Polylactic acid (PLA)/chitosan composites and their blend nanocomposites: A review
Vol. 19., No.11., Pages 1092-1132, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.82
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.82
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
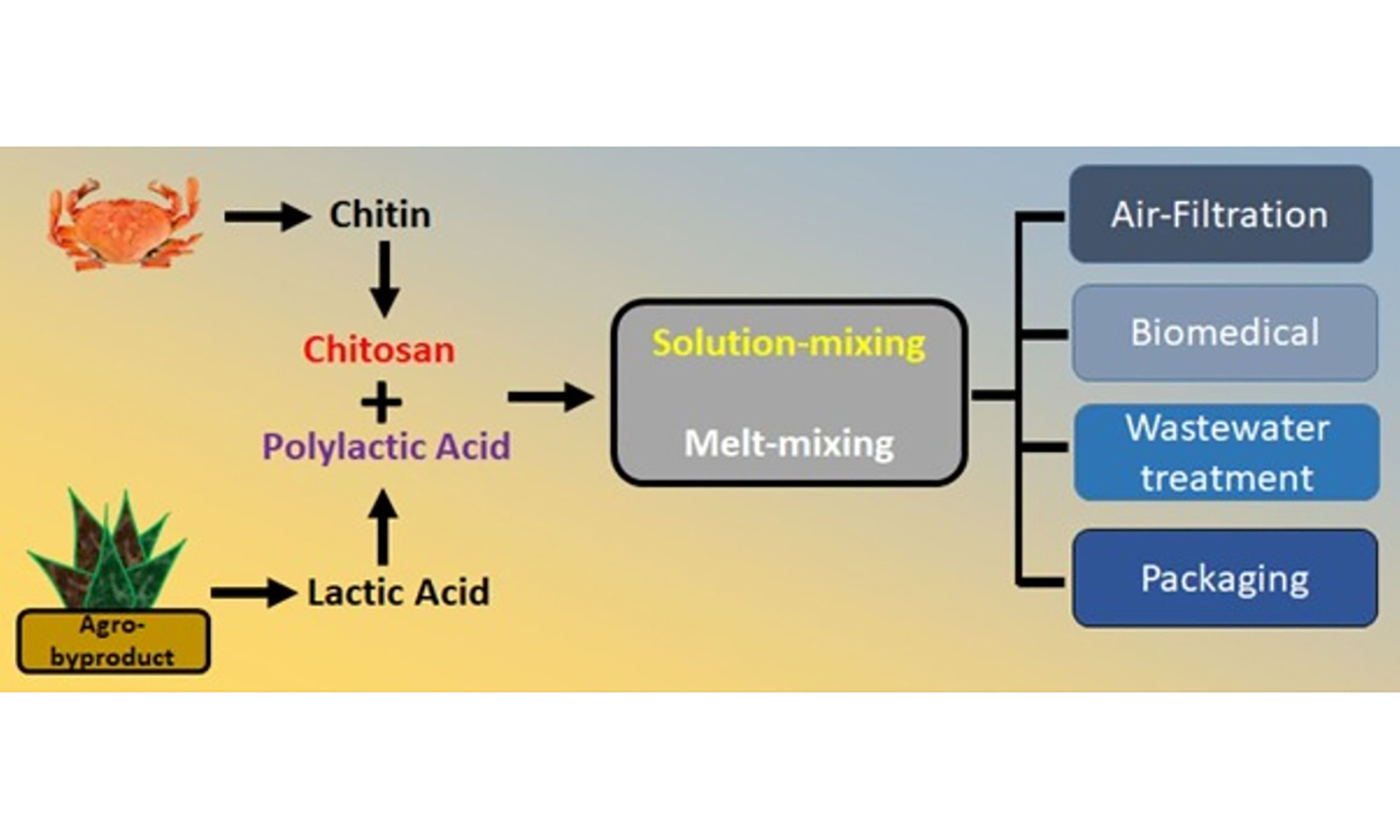
ABSTRACT
Polylactic acid (PLA) is one of the most widely used biopolymers, and it has demonstrated a huge potential for replacing some of the conventional plastics in certain application fields. However, due to a lack of other attributes such as antimicrobial properties and slow degradation rates, it is often blended with other polymers to impart these properties. Chitosan has desirable features including antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility, and environmental friendliness. Thus, it is widely blended with PLA to generate materials that can be applied in various fields. In recent years, PLA/chitosan blend composites and nanocomposites have been produced to develop sustainable and ecofriendly materials that can be suitable in active food packaging, water treatment, air filtration, and biomedical applications. This review provides an overview of the recent advancements in the development of PLA/chitosan blend composites and nanocomposites for various applications. The processing strategies, mechanical and thermal properties, together with utilization in biomedical, air filtration, water treatment, and packaging applications, are provided.
