The kinetics of swelling and migration: A case study of plasticized polylactic acid food contact plastics tested with ethanolic food simulants
Viktor Konstantin Dragan , Noémi Petrovics
, Noémi Petrovics , Csaba Kirchkeszner
, Csaba Kirchkeszner , Tamás Tábi
, Tamás Tábi , Bálint Sámuel Szabó
, Bálint Sámuel Szabó , Zsuzsanna Eke
, Zsuzsanna Eke
 , Noémi Petrovics
, Noémi Petrovics , Csaba Kirchkeszner
, Csaba Kirchkeszner , Tamás Tábi
, Tamás Tábi , Bálint Sámuel Szabó
, Bálint Sámuel Szabó , Zsuzsanna Eke
, Zsuzsanna Eke
Vol. 18., No.4., Pages 391-405, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.29
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.29
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
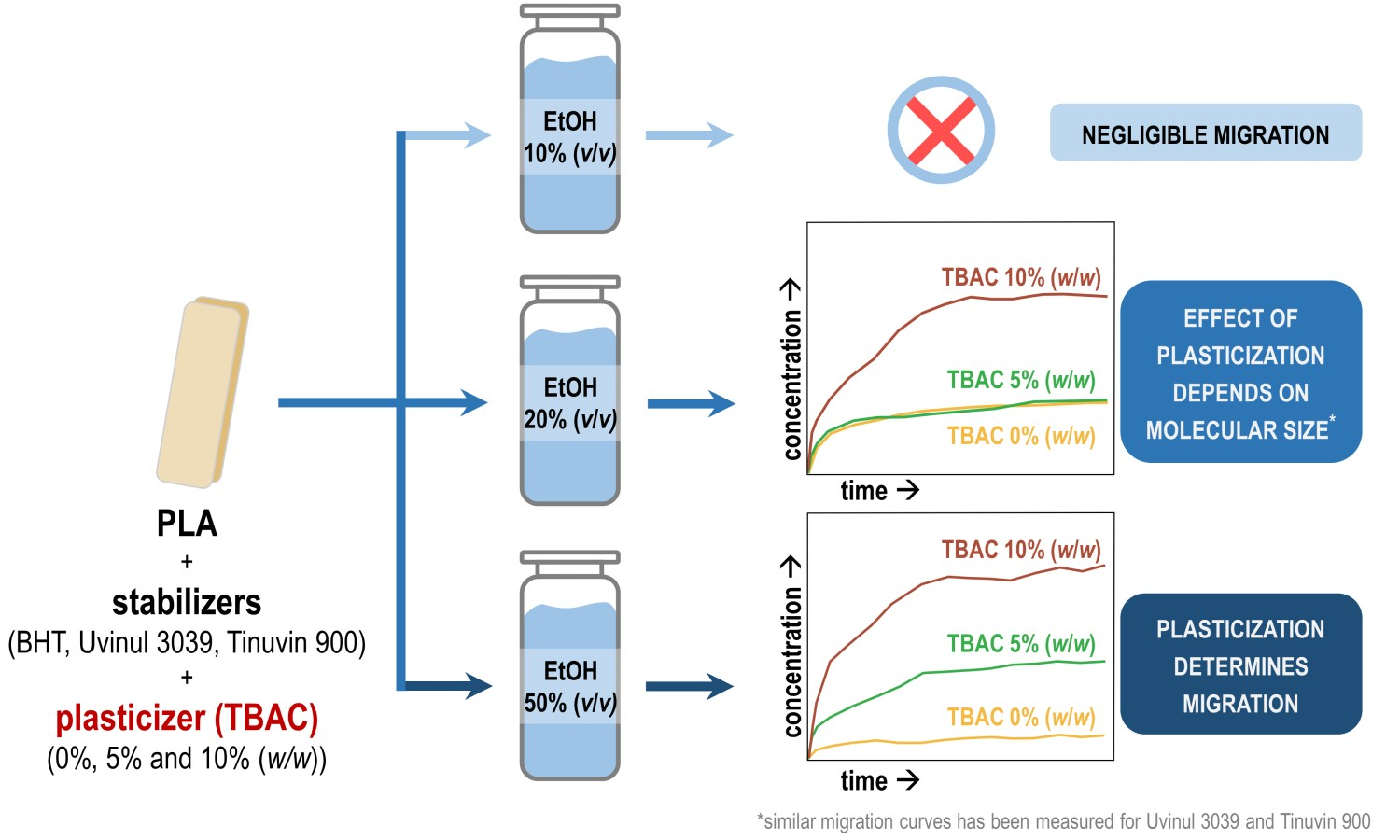
ABSTRACT
The
effect of swelling and plasticizer content of a plastic, as well as the ethanol
content of the food simulant on the migration kinetics of three stabilizer-type
additives from polylactic acid (PLA)-based food contact plastics has been
investigated. The results proved that the parameters that affect the diffusion
of substances inside the polymer matrix, i.e.,
swelling, plasticization, and the size of migrants, are the decisive factors in
the migration from PLA to ethanolic food simulants. Both swelling and migration
were negligible when ethanol 10% (v/v) was used. Contrarily, the specific
migration limits of Commission Regulation (European Union, EU) No. 10/2011 were
exceeded in ethanol 50% (v/v) for all investigated stabilizers. Migration was
promoted by plasticization, but this effect could only be observed when the
applied food simulant swelled the plastic (at least 20% (v/v) ethanol content).
