Bioinspired hierarchical structures for superhydrophobic polyethylene
Shuang Gao, Yuan Lyu, Jieting Geng, Lin Xia
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 279-291, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.22
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.22
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
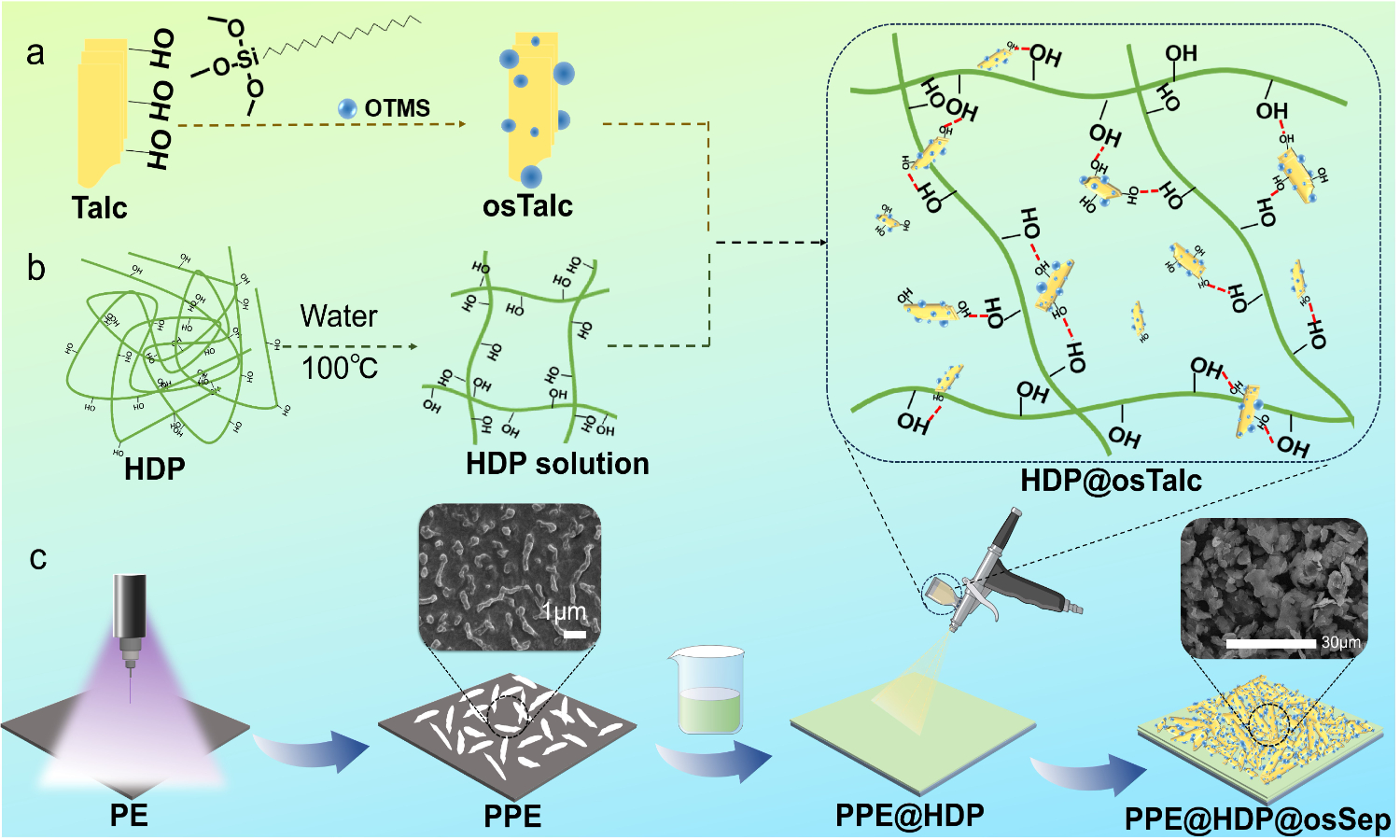
ABSTRACT
Inspired by natural structures, this study successfully developed innovative composites through the strategic integration of biomimetic concepts and advanced material engineering techniques. Using plasma-treated polyethylene (PPE) film as the substrate, hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (HDP) as the bioinspired adhesive layer, and modified talc (osTalc) as the functional modifier, a series of PPE@HDP@osTalc composites were fabricated via an optimized spray-coating process. The as-prepared composite demonstrates exceptional superhydrophobicity and mechanical flexibility. Chemical stability assessment of the PPE@HDP@osTalc composites demonstrated strong interfacial bonding between the PPE, HDP, and osTalc components. The development of this bioinspired smart composite not only provides new insights for designing functional materials but also demonstrates significant potential for applications in emerging fields such as flexible electronics, marine engineering, and biomedical devices.