RELATED ARTICLES
Nikita V. Eremin, Svetlana Y. Voronina, Taisiya A. Shalygina, Valery V. Vlasov, Semyon A. Fesik, Anna A. Sukhanova
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 168-185, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.14
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 168-185, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.14
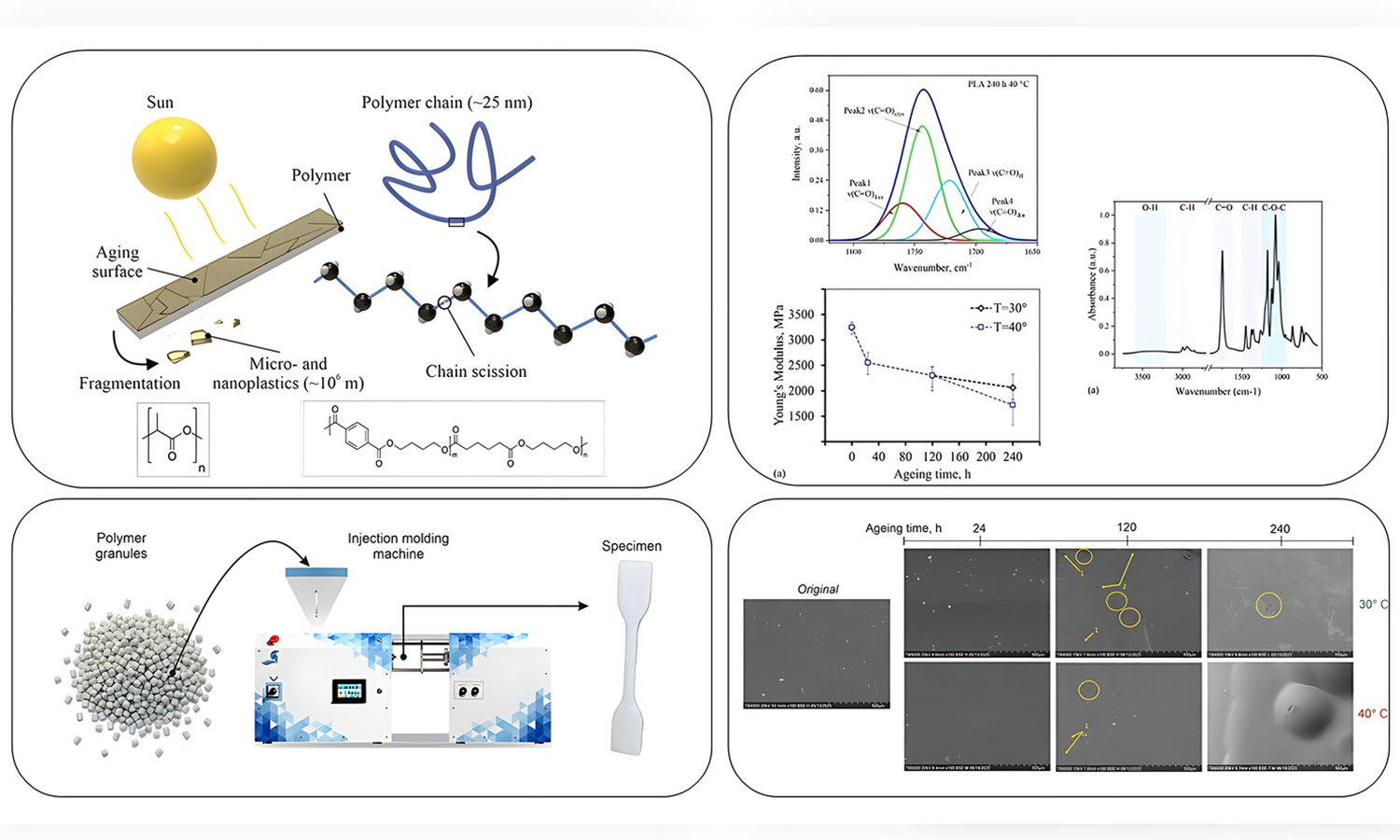
This article is devoted to the study of the degradation of two widely used biodegradable polymers, polylactic acid (PLA) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), which are in demand in packaging, medicine, and agriculture. The effect of ultraviolet radiation (UV) at elevated temperatures on polymer ageing was investigated for 24, 120, and 240 h using a specially designed setup. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and tensile testing were employed to provide a comprehensive assessment of changes. PLA showed rapid degradation: after 120 h, its surface developed cracks and voids, and at 240 h, it became heavily damaged with cavities. PBAT degraded more gradually: at 240 h, large cracks and cavities were observed. For PLA, early ageing led to a shift and broadening of the carbonyl band, reflecting disorder and ester scission. For PBAT, a decrease in the intensity of the carbonyl shoulder and a