Efficient single-step reactive compatibilization of hemp flour-reinforced PLA/TPS blends: Exploring eco-friendly alternatives and bio-based compatibilizers from maleinized hemp oil
Alejandro Lerma-Canto , Ivan Dominguez-Candela
, Ivan Dominguez-Candela , Jaume Gomez-Caturla
, Jaume Gomez-Caturla , Vicent Fombuena
, Vicent Fombuena , Daniel Garcia-Garcia
, Daniel Garcia-Garcia
 , Ivan Dominguez-Candela
, Ivan Dominguez-Candela , Jaume Gomez-Caturla
, Jaume Gomez-Caturla , Vicent Fombuena
, Vicent Fombuena , Daniel Garcia-Garcia
, Daniel Garcia-Garcia
Vol. 18., No.2., Pages 214-228, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.15
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.15
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
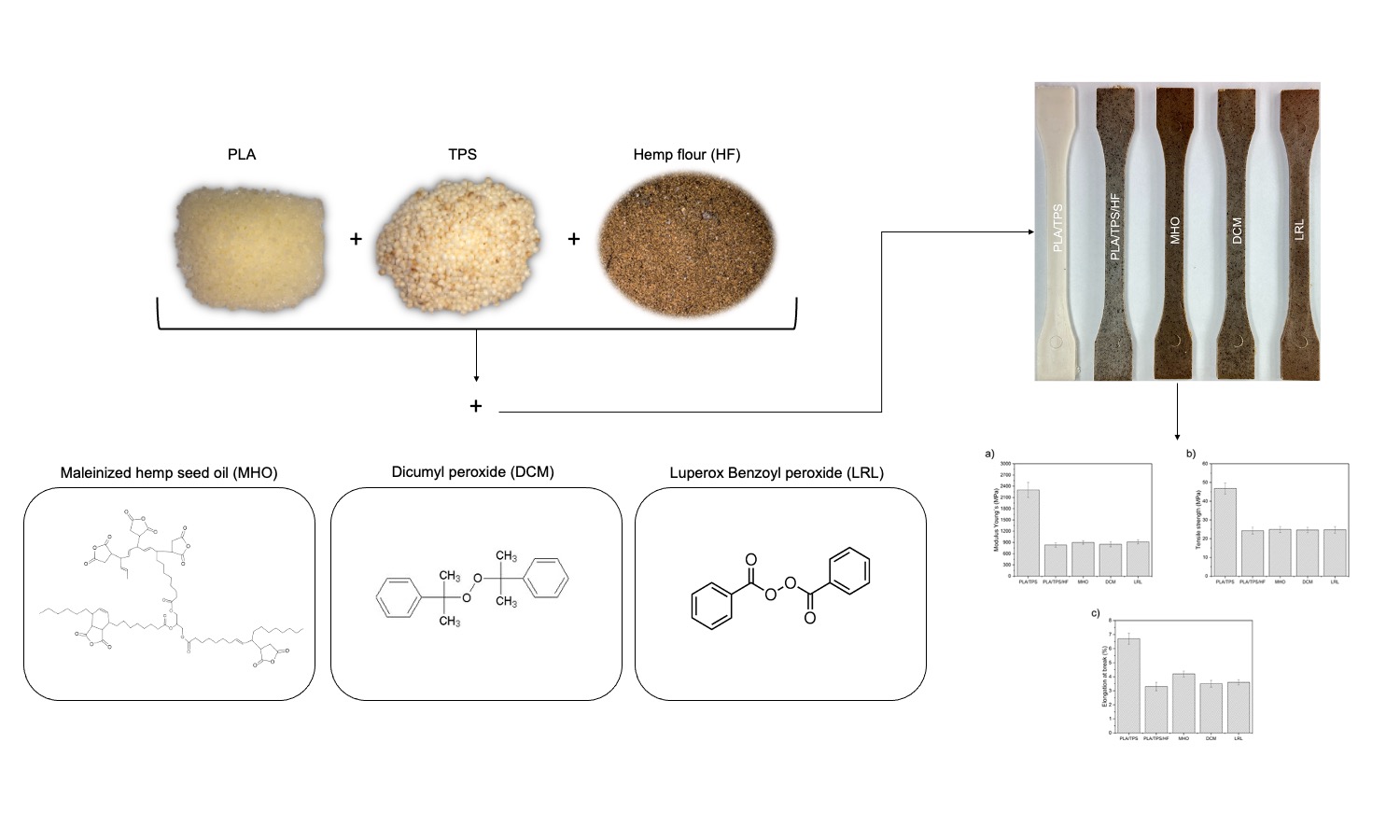
ABSTRACT
In a blend of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and thermoplastic starch (TPS), a 15% load of hemp seed lignocellulosic filler (HF) was incorporated. Additionally, separate petrochemical-based compatibilizers, such as dicumyl peroxide (DCM) and benzoyl peroxide (LRL), as well as a bio-based compatibilizer, maleinized hemp seed oil (MHO), were introduced. Adding HF to the PLA/TPS blend reduced tensile mechanical properties due to the