Direct-ink-written Ag–TiO2/chitosan membranes: Green synthesis, architecture–property relationships, and photocatalytic/antibacterial performance optimized by RSM
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 246-263, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.20
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.20
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
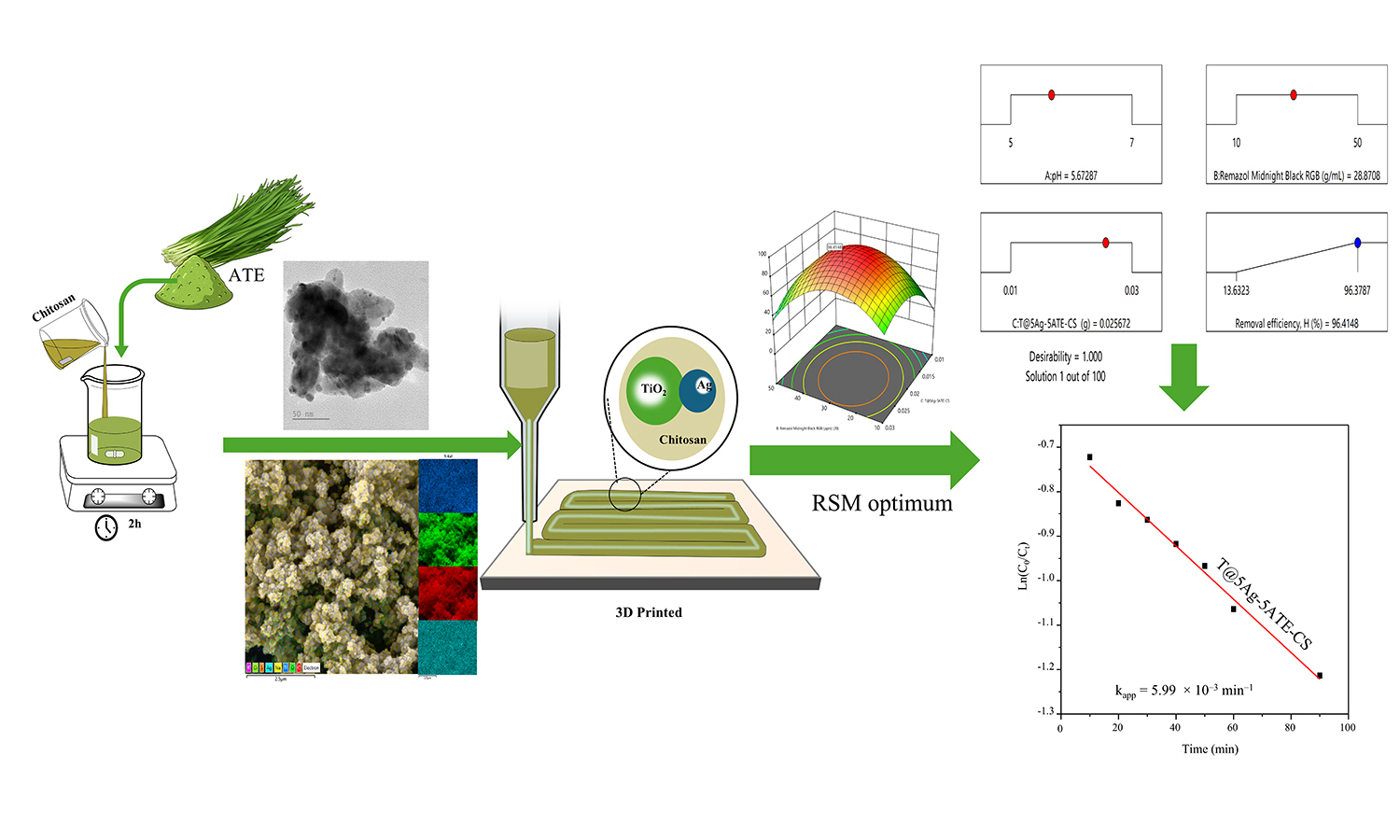
ABSTRACT
We report a green route to Ag–TiO2 nanocomposites using an Allium tuberosum extract, rich in organosulfur and polyphenolic constituents, as a dual-function biogenic reducer and stabilizer, enabling efficient Ag+→Ag0 conversion and capping of Ag–TiO2 without the use of harsh reagents. The nanocomposites are formulated into chitosan-based inks for direct ink writing (DIW) of porous, mechanically robust, reusable membranes (optimal formulation T@5Ag–5ATE–CS) with a homogeneous Ag dispersion. Multiscale characterization (SEM/TEM, XRD, FTIR, UV–vis DRS, EDS mapping) confirms metallic Ag0 uniformly decorating TiO2 and an extended visible-light response attributable to strong localized surface plasmon resonance. Under near-UV/visible irradiation, the membranes decolorize Remazol Midnight Black RGB dye with pseudo-first-order kinetics, yielding kapp up to 5.99·10–3 min–1 with R2 ≈ 0.99 and outperforming pristine TiO2. Response surface methodology identifies an optimum at pH 5.67, 28.87 mg·L–1 dye, and 0.0257 g catalyst, delivering a predicted 96.41% versus experimental 95.07% removal (validation error 1.39%) with excellent model statistics (R2 ≈ 0.995). The combined