slight shift of the main peak at elevated temperature indicated phase redistribution and the formation of new functional groups. Mechanically, PLA exhibited a sharp loss of strength and ductility in the first day of ageing, while PBAT showed greater stability, with slower reductions in stiffness and strength but a strong temperature-dependent decline in elongation. These findings are important for guiding the design of biodegradable polymers with improved durability.
Soni Thakur, Amal M. Sindi, Rahul Dev Bairwan, Rasha A. Mahmoud, Eman Alfayez, Nurul Fazita Mohammad Rawi, Kanchan Jha, H.P.S. Abdul Khalil
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
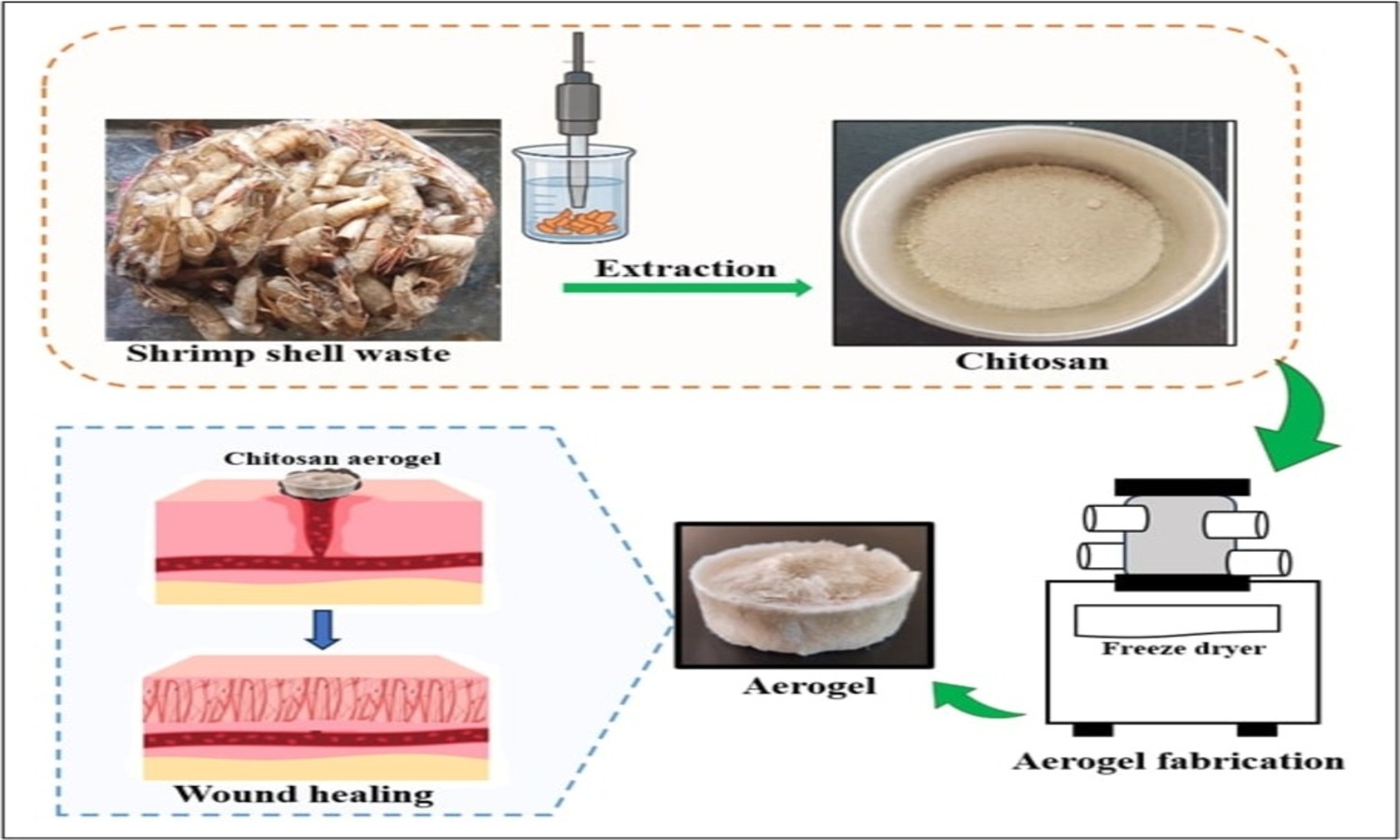
This research presents an eco-friendly approach for extracting chitosan from shrimp shell waste through ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) to prepare biocompatible aerogel scaffolds for biomedical applications. The study investigates the influence of various ultrasonic treatment times (10, 20, 30, 40 min) on the yield and structural and physicochemical properties of the extracted chitosan via characterization using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Among the tested conditions, the 30 min UAE-treated chitosan aerogels showed optimal porosity and structural integrity. Biocompatibility of the aerogels