stress concentration phenomenon arising from the lack of interaction between components, yielding a more brittle material. This issue was mitigated by adding compatibilizers, notably the incorporation of MHO into the PLA/TPS/HF blend this increased elongation at break by enhancing compatibility among the blend components and providing a plasticizing effect. Moreover, regarding thermal properties, it was observed that the inclusion of HF led to a decrease in the glass transition temperature (Tg), cold crystallization temperature (Tcc), and melting temperature (Tm). Conversely, adding MHO to this blend increased all these values compared to the PLA/TPS/HF mixture, attributed to the plasticizing effect imparted by the modified oil. Additionally, following fracture in Charpy impact testing, the samples were subjected to field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) analysis to examine the fractured surface of the various samples.
RELATED ARTICLES
Paulina Bednarczyk, Kamil Rożniakowski
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
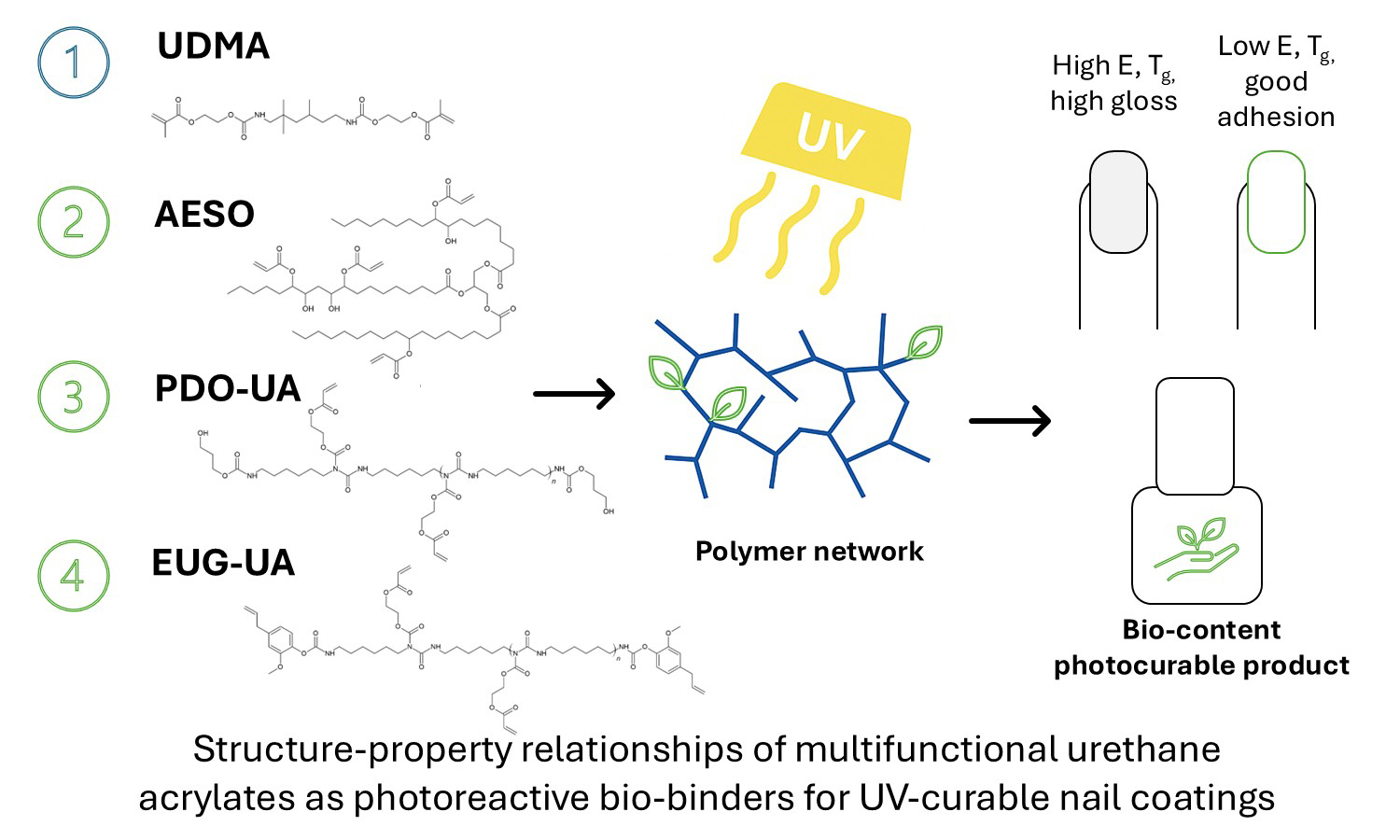
This study investigates the structure–property relationships of multi-functional urethane acrylate resins designed as photoreactive binders for UV-curable nail coatings. Four systems were examined: a commercial resin urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA), a bio-based acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO), and two newly synthesized bio-based urethane acrylates derived from 1,3-propanediol (PDO–UA) and eugenol (EUG–UA). Photopolymerization kinetics were analyzed by realtime FTIR, while the properties of the cured coatings were also determined. The mechanical and thermal behavior of selfsupporting polymer films was evaluated by tensile testing and DSC analysis. The UDMA network exhibited the highest crosslink density, reflected in its high modulus (≈0.5 GPa), tensile strength (≈15 MPa), and Tg (≈60°C), making it suitable for use as a top coat. AESO showed moderate stiffness and flexibility, whereas PDO–UA and EUG–UA formed soft, low-Tg (–12 and –17°C) and highly deformable networks typical of elastomeric materials. The combined mechanical and thermal results confirmed that crosslink density strongly governs coating performance and applicability. This study demonstrates that blending UDMA with bio-based oligomers enables the design of sustainable, UV-curable nail lacquers with an optimal balance of hardness, flexibility, and adhesion to the natural nail plate.
