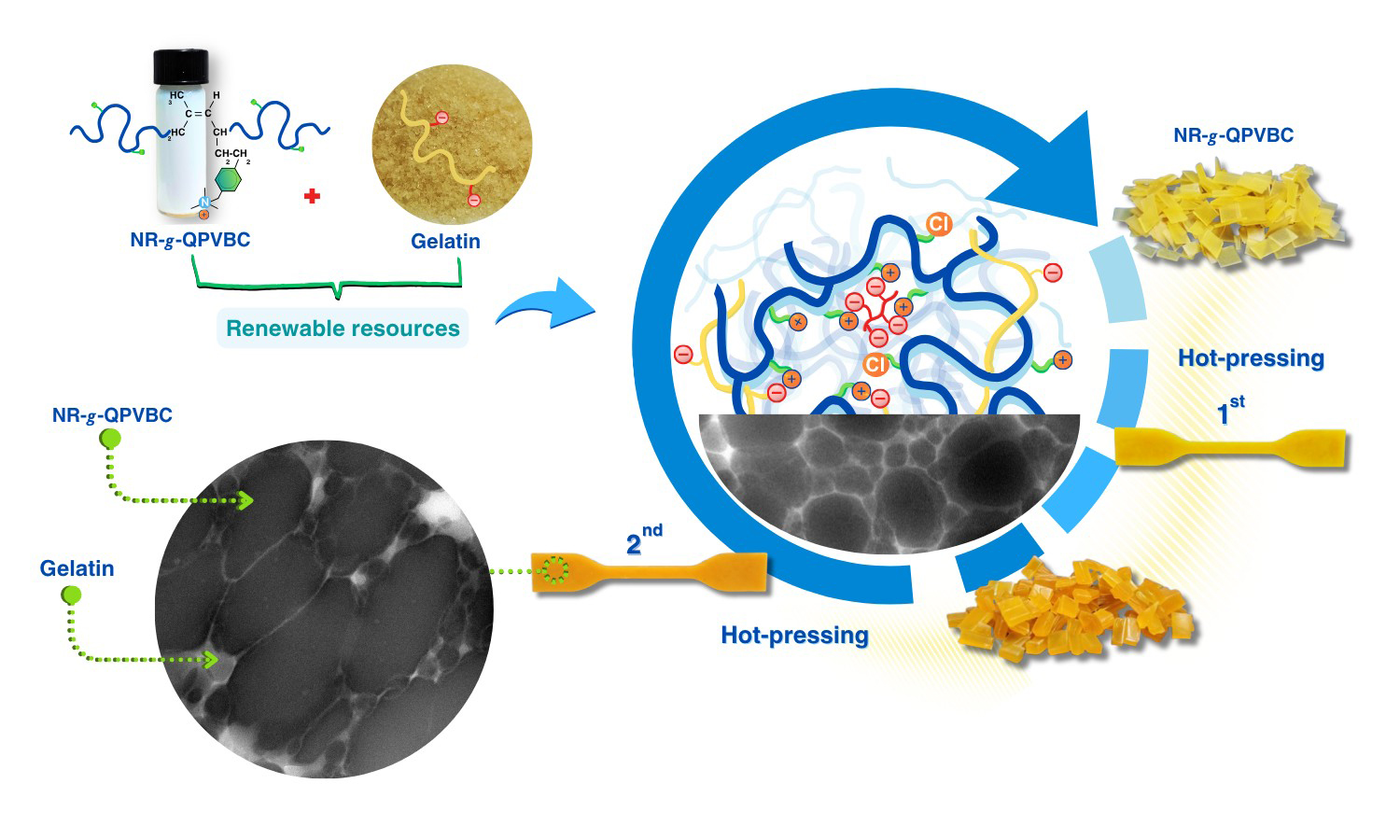
The present study has proposed a straightforward method to improve the reprocessability of modified natural rubber (NR) by blending it with gelatin (GT). The reprocessable characteristics of these blends were evaluated based on their remolding capabilities and mechanical recovery performance. In this method, poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) (PVBC) was first grafted onto NR chains to create graft copolymers known as NR-g-PVBC. The benzyl chloride groups in the graft copolymers were subsequently converted into quaternary ammonium groups, referred to as NR-g-QPVBC. This modification enabled ionic crosslinking when NR-g-QPVBC reacted with ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid. Blends were created by incorporating GT powder into the NR-g-QPVBC latex. The optimal loading level of GT was determined to be 30 wt%, as the resulting film exhibited the highest recovery of tensile properties. Initially, the film's tensile strength was measured at 15 MPa. After being remolded at 160 °C, the tensile strength decreased to 9.3 MPa, resulting in a recovery rate of 60.7% and withstanding a tensile strain of 144%. Although the NR-g-QPVBC/GT films could be remolded, their tensile properties declined with increasing remolding cycles. Therefore, this work demonstrated a practical method for producing NR-based films that could be reshaped through hot-pressing after being formed into products, increasing their reusability.