The dependence of the plasticizer’s migration-enhancing effect on the swelling
has not been shown before. When the plasticization caused increased migration,
it also led to specific migration limit exceeding within a shorter period of
time. It happens even if PLA-based plastics are dedicated to the storage of
hydrophilic food, which is the most common application area of these products.
These results can support the improvement of both consumer safety and active
packaging development.
RELATED ARTICLES
Katalin Litauszki, Tamás Tábi, László Mészáros
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 455-456, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
Vol. 19., No.5., Pages 455-456, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.33
This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Konrad Stefaniak, Anna Masek
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 386-408, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.29
This review is focused on recent achievements in poly(lactic acid) (PLA) synthesis and copolymerization with special regard to biotechnological routes of PLA synthesis, which use bacteria/enzymes (e.g., enzymatic ring opening polymerization (eROP)). Besides PLA, also lactic acid (LA) synthesis is described and an emphasis is put on the biotechnological methods. Having regard to PLA copolymerization, this paper attempts to describe different types of PLA copolymers (such as block copolymers, PLA copolymers with polysaccharides, PLA-cellulose copolymer composites, and PLA polymer brushes). A detailed overview of the recent accomplishments in the field of PLA copolymers is presented. Various enhanced properties and applications of presented PLA copolymers are discussed. The attention is placed mainly on applications in the field of tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and the packaging sector. Furthermore, a PLA market study and its economic forecast are presented. Eventually possible directions for future research in the field of PLA synthesis and copolymerization are indicated.