Cláudia Andréa Batista dos Santos, Bartłomiej Kryszak, Rafał Malinowski, Aleksandra Ujćič, Konrad Szustakiewicz
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
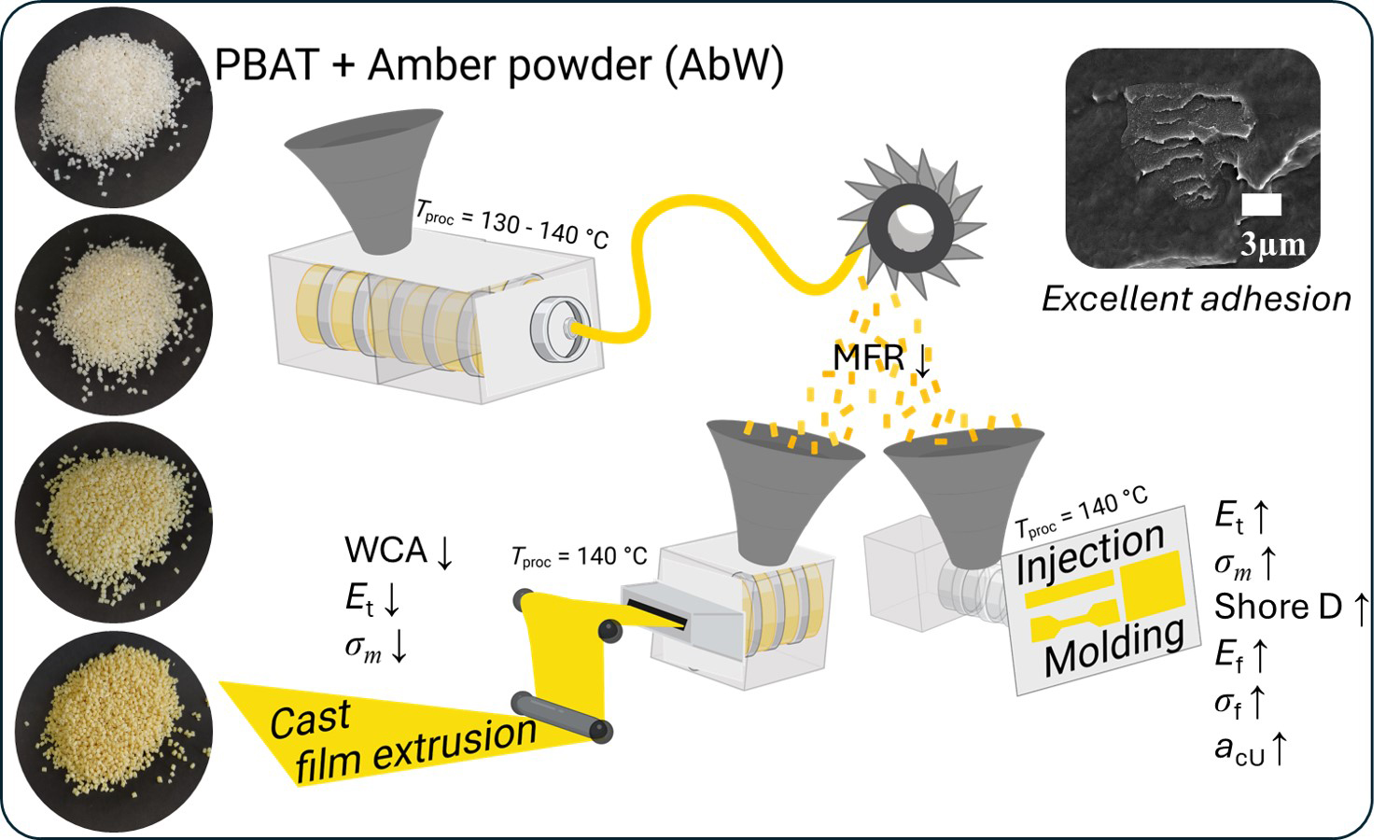
This study investigates the interaction between poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and amber powdered waste (AbW) from jewelry at different filler concentrations (0, 1, 2.5, and 5 wt%) obtained via melt mixing in a corotating twin screw extruder. The resulting materials were pelletized and processed using two techniques: 1) cast film extrusion and 2) injection molding. The shaped specimens exhibited excellent interfacial adhesion. Thermal behavior, as assessed by Vicat softening temperature (VST), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), showed minimal variation among the composites. Despite similar melt flow rate (MFR) values among the samples, the incorporation of AbW affected the behavior of the polymer during cast film extrusion. Consequently, the composite films exhibited lower tensile mechanical parameters (tensile strength, Young’s modulus, stress and strain at break) compared to the neat PBAT film. In turn, the injection molded composites showed improved tensile, flexural, and impact parameters compared to their neat counterpart. Additionally, a slight decrease in water contact angle (WCA) suggested increased surface hydrophilicity of the extruded films. These findings demonstrate the potential of AbW as an additive for biopolymer composites with enhanced mechanical performance. The increased surface hydrophilicity is particularly relevant for applications targeting biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Evangelia Balla, Panagiotis Klonos, Apostolos Kyritsis, Dimitrios Bikiaris