was evaluated, and the results confirmed their non-cytotoxic nature. The bioactivity of the chitosan aerogels was evaluated in terms of their in vitro wound closure ability and antibacterial properties. The aerogels demonstrated a wound closure rate of around 51% after 72 h, significantly higher than the untreated control (37%). In addition, they exhibited clear antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. This sustainable extraction and fabrication method not only adds value to marine waste but also produces functional biomaterials with potential applications in wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, supporting global efforts toward sustainability and circular bioeconomy.
Narayanapura Mahadevappa Tanuja, Sommenahalli Machegowda Chaithra, Chikkahalkur Shivanandappa Kaliprasad, Mangaravalli Hombalegowda Harshitha, Shivapura Manchaiah Anush, Kalappa Prashantha
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
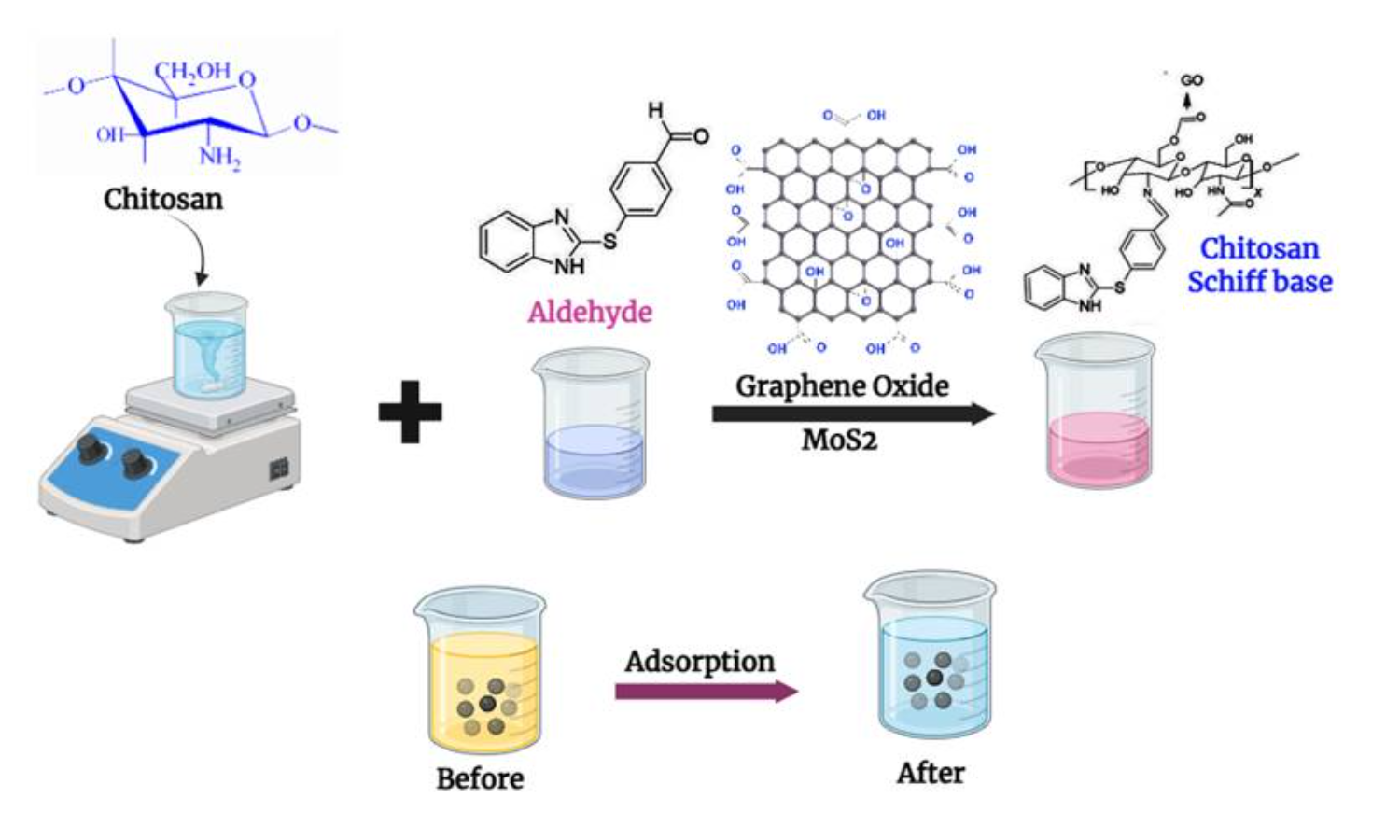
In this work, we have developed a novel absorbent material using chitosan (CS), and further it was structurally modified via reaction with thiocarbaldehyde, forming a Schiff base intermediate. Simultaneously, graphene oxide was functionalized at the C-6 position of CS through an effective esterification process and composited with the incorporation