RELATED ARTICLES
Abdulaziz Al-Shehri, John Sweeney, Paul Spencer, Phil Coates, Fin Caton-Rose, Ajay Taraiya
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1238-1255, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.92
Vol. 19., No.12., Pages 1238-1255, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.92
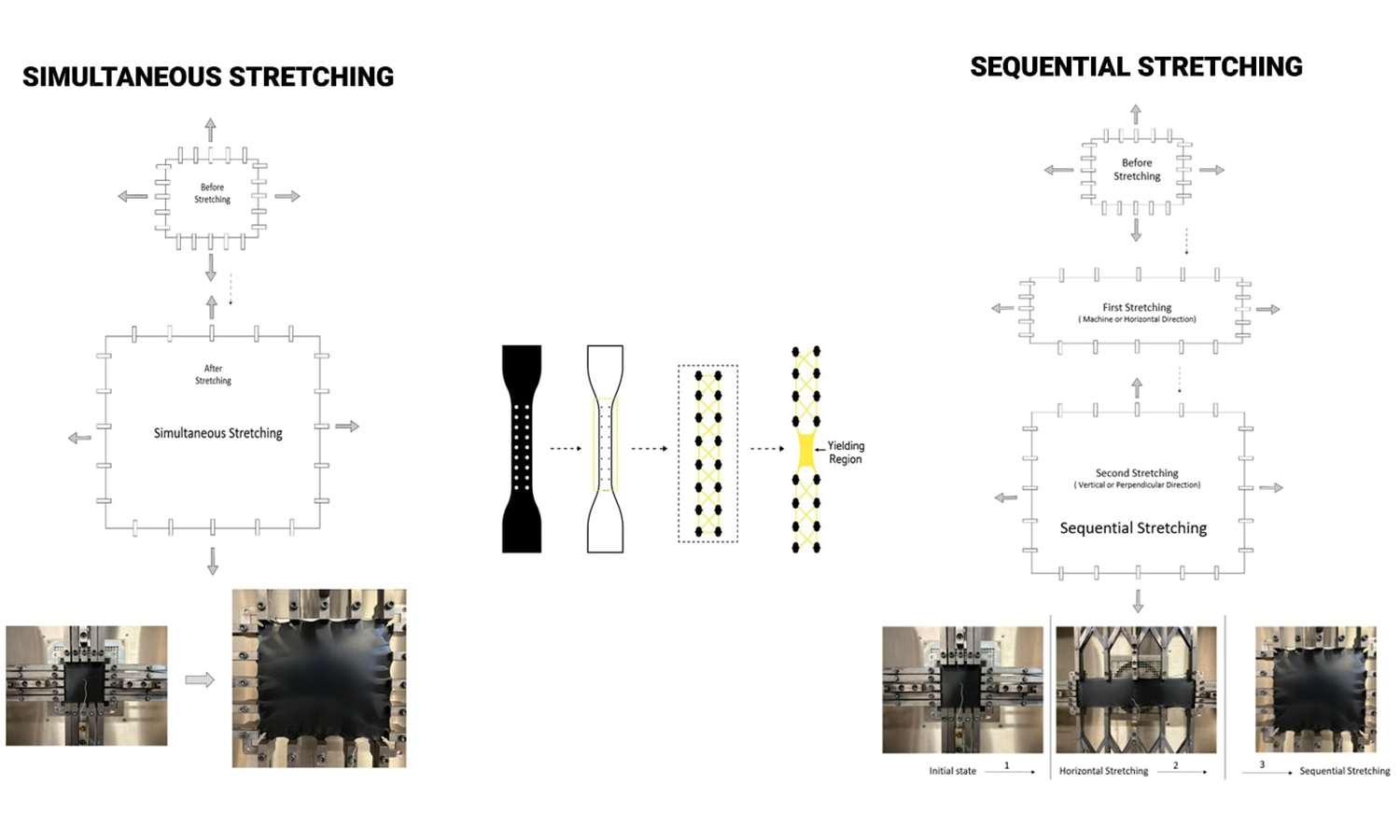
This study examines the combined effects of molecular modalities (unimodal, bimodal, trimodal) and biaxial stretching modes (sequential and simultaneous) on the yielding, stiffness, and necking behaviour of stretched high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Yield strength and stiffness were examined in relation to oriented material produced by drawing at linear strain rates 5.4·10–3, 2.2·10–2, and 8.6·10–2 s–1 under both stretching modes. Simultaneous stretching outperformed sequential stretching, with yield strength increasing with draw rate. Unimodal HDPE showed higher yield strength and stiffness than bimodal and trimodal grades, while trimodal HDPE had the lowest necking tendency from greater flexibility and uniformity. The highest necking tendency was observed in unimodal HDPE in strain localization analysis using the maximum strain/average strain ratio, while trimodal HDPE deformed more uniformly due to improved molecular weight distribution and strain hardening. Increasing the draw rate reduced strain localization, improving mechanical performance. Insights for optimising polyethylene materials in industry are provided by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and mechanical analyses, establishing the correlation between HDPE structure, processing, and properties.