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 154-167, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.13
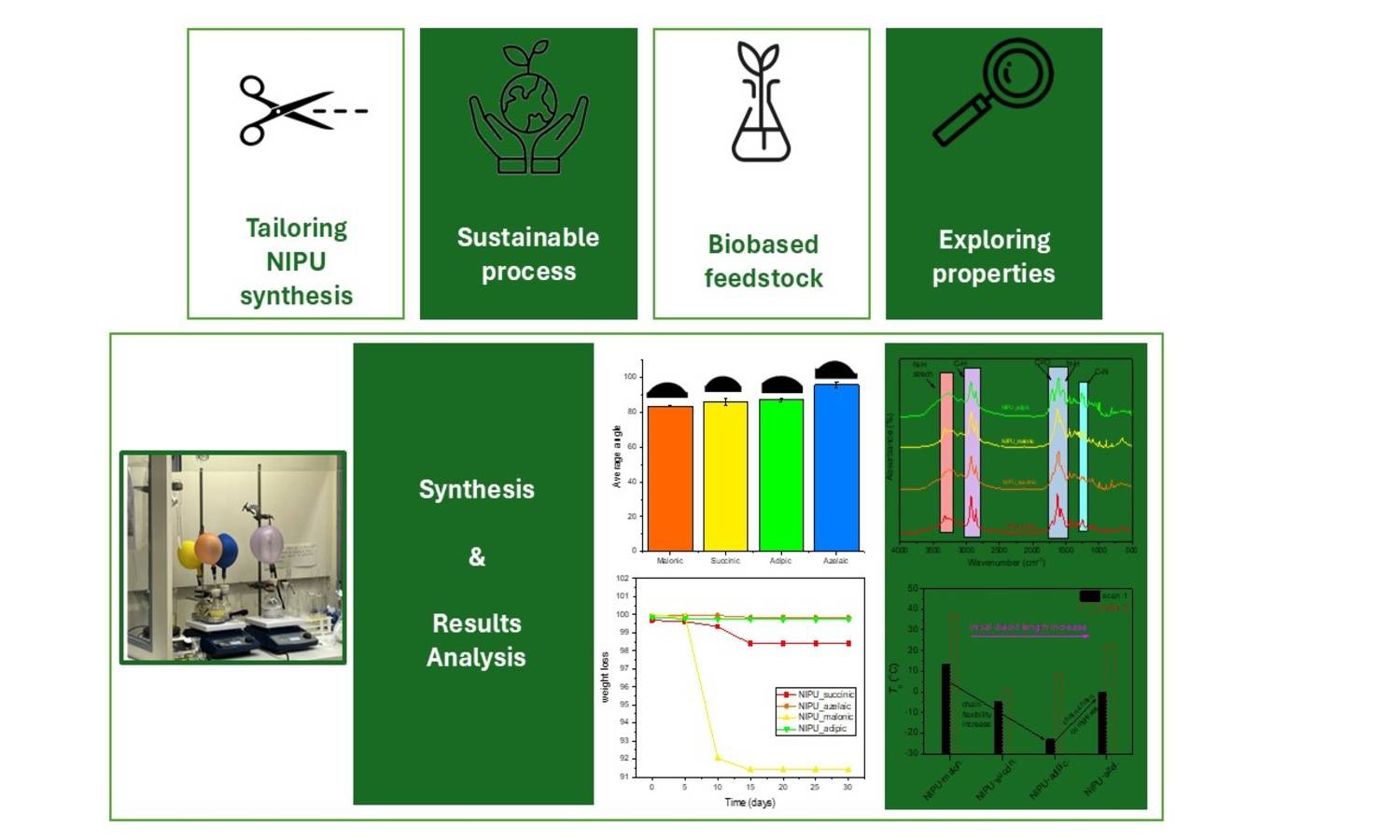
In recent decades, numerous efforts have been dedicated to the investigation of eco-friendly non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) as alternatives to conventional polyurethanes (PUs). Since isocyanates are classified by the EU as hazardous and toxic compounds, NIPUs offer a promising route to mitigate isocyanate-related health risks as well as other environmental concerns associated with traditional PU synthesis. In the present study, we report the synthesis as well as the detailed structural and thermal characterization of a new series of fully biobased non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) based on aliphatic dicarboxylic acids of different chain lengths. The NIPUs were prepared via a two-step polyaddition reaction involving glycerol carbonate and diamine. Their synthesis enables a sustainable pathway to tailor NIPUs’ physicochemical properties via diacid structure control. Studies of their structure, thermal behavior and trends, morphological, and hydrolytic findings confirmed strong diacid chain length dependence on glass transition temperature (Tg ~13, 0, ‒5 and –23 °C), molecular weight, surface wettability, and enzymatic degradability. Short-chain diacids yielded NIPUs with rapid hydrolytic degradation, while their longer-chain analogs were hydrophobic and thermally stable. Contact angle measurements (~75–85°) also confirm these trends. The tunable properties position these materials among strong candidates for biomedical applications.