Emir Avcioglu
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 3-14, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.2
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 3-14, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.2
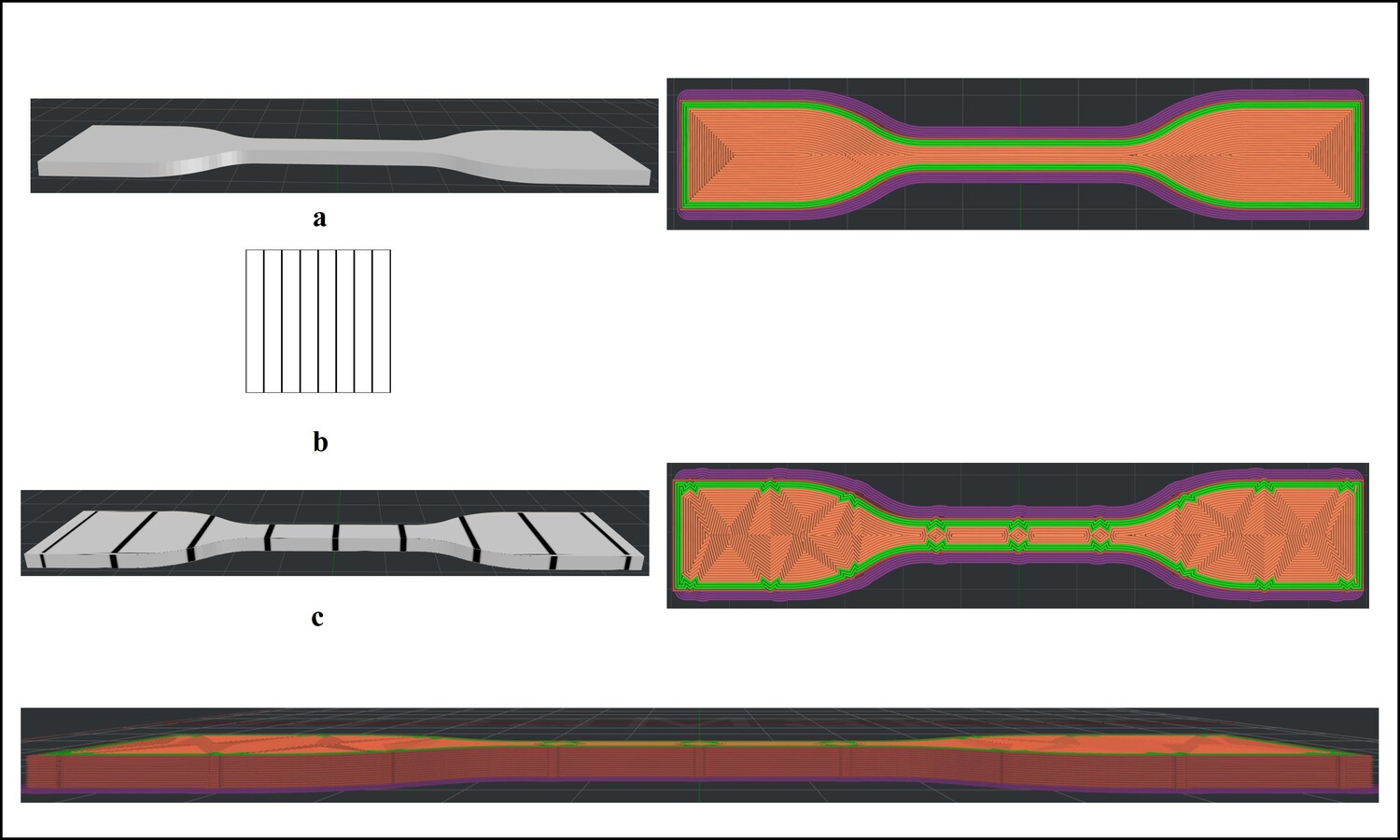
Additive manufacturing is favored for its capacity to create intricate geometries and enhance component functionality more efficiently than traditional methods. Applying texture to materials is one of the processes used to add functionality to products, wherein it can improve adhesion and tribological behavior in biomedical applications while also controlling mechanical properties and providing perceptual and aesthetic improvements. In this study, custom black-white images containing vertical lines were prepared and added as textures to the design of tensile test specimens during slicing. Custom textured and untextured tensile test specimens were fabricated using the Fused Deposition Method with polylactic Acid filament to evaluate the effect of texture parameters, such as protrusion offset (0.25, 0.50, 0.75 mm), number of protrusions (3, 6) and infill pattern (rectilinear, line, concentric), on the tensile strength of the specimens. Through the analysis of tensile test results and examination of microscopic and slicing software images, it was found that texturing resulted in a reduction in ultimate tensile strength due to nozzle trajectory deviations and stress concentration. The least detrimental texturing parameters observed in this study were 0.5 mm protrusion offset and 3 protrusions with concentric and line infill patterns, resulting in a reduction in tensile strength of 2.36 and 5.79%, respectively when compared to untextured specimens.