Hatay Cöcen, Nilgün Kızılcan
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 82-96, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.7
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 82-96, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.7
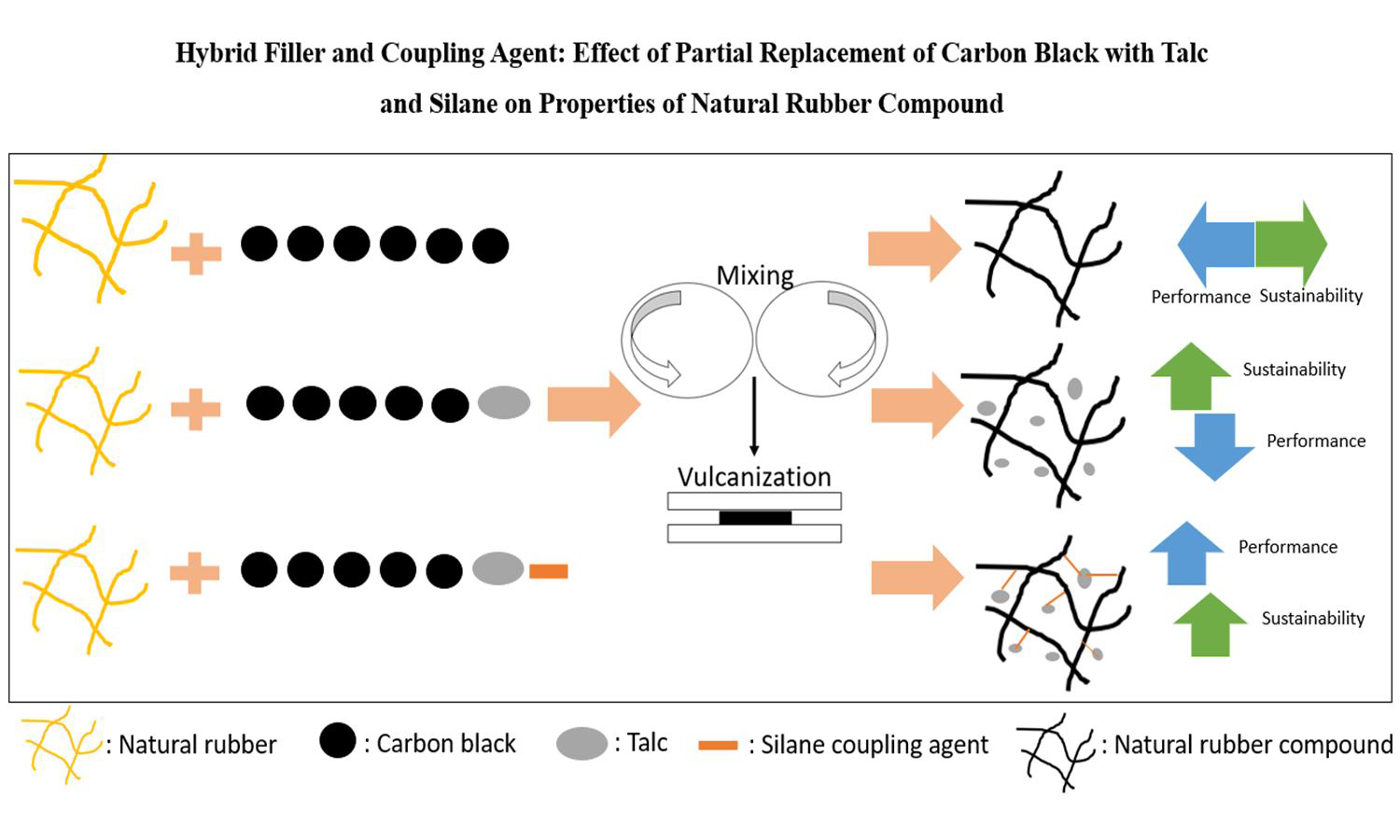
This study investigates a sustainable hybrid-filler strategy for natural rubber (NR) compound by partially replacing petroleum-based carbon black (CB) with talc and introducing a silane coupling agent to mitigate interfacial incompatibility. Compounds containing CB, CB+talc and CB+talc+increasing silane were produced via two-stage mixing and characterized for morphology (dispersion/mapping), curing and flow behavior (differential scanning calorimetry DSC/moving die rheometer, MDR/Mooney), crosslink density (Flory–Rehner), physical–mechanical properties, dynamic performance (Payne effect/heat build-up/tension–fatigue), and thermal stability (aging/thermogravimetric analysis,TGA). Talc reduced the compound viscosity, offering processing benefits. The swelling test indicated that talc decreased crosslink density, but silane recovered it, forming covalent linkages. Tensile strength and elongation at break were improved without altering hardness. Dynamically, talc increased heat build-up, whereas silane inverted the trend and reduced the temperature rise gradually from 41.5 to 29.4°C at 2 phr. Fatigue life was improved with talc (~10%), and further with silane (up to 36% at 2 phr), highlighting a favorable stiffness–fatigue balance with compatibilization. Overall, partial CB replacement by talc, in combination with silane, delivers meaningful sustainability gains with improved dynamic performance while preserving key mechanical properties of NR compounds.