Soni Thakur, Amal M. Sindi, Rahul Dev Bairwan, Rasha A. Mahmoud, Eman Alfayez, Nurul Fazita Mohammad Rawi, Kanchan Jha, H.P.S. Abdul Khalil
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
Vol. 20., No.2., Pages 197-214, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.16
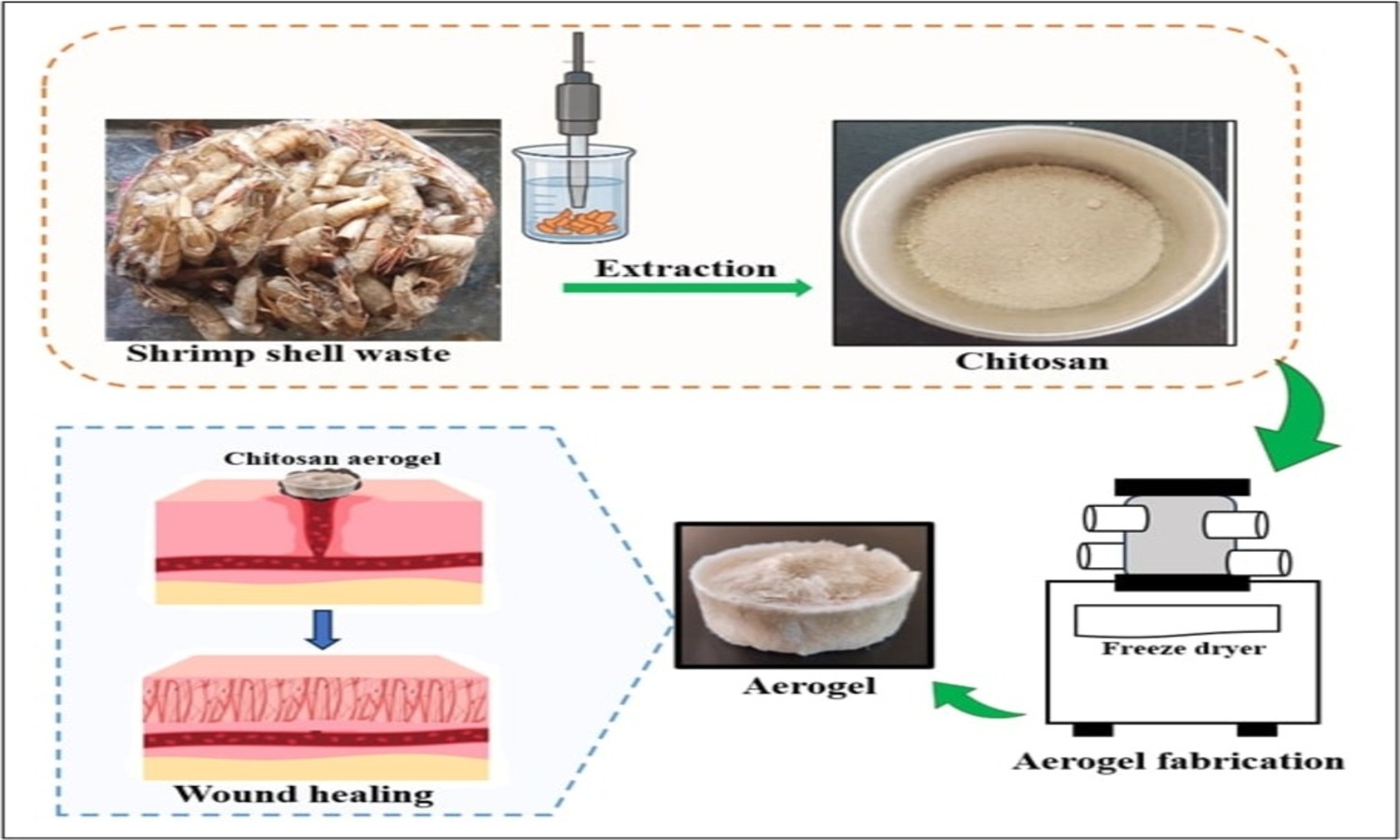
This research presents an eco-friendly approach for extracting chitosan from shrimp shell waste through ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) to prepare biocompatible aerogel scaffolds for biomedical applications. The study investigates the influence of various ultrasonic treatment times (10, 20, 30, 40 min) on the yield and structural and physicochemical properties of the extracted chitosan via characterization using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Among the tested conditions, the 30 min UAE-treated chitosan aerogels showed optimal porosity and structural integrity. Biocompatibility of the aerogels was evaluated, and the results confirmed their non-cytotoxic nature. The bioactivity of the chitosan aerogels was evaluated in terms of their in vitro wound closure ability and antibacterial properties. The aerogels demonstrated a wound closure rate of around 51% after 72 h, significantly higher than the untreated control (37%). In addition, they exhibited clear antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. This sustainable extraction and fabrication method not only adds value to marine waste but also produces functional biomaterials with potential applications in wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine, supporting global efforts toward sustainability and circular bioeconomy.
Effect of natural cinnamon extract on the stabilizing properties of biodegradable packaging polymers
Anna Kosmalska-Olańska, Anna Masek
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5
Vol. 20., No.1., Pages 52-71, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.5

The growing focus on sustainability, eco-friendly technologies, decarbonization, and reducing carbon footprints shapes current industry challenges. This article reviews the potential of cinnamon as a bio-additive for polymer stabilization in packaging. Samples were prepared from ethylene-norbornene copolymer (Topas), a cyclic olefin copolymer known for purity, transparency, and low gas permeability, and poly(lactic acid) (PLA), a bio-based alternative to petroleum plastics. Cinnamon powder was added in 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 wt%. After solar and thermo-oxidative aging, hydrophobicity, chemical composition, mechanical, and color properties were analyzed. Results showed higher hydrophobicity and resistance to hydrolytic degradation due to reduced water penetration. PLA, normally brittle, became more flexible, with 0.5 wt% cinnamon showing optimal performance after 100 h of solar aging, similar to Topas composites. Overall, PLA and cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) films with cinnamon improved durability, extended food shelf life, and acted as natural color indicators of material aging.