of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles to synthesize a hybrid adsorbent material. The resulting material was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The synthesized adsorbent was subjected to the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from dilute solutions. The maximum uptake of 66.66 mg/g for Cu(II) and 76.92 mg/g for Cr(VI) were recorded during the adsorption process, further following pseudo-second-order kinetics adsorptive nature and fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm model. Desorption studies indicated the material’s reusability, and the thermodynamic studies indicated a spontaneity with an endothermic adsorptive nature. These studies highlight the material’s potential as an effective adsorbent as a sustainable approach for efficient environmental remediation.
Elumalai Vengadesan, Swaminathan Muralidharan, Dhanjit Das, Thirugnanasambandam Arunkumar
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 822-842, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.63
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 822-842, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.63
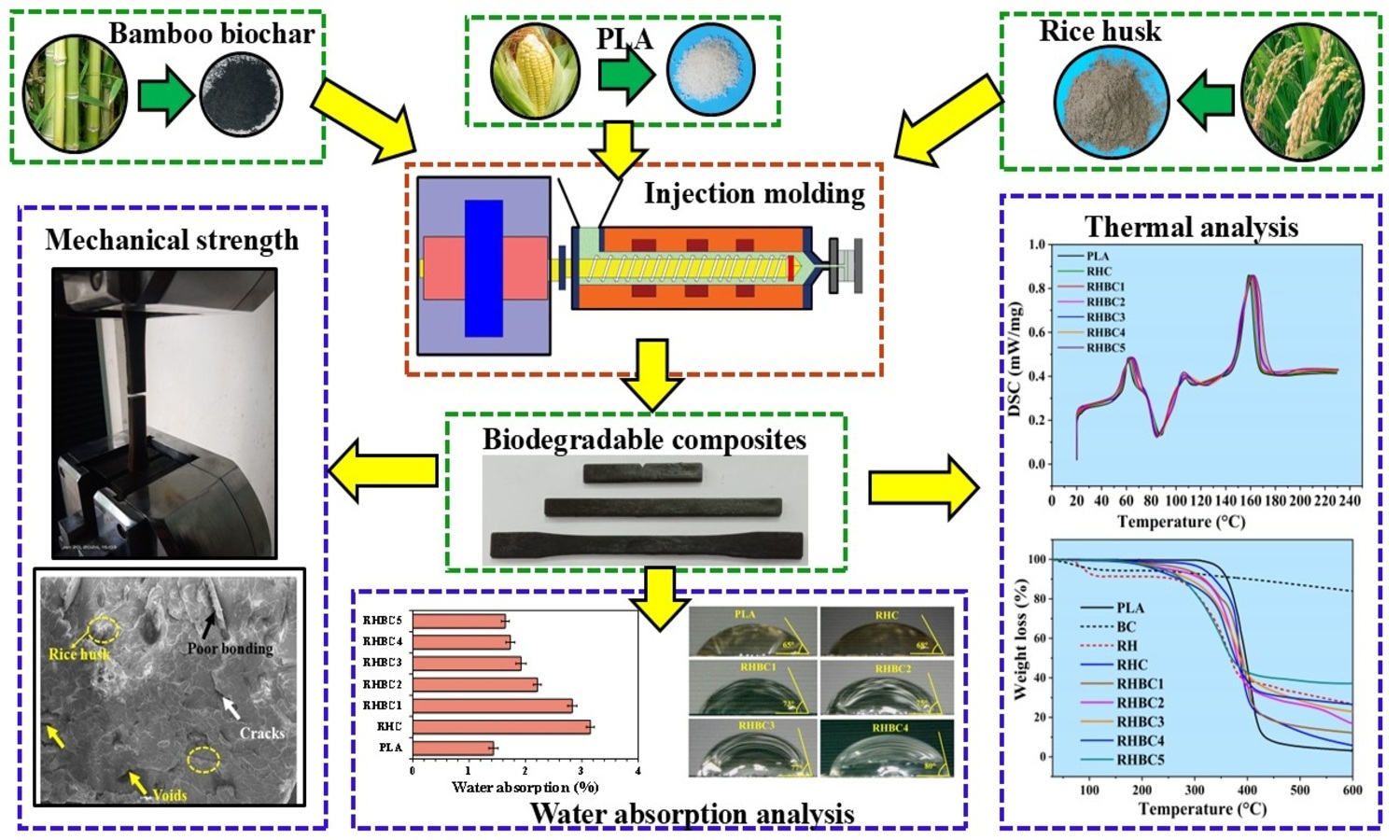
