Let's talk about the definitions: Bioplastics, biopolymers, biodegradable polymers and others
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 455-456, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
RELATED ARTICLES
Paulina Bednarczyk, Kamil Rożniakowski
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
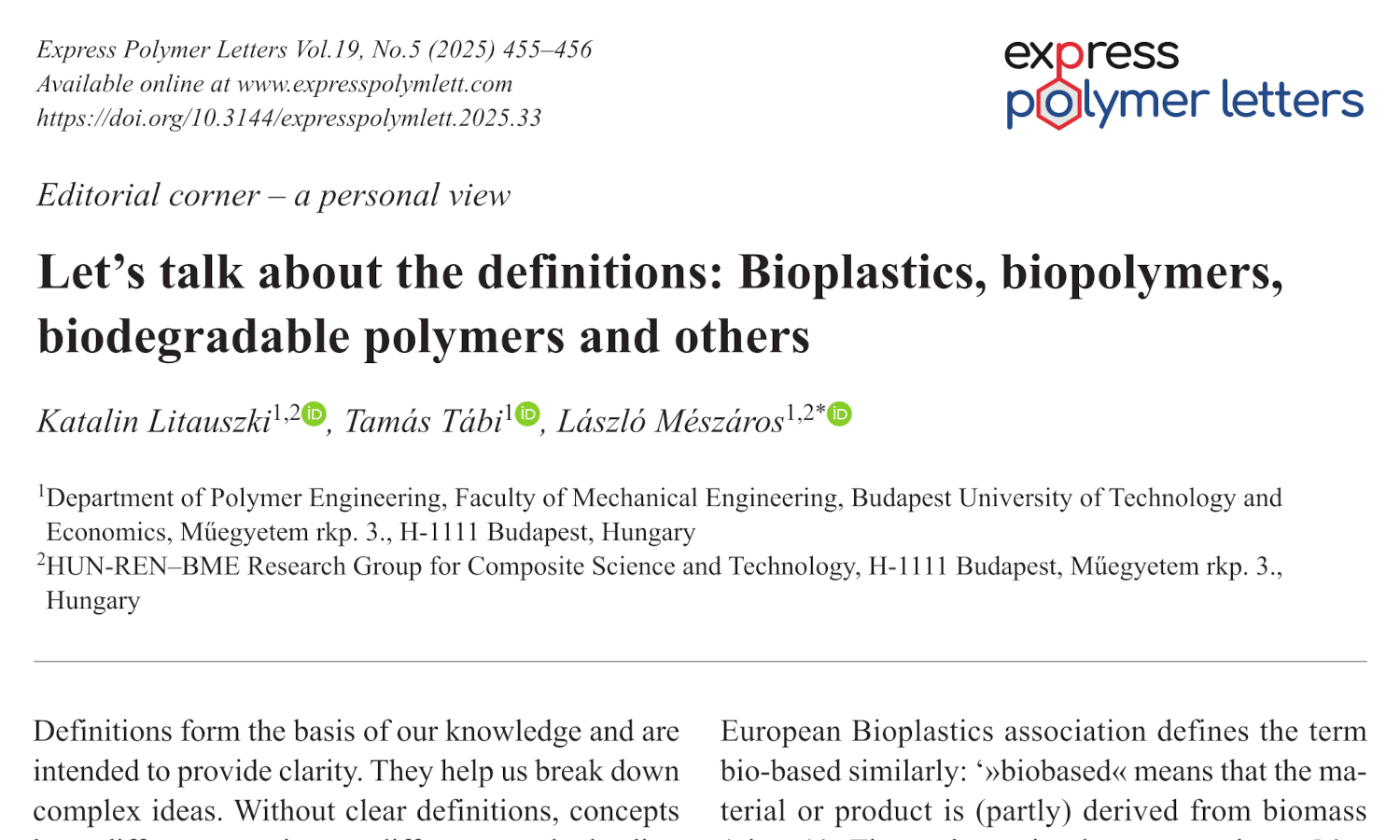
This study investigates the structure–property relationships of multi-functional urethane acrylate resins designed as photoreactive binders for UV-curable nail coatings. Four systems were examined: a commercial resin urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA), a bio-based acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO), and two newly synthesized bio-based urethane acrylates derived from 1,3-propanediol (PDO–UA) and eugenol (EUG–UA). Photopolymerization kinetics were analyzed by realtime FTIR, while the properties of the cured coatings were also determined. The mechanical and thermal behavior of selfsupporting polymer films was evaluated by tensile testing and DSC analysis. The UDMA network exhibited the highest crosslink density, reflected in its high modulus (≈0.5 GPa), tensile strength (≈15 MPa), and Tg (≈60°C), making it suitable for use as a top coat. AESO showed moderate stiffness and flexibility, whereas PDO–UA and EUG–UA formed soft, low-Tg (–12 and –17°C) and highly deformable networks typical of elastomeric materials. The combined mechanical and thermal results confirmed that crosslink density strongly governs coating performance and applicability. This study demonstrates that blending UDMA with bio-based oligomers enables the design of sustainable, UV-curable nail lacquers with an optimal balance of hardness, flexibility, and adhesion to the natural nail plate.