effects of Allium-tuberosum-assisted Ag plasmonics, TiO2 photocatalysis, and chitosan-enhanced adsorption underpin the high photocatalytic activity and reusability, highlighting a scalable, eco-friendly pathway to printable photocatalytic/antimicrobial membranes for wastewater treatment.
RELATED ARTICLES
Soni Thakur, Amal M. Sindi, Rahul Dev Bairwan, Rasha A. Mahmoud, Eman Alfayez, Nurul Fazita Mohammad Rawi, Kanchan Jha, H.P.S. Abdul Khalil
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
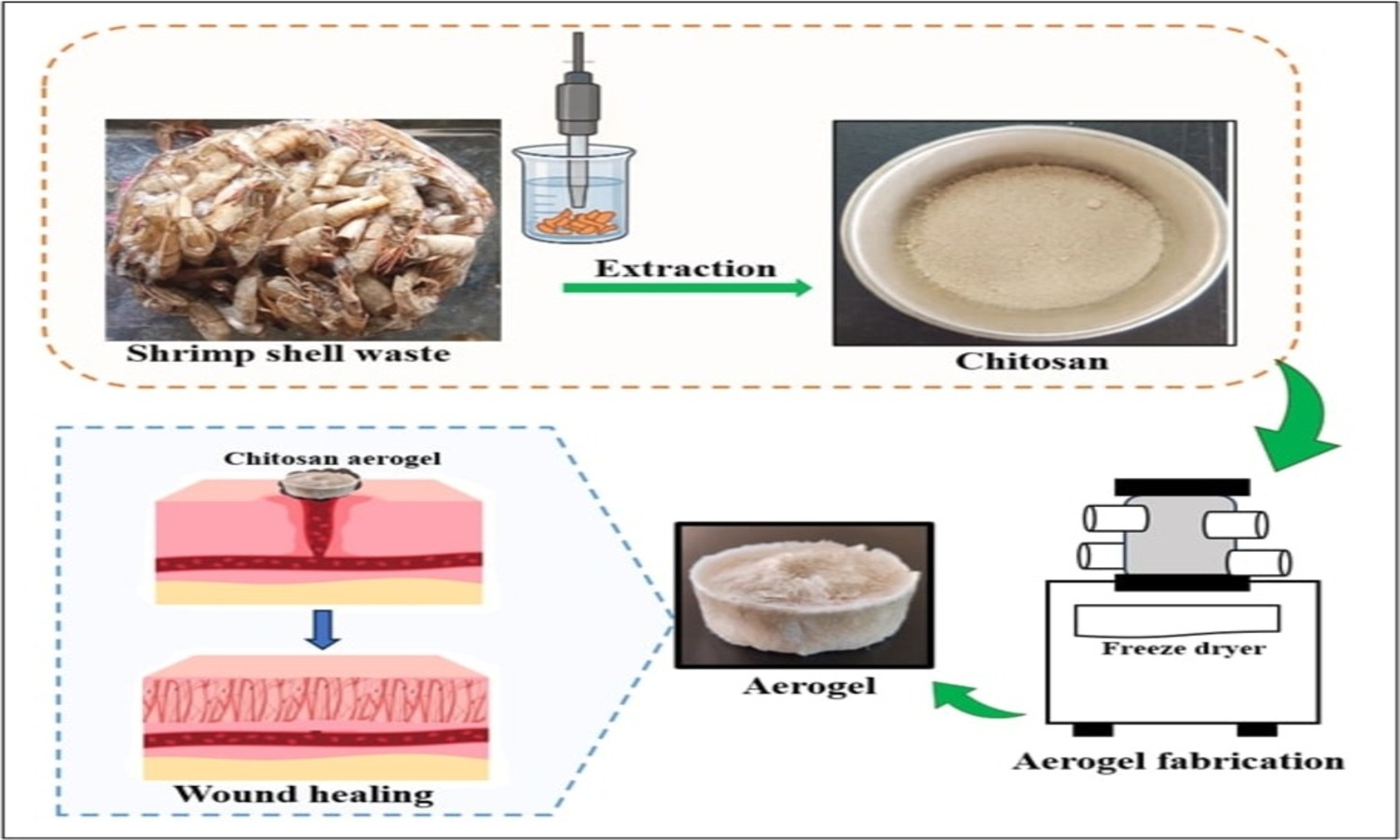
This research presents an eco-friendly approach for extracting chitosan from shrimp shell waste through ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) to prepare biocompatible aerogel scaffolds for biomedical applications. The study investigates the influence of various ultrasonic treatment times (10, 20, 30, 40 min) on the yield and structural and physicochemical properties of the extracted chitosan via characterization using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Among the tested conditions, the 30 min UAE-treated chitosan aerogels showed optimal porosity and structural integrity. Biocompatibility of the aerogels was evaluated, and the results confirmed their non-cytotoxic nature. The bioactivity of the chitosan aerogels was evaluated in terms of their in vitro wound closure ability and antibacterial properties. The aerogels demonstrated a wound closure rate of around 51% after 72 h, significantly higher than the untreated control (37%). In addition, they exhibited clear antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. This sustainable extraction and fabrication method not only adds value to marine waste but also produces functional biomaterials with potential applications in wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, supporting global efforts toward sustainability and circular bioeconomy.
Effect of natural cinnamon extract on the stabilizing properties of biodegradable packaging polymers
Anna Kosmalska-Olańska, Anna Masek
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5

The growing focus on sustainability, eco-friendly technologies, decarbonization, and reducing carbon footprints shapes current industry challenges. This article reviews the potential of cinnamon as a bio-additive for polymer stabilization in packaging. Samples were prepared from ethylene-norbornene copolymer (Topas), a cyclic olefin copolymer known for purity, transparency, and low gas permeability, and poly(lactic acid) (PLA), a bio-based alternative to petroleum plastics. Cinnamon powder was added in 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 wt%. After solar and thermo-oxidative aging, hydrophobicity, chemical composition, mechanical, and color properties were analyzed. Results showed higher hydrophobicity and resistance to hydrolytic degradation due to reduced water penetration. PLA, normally brittle, became more flexible, with 0.5 wt% cinnamon showing optimal performance after 100 h of solar aging, similar to Topas composites. Overall, PLA and cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) films with cinnamon improved durability, extended food shelf life, and acted as natural color indicators of material aging.