Karol Tutek, Anna Masek
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 107-121, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.8
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 107-121, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.8
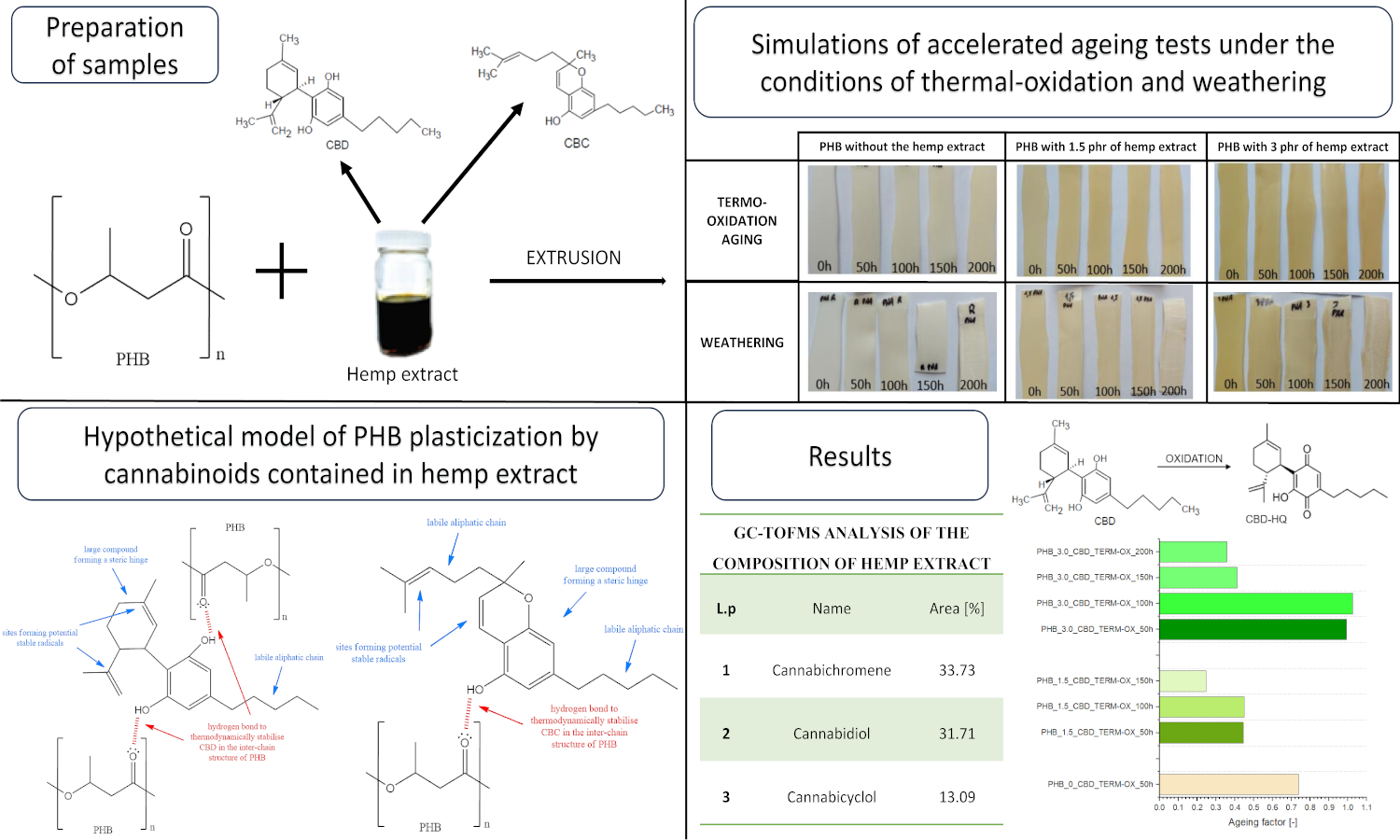
Biodegradable biopolymers like polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) hold promise for sustainable packaging, but their inherent degradability reduces material stability. Synthetic stabilizers, though effective, raise environmental and potential toxicity concerns. This study explores a multifunctional natural anti-aging agent: a hemp extract rich in cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabichromene (CBC). PHB composites with varying hemp extract concentrations were prepared and subjected to thermooxidative and weathering aging. Characterization employed FTIR-ATR, carbonyl index, and spectrophotometry. Static mechanical properties, DSC, and surface free energy (SFE) were also assessed. Notably, the hemp extract exhibited stability under ambient conditions but showed migration with time and aging. The results suggest a plasticizing effect on PHB and highlight the contrasting roles of the extract: inhibiting thermooxidative aging while potentially accelerating aging under atmospheric conditions. This opens avenues for tailoring material durability, further evaluated by life cycle analysis (LCA). This work represents one of the first investigations into hemp extract as an anti-aging agent for eco-friendly polymers, expanding the knowledge base of natural multifunctional additives.