Evangelia Balla, Panagiotis Klonos, Apostolos Kyritsis, Dimitrios Bikiaris
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
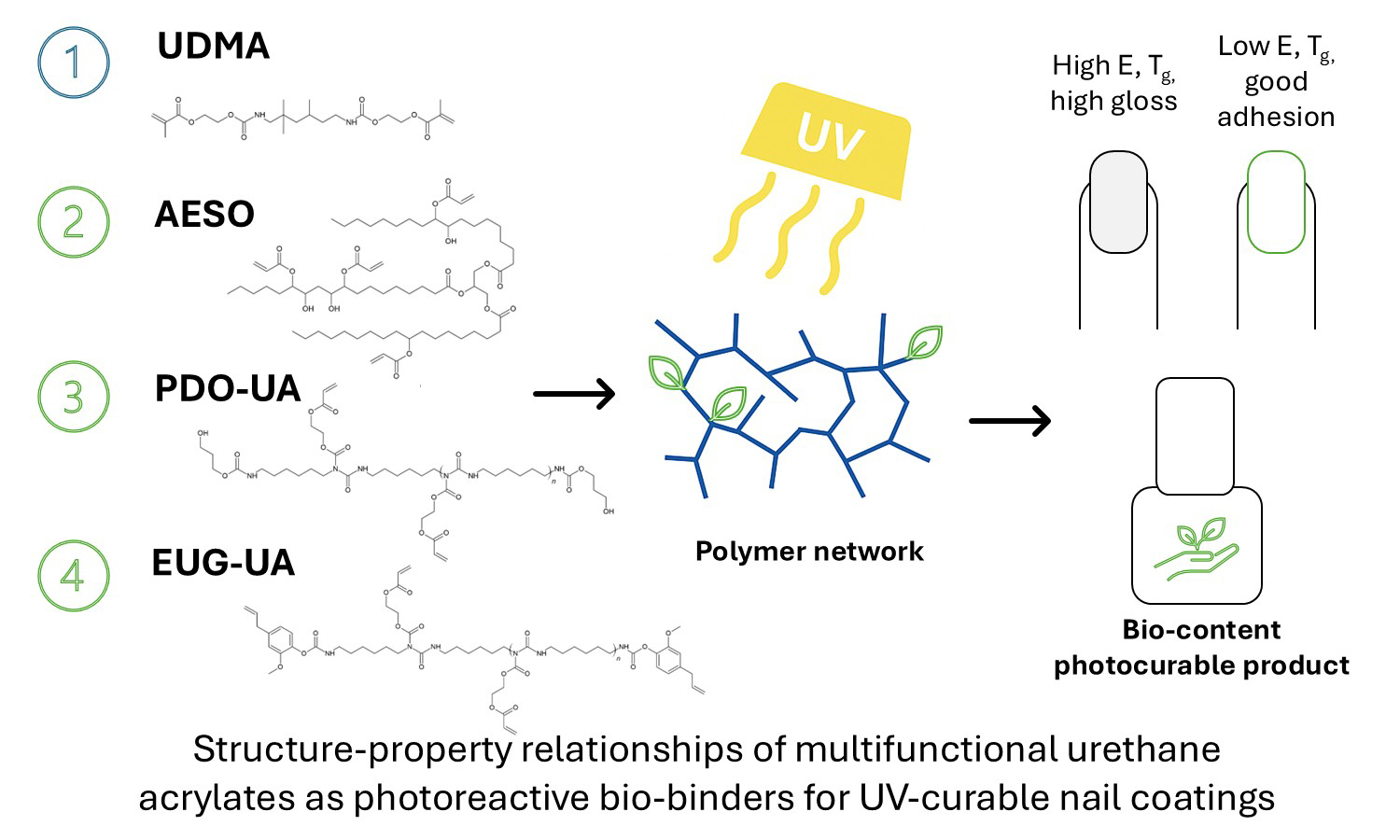
In recent decades, numerous efforts have been dedicated to the investigation of eco-friendly non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) as alternatives to conventional polyurethanes (PUs). Since isocyanates are classified by the EU as hazardous and toxic compounds, NIPUs offer a promising route to mitigate isocyanate-related health risks as well as other environmental concerns associated with traditional PU synthesis. In the present study, we report the synthesis as well as the detailed structural and thermal characterization of a new series of fully biobased non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) based on aliphatic dicarboxylic acids of different chain lengths. The NIPUs were prepared via a two-step polyaddition reaction involving glycerol