Rafael Affonso Netto, Guilherme Ribeiro de Carvalho, Lucas Henrique Staffa, Liliane Maria Ferrareso Lona
Vol. 19., No.2., Pages 161-175, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.12
Vol. 19., No.2., Pages 161-175, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.12

This study aimed first to promote the alkylation of polyethyleneimine (PEI), developing its alkylated (quaternary) form (QA-PEI) by inserting alkyl groups into amine groups. Subsequently, polymer blends with poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) were prepared via solvent casting, and finally, the physicochemical, optical, and mechanical behavior of the resulting PMMA/QA-PEI were assessed. Elemental analyses, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR) confirmed that the PEI alkylation successfully converted the amine groups into quaternary ammonium groups. When added to PMMA, QA-PEI altered its coloration, making it yellow. In addition, higher contents of QA-PEI hindered PMMA transmittance and increased its opacity due to the larger QA-PEI domains. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showed that PMMA and QA-PEI formed a phase-separated system, establishing a droplet-matrix morphology. The thermal and mechanical behavior showed some compatibility between PMMA and QA-PEI as thermal resistance slightly improved and PMMA glass transition temperature (Tg) decreased. The tensile strength was also improved in the PMMA/QA-PEI blends without significant change in strain at break and tensile modulus.
Markus Zach, Davide Tranchida, Enrico Carmeli, Jingbo Wang, Markus Gahleitner, Bernhard Hofko, Elena Pomakhina, Minna Aarnio-Winterhof
Vol. 18., No.7., Pages 715-727, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.53
Vol. 18., No.7., Pages 715-727, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.53

Blown films from ethylene-propylene random copolymers (C2C3-RACOs) are used in many packaging applications today, constituting a major fraction of both mono- and multilayer packaging film constructions. Combining high processing speed and output with good mechanical and optical performance, mostly high toughness and low haze, requires understanding the structure-property-processing relations. To improve said understanding for C2C3-RACO blown films, two commercial grades with a nearly identical C2 content of ~4.4 wt% and identical melt flow rate (MFR) but different nucleation were selected. These were tested in a processing study, varying melt temperature, blow-up ratio (BUR) and neck length. The film structure was analysed by wide angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), and the performance by standard mechanical and optical tests. Variation of film crystallinity was found to be in the range of 62 to 65%, much smaller than in earlier cast film studies on comparable polymers. The tensile modulus is the only performance parameter for which a general positive correlation to crystallinity can be found, blown films being about 50% stiffer than the softest cast films of a comparable polymer. Ductility and toughness are enhanced by higher orientation, resulting from higher BUR and/or higher neck length. For transparency and haze, low surface roughness is decisive at comparable crystallinity, which can be achieved by increasing melt temperature.
Xianli Sun, Jiahao Xu, Xiaoke Zhi, Jingpeng Zhang, Kangwei Hou, Yuhan Bian, Xiaolin Li, Li Wang, Guangchuan Liang
Vol. 18., No.6., Pages 575-591, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.43
Vol. 18., No.6., Pages 575-591, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.43

As a key component of lithium-ion batteries, a separator with excellent electrolyte wettability and good thermal stability has an important impact on the overall performance of lithium-ion batteries. Herein, a PVDF/sepiolite electrospun layer was coated on one side of the PP separator via electrospinning technology to prepare the composite separator (xMS-PVDF@PP) with sepiolite nanofibers modified with vinyltriethoxysilane (VTES) to ameliorate their dispersibility and compatibility with PVDF polymer matrix. The effect of modified sepiolite addition amounts on the physical and electrochemical properties of composite separator was intensively studied. It is found that the as-prepared xMS-PVDF@PP composite separator displays enhanced porosity, electrolyte uptake, thermal stability and Li+ ion transport kinetics than pristine PP separator. Specifically, Li|LiFePO4 battery with 20MS-PVDF@PP as separator shows the best rate and cycling performance, with a specific discharge capacity of 115.3 mAh·g–1 at 10C rate and a capacity retention rate of 97.06% after 200 cycles at 1C rate. The sepiolite in the electrospun layer can immobilize PF6– anion to facilitate the uniform distribution of Li+ ions and then inhibit the lithium dendrite growth, as well as absorb HF to alleviate Fe2+ dissolution from LiFePO4 cathode, thereby further improving the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 battery.
Saikrishnan Ganesh, Jayakumari Lakshmanan Saraswathy, Vijay Raghunathan, Vinod Ayyappan, Sundarrajan Dharmakrishnan, Sanjay Mavinkere Rangappa, Suchart Sienghcin
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 144-159, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.12
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 144-159, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.12

The increase in environmental consciousness and waste-to-wealth concepts in the automobile sector has led to the use of natural fibers in desirable quantities. The current study deals with the extraction, treatment, and utilization of Lycium ferocissimum stem fibers for friction composite in braking applications. The fibers of Lycium ferocissimum were extracted through manual retting and subsequently treated with benzoyl chloride. Both the benzoyl chloride treated and untreated fibers of Lycium ferocissimum were employed as reinforcements in the formulation of a friction composite, following the standard practices of the industry, and the comparison was made using commercially available friction composite. The developed friction composites were tested for original equipment manufacturer quality requirements following industrial Standards. The friction composite’s tribological behavior was analyzed using the Chase test following the Society of Automotive Engineers standards. The worn surface characteristics were analyzed using scanning electron microscope. The test results elucidated that benzoyl chloride-treated Lycium ferocissimum fibers-based friction composites showed good frictional properties with better wear resistance compared to others, having a weight loss of 5.4%.