The growing need for sustainable materials has stimulated research into eco-friendly composites, with biochar emerging as an important reinforcement in polymer matrices. Biochar is a carbon-rich material produced by pyrolyzing organic biomass, offering various benefits over traditional fillers, including sustainability, waste reduction, and carbon sequestration. This study explores the effects of bamboo biochar as a hybrid reinforcement on the properties of polylactic acid (PLA)-rice husk composites. The present hybrid composites are prepared by varying the bamboo biochar from 5–25% and have better mechanical properties than PLA and its composite reinforced with a rice husk filler. The tensile, flexural, and compressive strengths of 51.5, 166.0, and 77.5 MPa are measured for the biochar percentage of 10%, representing increases of 73.1, 150.0, and 58.2% compared to PLA, and 158.2, 98.6, and 31% compared to the PLA composite with rice husk. Higher tensile and flexural moduli of 1.46 and 7.34 GPa are observed for 10 and 15%, respectively. However, the impact strength decreases with higher biochar content due to increased rigidity. The material’s hardness increases at higher biochar content due to enhanced stiffness. Thermal transition and degradation points rise due to increased crystallinity from the biochar reinforcement’s nucleation effect. Additionally, the hydrophobic biochar reinforcement reduces water absorption of PLA composite from 3.2 to 1.6%.