carbonate and diamine. Their synthesis enables a sustainable pathway to tailor NIPUs’ physicochemical properties via diacid structure control. Studies of their structure, thermal behavior and trends, morphological, and hydrolytic findings confirmed strong diacid chain length dependence on glass transition temperature (Tg ~13, 0, ‒5 and –23 °C), molecular weight, surface wettability, and enzymatic degradability. Short-chain diacids yielded NIPUs with rapid hydrolytic degradation, while their longer-chain analogs were hydrophobic and thermally stable. Contact angle measurements (~75–85°) also confirm these trends. The tunable properties position these materials among strong candidates for biomedical applications.
Soni Thakur, Amal M. Sindi, Rahul Dev Bairwan, Rasha A. Mahmoud, Eman Alfayez, Nurul Fazita Mohammad Rawi, Kanchan Jha, H.P.S. Abdul Khalil
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
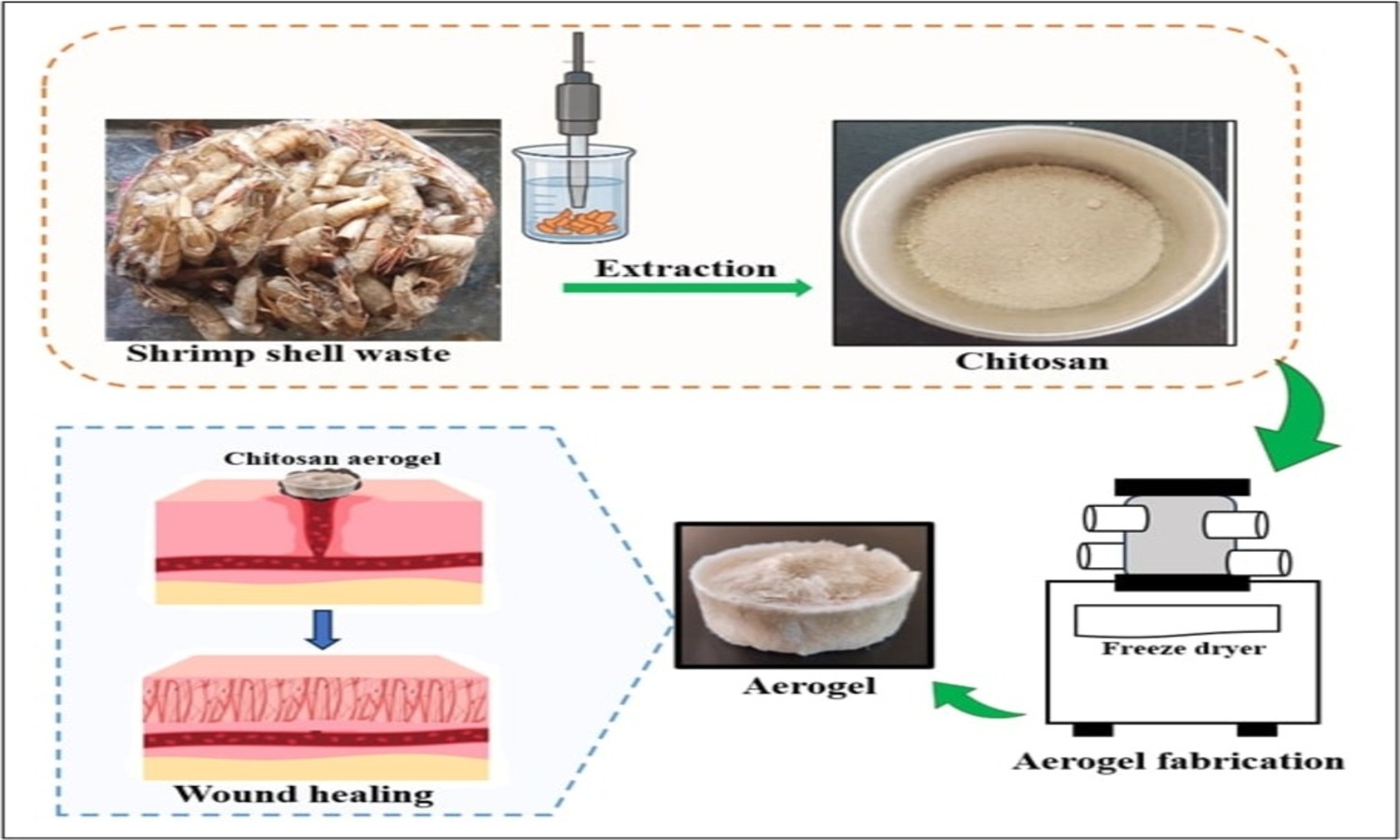