Ju Li, Lize Yang, Shuo Chen, Guotao Sun
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 47-59, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.4
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 47-59, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.4
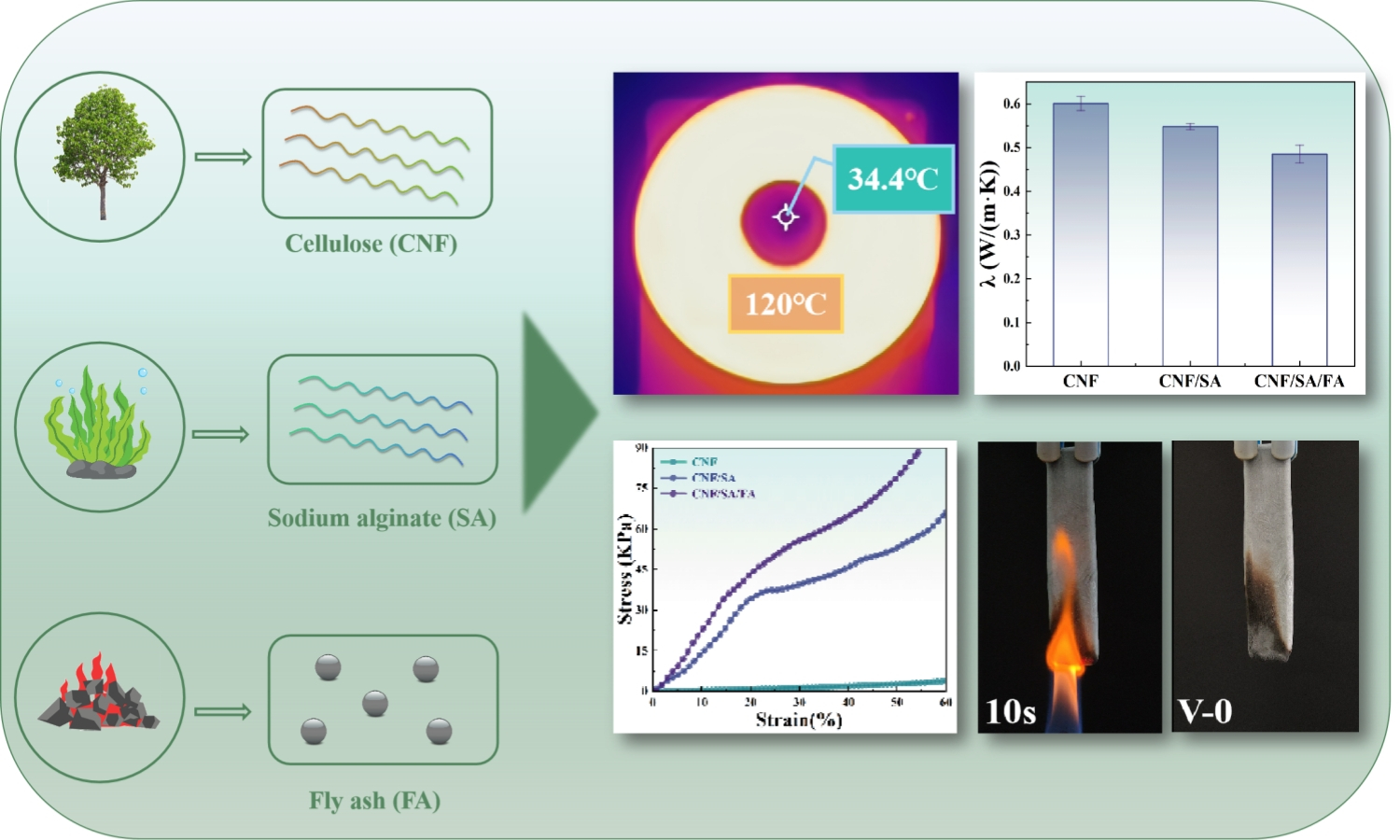
The widespread use of cellulose nanofiber (CNF)-based aerogels is hindered by their limited flame retardancy and mechanical properties. This study addresses these challenges by developing cellulose nanofiber/sodium alginate/fly ash (CNF/SA/FA) aerogel through a one-pot method, utilizing industrial waste fly ash (FA) as a reinforcing material. Various characterization and analytical techniques were employed to evaluate the properties of the CNF/SA/FA aerogel. The findings have revealed that resulting aerogel exhibited excellent thermal insulation performance, with a thermal conductivity of 0.485 W/(m·K), along with an impressive compressive strength of 88.4 kPa and favorable shape processability. Vertical combustion tests demonstrated a V-0 rating, indicating superior flame retardancy, and the aerogel achieved a remarkable 79.16% residual carbon, confirming their effective heat shielding capabilities. Notably, the incorporation of FA significantly enhanced both the thermal and mechanical properties of the composite aerogel, presenting a sustainable and effective solution to optimizing the properties of aerogel for thermal insulation.