Lilla Bubenkó, Násfa Németh, Sára Frey, Tamás Molnár, Károly Belina, Orsolya Viktória Semperger
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 726-735, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.55
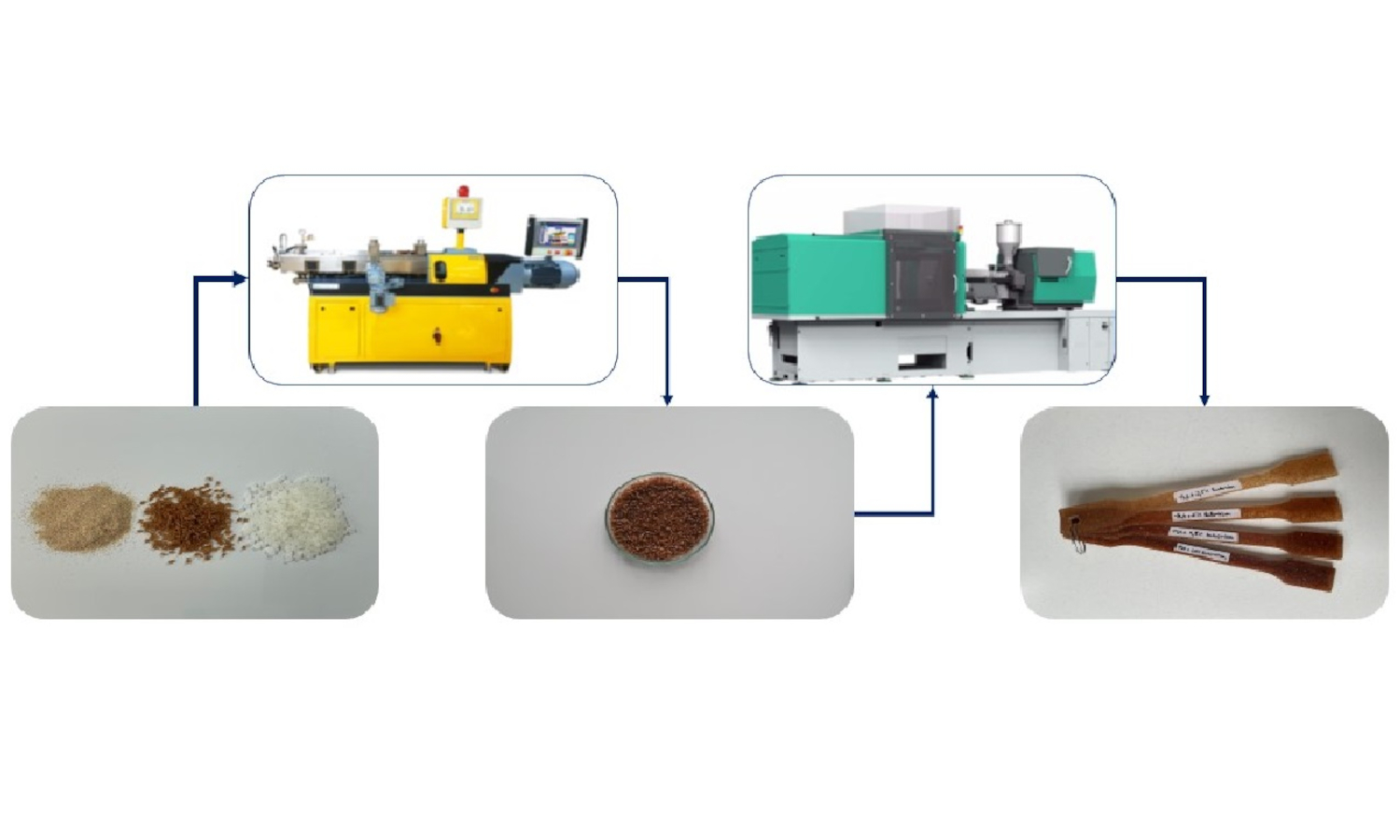
Biocomposites have recently received more attention because of raising environmental awareness and the drive toward sustainable technologies. The most common biodegradable polymer is poly(lactic acid) (PLA), which has an excellent balance of physical and rheological properties, but there is some limit to its usage. PLA properties can be improved by adding different types of fibers or fillers that come from agricultural waste. In this study, corn cob and lavender stem were used to reinforce PLA without any coupling agent, and the properties of the composites were investigated. The melt flow rate (MFR) values decreased with the corn cob content and increased with the addition of lavender stem. Mechanical tests showed that the tensile and flexural modulus of the composites increased and the strengths decreased with the reinforcement material content. The rigidness of PLA slightly decreased with the addition of fillers. There was no significant effect on the thermal properties. The unremarkable improvement of the reinforcement was due to the lack of appropriate adhesion of the two phases. The structure of the compounds was found to be homogenous on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs. The incorporation of corn cob and lavender stem can reduce the production cost of materials.