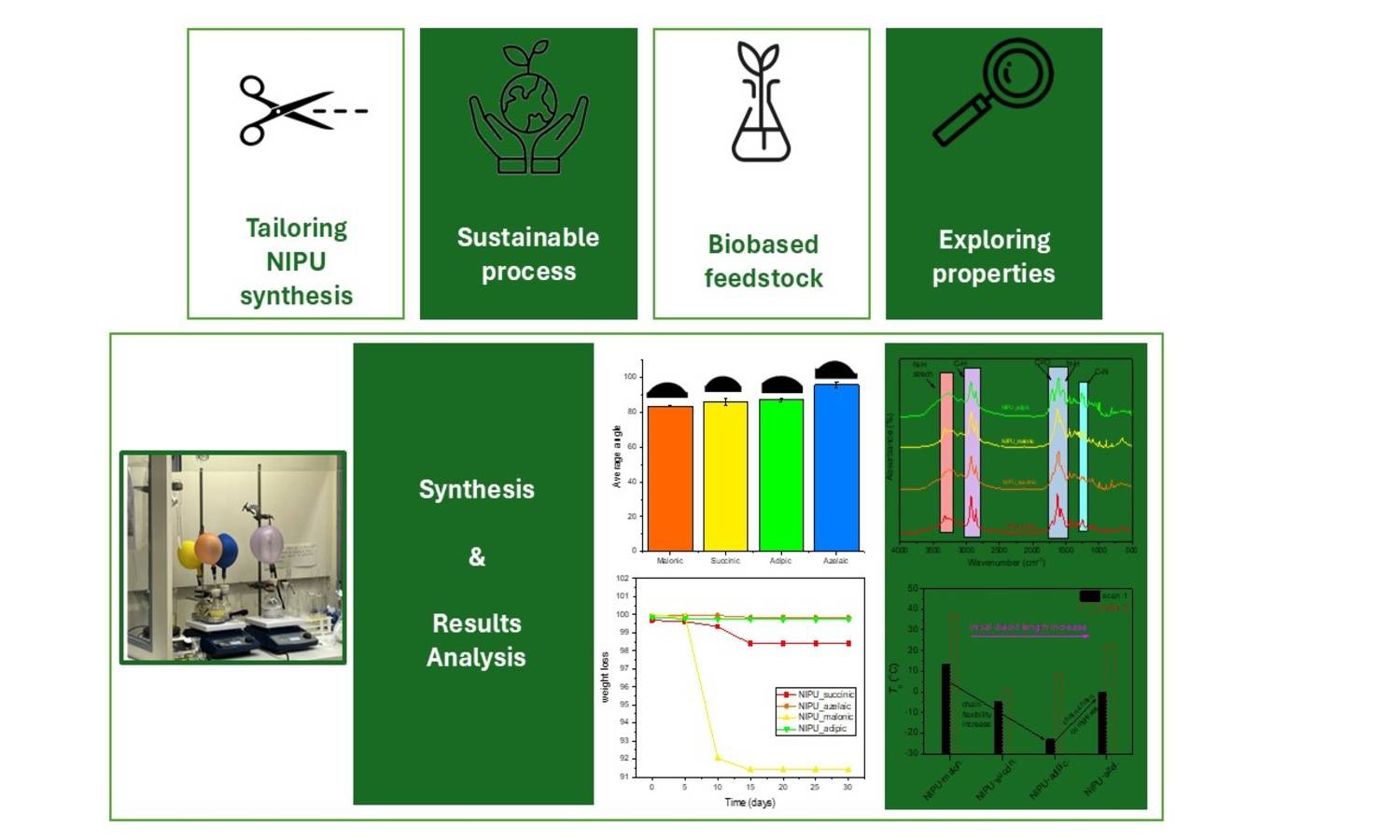
This research presents an eco-friendly approach for extracting chitosan from shrimp shell waste through ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) to prepare biocompatible aerogel scaffolds for biomedical applications. The study investigates the influence of various ultrasonic treatment times (10, 20, 30, 40 min) on the yield and structural and physicochemical properties of the extracted chitosan via characterization using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Among the tested conditions, the 30 min UAE-treated chitosan aerogels showed optimal porosity and structural integrity. Biocompatibility of the aerogels was evaluated, and the results confirmed their non-cytotoxic nature. The bioactivity of the chitosan aerogels was evaluated in terms of their in vitro wound closure ability and antibacterial properties. The aerogels demonstrated a wound closure rate of around 51% after 72 