Narayanapura Mahadevappa Tanuja, Sommenahalli Machegowda Chaithra, Chikkahalkur Shivanandappa Kaliprasad, Mangaravalli Hombalegowda Harshitha, Shivapura Manchaiah Anush, Kalappa Prashantha
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 36-51, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.4
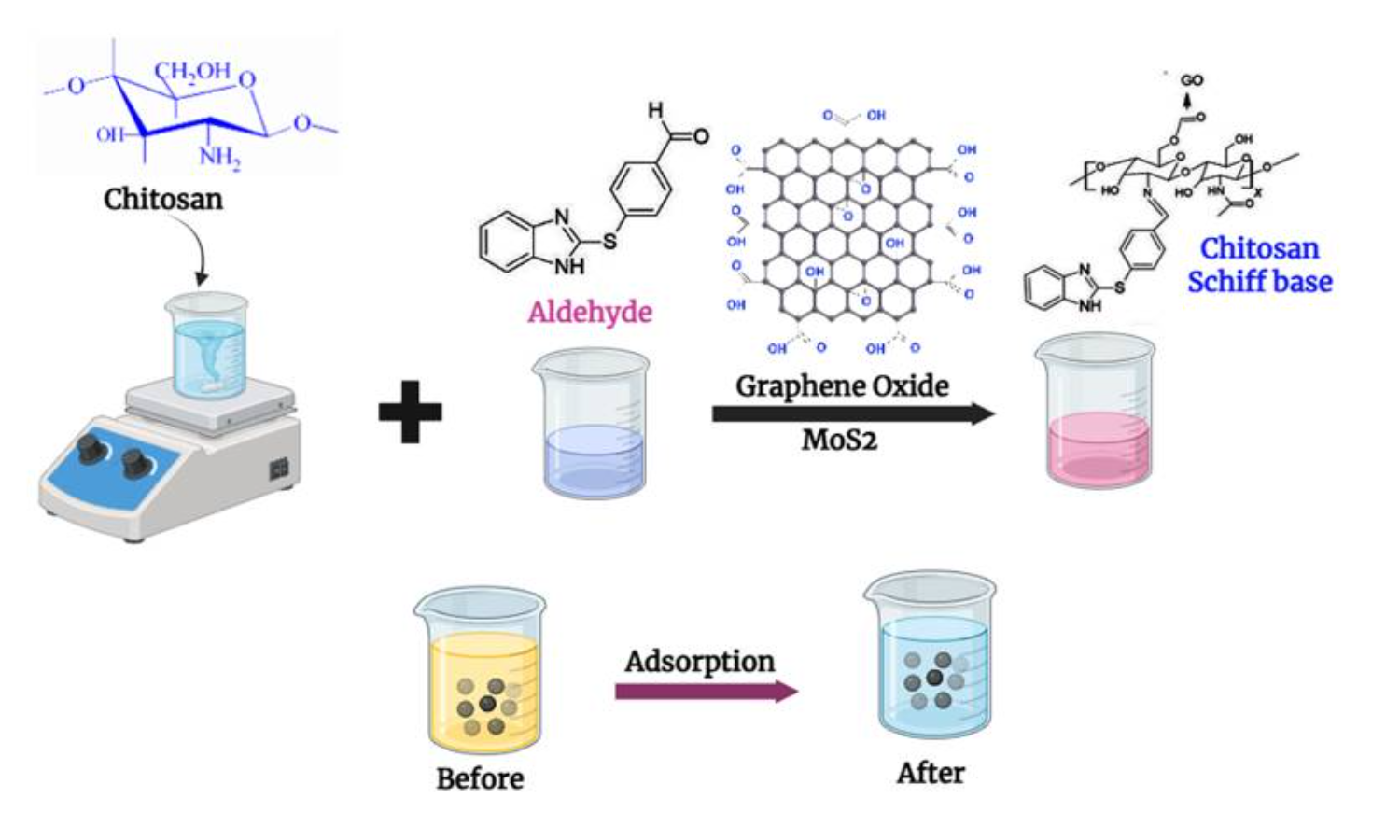
In this work, we have developed a novel absorbent material using chitosan (CS), and further it was structurally modified via reaction with thiocarbaldehyde, forming a Schiff base intermediate. Simultaneously, graphene oxide was functionalized at the C-6 position of CS through an effective esterification process and composited with the incorporation of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles to synthesize a hybrid adsorbent material. The resulting material was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The synthesized adsorbent was subjected to the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) ions from dilute solutions. The maximum uptake of 66.66 mg/g for Cu(II) and 76.92 mg/g for Cr(VI) were recorded during the adsorption process, further following pseudo-second-order kinetics adsorptive nature and fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm model. Desorption studies indicated the material’s reusability, and the thermodynamic studies indicated a spontaneity with an endothermic adsorptive nature. These studies highlight the material’s potential as an effective adsorbent as a sustainable approach for efficient environmental remediation.