h, significantly higher than the untreated control (37%). In addition, they exhibited clear antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. This sustainable extraction and fabrication method not only adds value to marine waste but also produces functional biomaterials with potential applications in wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, supporting global efforts toward sustainability and circular bioeconomy.
Narayanapura Mahadevappa Tanuja, Sommenahalli Machegowda Chaithra, Chikkahalkur Shivanandappa Kaliprasad, Mangaravalli Hombalegowda Harshitha, Shivapura Manchaiah Anush, Kalappa Prashantha
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
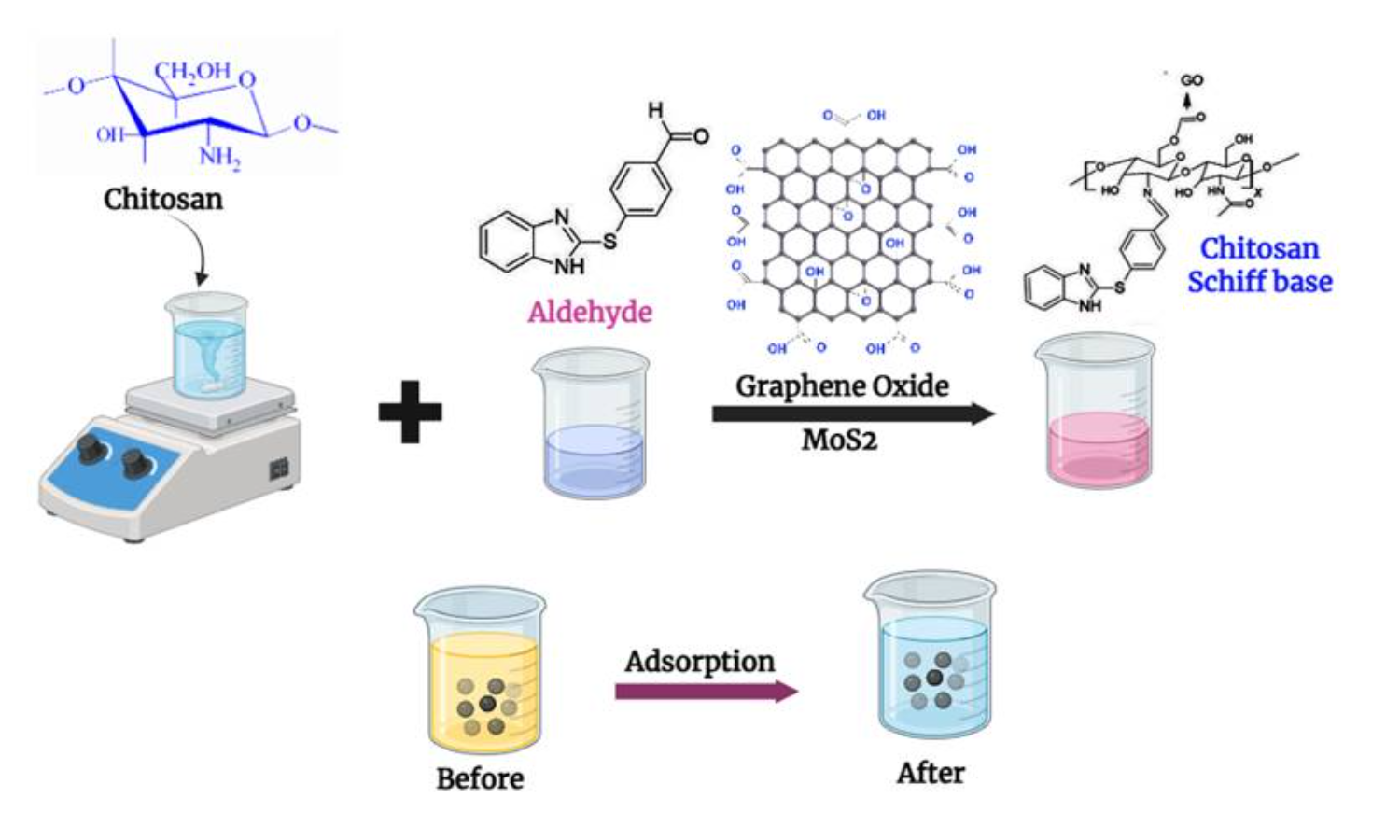
In this work, we have developed a novel absorbent material using chitosan (CS), and further it was structurally modified via reaction with thiocarbaldehyde, forming a Schiff base intermediate. Simultaneously, graphene oxide was functionalized at the C-6 position of CS through an effective esterification process and composited with the incorporation of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles to synthesize a hybrid adsorbent material. The resulting material was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The synthesized adsorbent was subjected to the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from dilute solutions. The maximum uptake of 66.66 mg/g for Cu(II) and 76.92 mg/g for Cr(VI) were recorded during the adsorption process, further following pseudo-second-order kinetics adsorptive nature and fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm model. Desorption studies indicated the material’s reusability, and the thermodynamic studies indicated a spontaneity with an endothermic adsorptive nature. These studies highlight the material’s potential as an effective adsorbent as a sustainable approach for efficient environmental remediation.
Isabel Milagros Gavilan-Figari
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
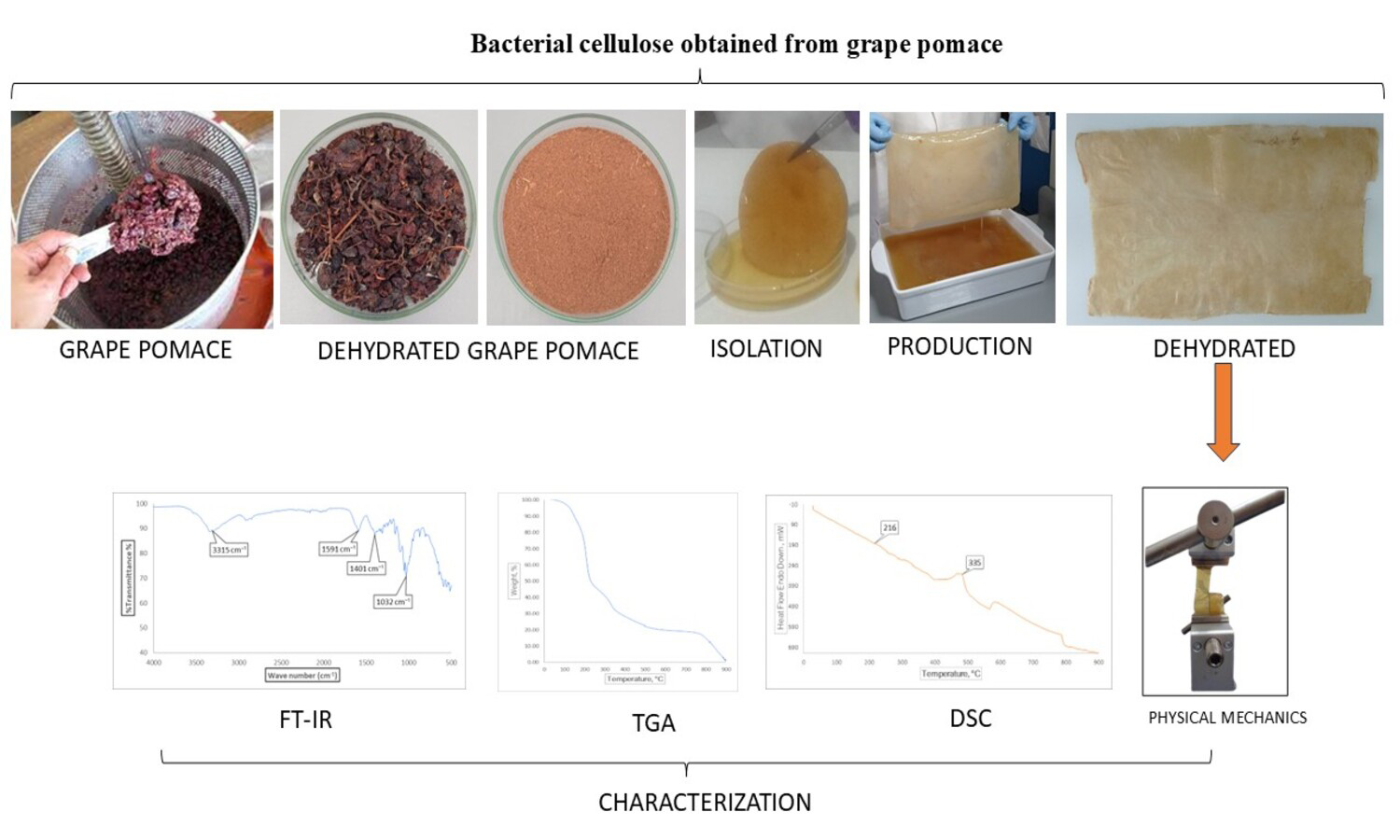
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is an eco-friendly biopolymer with outstanding structural and functional properties, offering promising applications in sustainable packaging and bio-based materials. In this study, we demonstrate the feasibility of producing BC via spontaneous fermentation, using grape pomace supplemented with sucrose as the sole carbon source, nutrient substrate, and microbial inoculum, without the addition of commercial strains or nitrogen supplements. Fermentation was conducted under static conditions, yielding biofilms with stable structural characteristics and BC production of up to 14.1 g/L, thereby confirming the efficiency of this low-cost, residue-based process. The films obtained exhibited well-organized polymeric networks, with thermal stability in the range of Tg ≈ 159–266 °C and mechanical resistance comparable to or higher than conventional biopolymers. Characterization confirmed reproducible chemical profiles, thermal stability, and measurable variation in mechanical performance, with a tensile strength ranging from 0.0001 to 105 MPa and an elongation at break of 15±5%. The process highlights a resource-efficient and sustainable pathway, adaptable to rural contexts and aligned with circular economic principles. While minor variations among replicates reflected the intrinsic variability of biological systems, mean values and standard deviations demonstrated reproducible physicochemical and mechanical properties. These findings demonstrate that BC derived from agro-industrial residues can be produced under simple, low-input conditions, opening opportunities for scalable valorization in functional and sustainable materials.