Isabel Milagros Gavilan-Figari
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 72-81, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.6
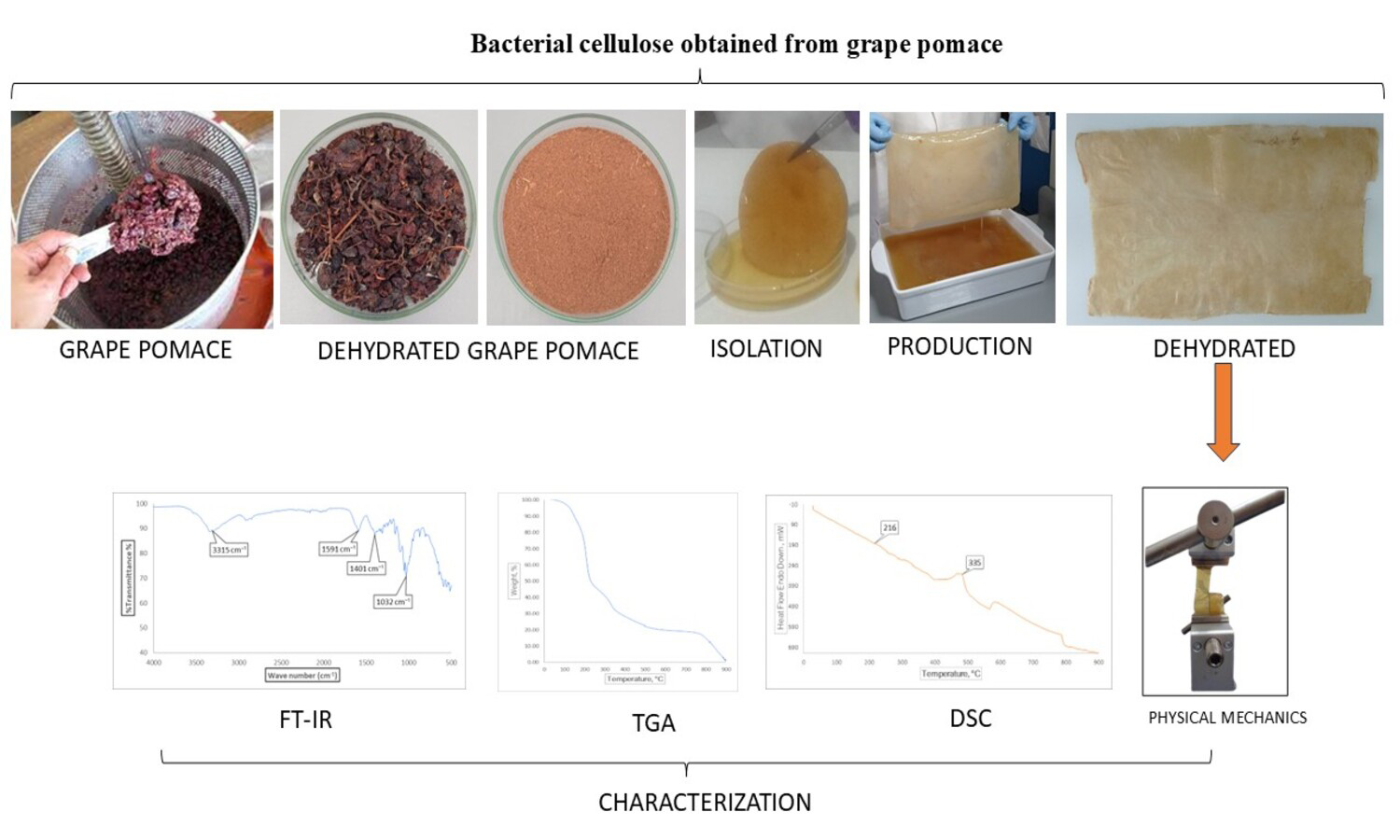
Bacterial cellulose (BC) is an eco-friendly biopolymer with outstanding structural and functional properties, offering promising applications in sustainable packaging and bio-based materials. In this study, we demonstrate the feasibility of producing BC via spontaneous fermentation, using grape pomace supplemented with sucrose as the sole carbon source, nutrient substrate, and microbial inoculum, without the addition of commercial strains or nitrogen supplements. Fermentation was conducted under static conditions, yielding biofilms with stable structural characteristics and BC production of up to 14.1 g/L, thereby confirming the efficiency of this low-cost, residue-based process. The films obtained exhibited well-organized polymeric networks, with thermal stability in the range of Tg ≈ 159–266 °C and mechanical resistance comparable to or higher than conventional biopolymers. Characterization confirmed reproducible chemical profiles, thermal stability, and measurable variation in mechanical performance, with a tensile strength ranging from 0.0001 to 105 MPa and an elongation at break of 15±5%. The process highlights a resource-efficient and sustainable pathway, adaptable to rural contexts and aligned with circular economic principles. While minor variations among replicates reflected the intrinsic variability of biological systems, mean values and standard deviations demonstrated reproducible physicochemical and mechanical properties. These findings demonstrate that BC derived from agro-industrial residues can be produced under simple, low-input conditions, opening opportunities for scalable valorization in functional and sustainable materials.
Ha Ngoc Giang, Thanh Thai Nguyen, Thu Thi Trang Luu, Anh Thi Ngoc Pham, Tuan Nguyen Anh Huynh
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 519-530, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.38
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 519-530, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.38

Freeze-thaw (F-T) poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) as a soft network and ionic-crosslinked sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as a hard network were applied to fabricate a double network (DN) gel using a one-step process. Mechanical properties of the DN gel using a high degree of hydrolysis PVA (PVA-CMC of 60-1) were significantly improved compared to that of a single network gel of PVA. The tensile strength of ~0.55 MPa and elongation at break of 179% could be achieved. The mechanical properties of PVA-poly(acrylic acid) DN gel were lower than that of PVA-CMC samples. Fourier-transformed infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy results showed less compatibility between polyacrylic acid (PAA) and PVA compared to that of CMC. The solution made from the lower hydrolysis degree PVA (PVA1788) could form a strong gel after being treated with NaOH 1 M. The FTIR result showed the disappearance of acetate groups. A large melting peak in differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) results showed high crystallinity of the hydrolyzed-PVA1788. The effect of various multivalent cations on the mechanical properties of PVA1788-CMC DN gel was performed. The properties of the samples followed the order: Fe3+<Co2+<Ni2+<Cu2+<Zn2+<Ca2+~Ba2+<Al3+. The tensile strength of DN gel fabricated using AlCl3 solution could reach 0.87 MPa, and the elongation at break was 330%.




