Content
All issues / Volume 16 (2022) / Issue 10 (October)
Ming Qiu Zhang
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1011-1011, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.73
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1011-1011, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.73

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Umut Bulut, Vuslat Oyku Sayin, Sevki Can Cevher, Ali Cirpan, Saniye Soylemez
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1012-1021, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.74
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1012-1021, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.74
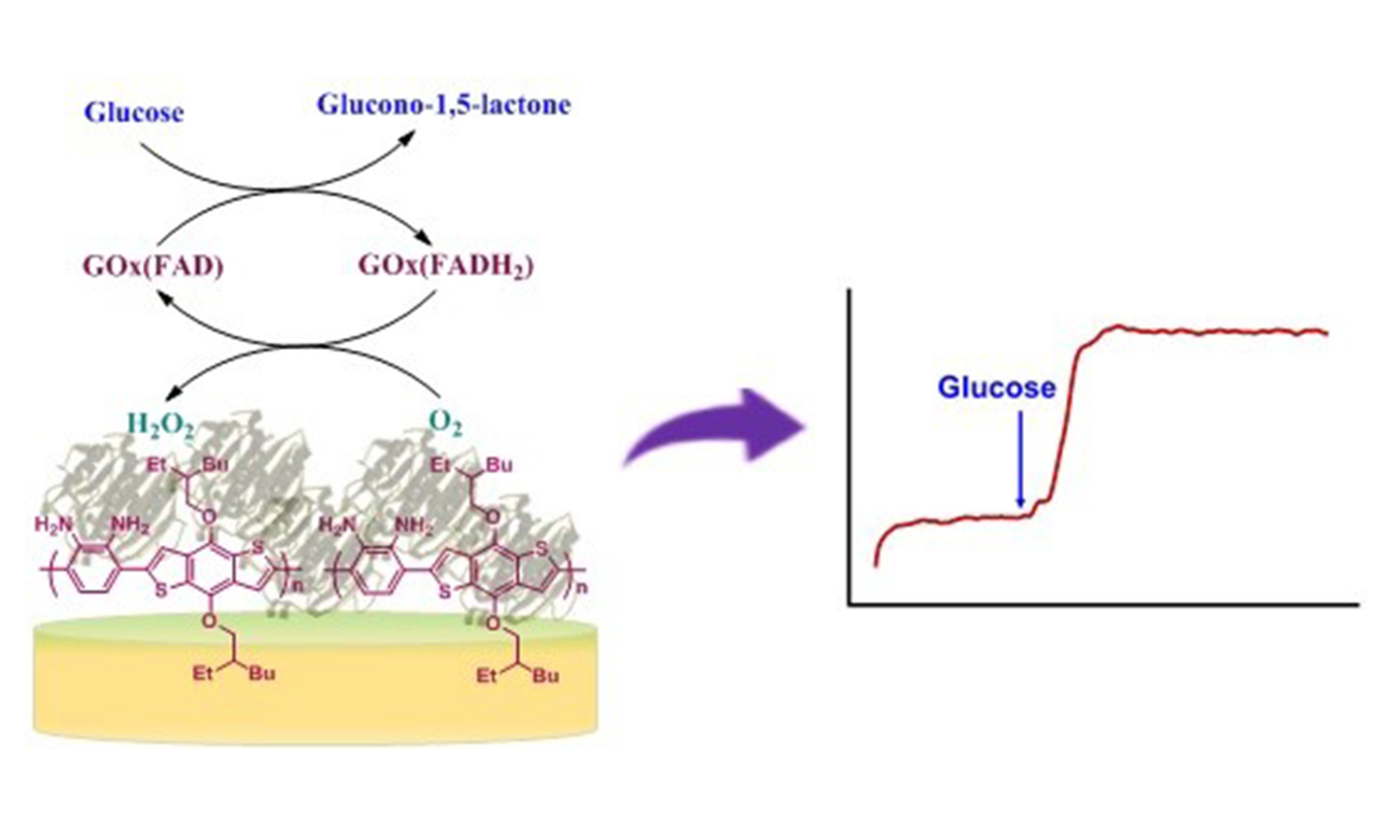
An amino-functionalized, conjugated polymer (P(BDBT)) modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was employed as an immobilization platform for glucose oxidase (GOx) enzyme to assemble a novel glucose biosensor. Amino groups available on the polymer backbone served as bioconjugation sites for GOx via glutaraldehyde (GA). The biosensor response to the reduction in oxygen amount because of the enzyme reaction was monitored at –0.7 V potential versus Ag/AgCl. The biosensor displayed a broad linear range between 0.1–1.0 mM glucose with a detection limit of 0.17 mM. The values of the apparent Michaelis-Menten constant (KMapp) and sensitivity were determined as 1.74 mM, and 28.17 μA/(mM·cm2), respectively. GOx immobilized P(BDBT) film displayed high stability, selectivity, and reproducibility. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques were utilized for the characterization of surface modifications. The fabricated biosensor was adept at determining the amount of glucose in a commercial beverage. The simple electrochemical method for the construction of P(BDBT)/GOx biosensors could pave the way to new perspectives in developing profitable biosensors.
Aamna Bibi, Ying-Hsuan Li, Hsi-Wei Jia, Hsien-po Kuo, Nadaraj Sathishkumar, Hsin-Tsung Chen, Karen S. Santiago, Jui-Ming Yeh
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1022-1037, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.75
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1022-1037, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.75
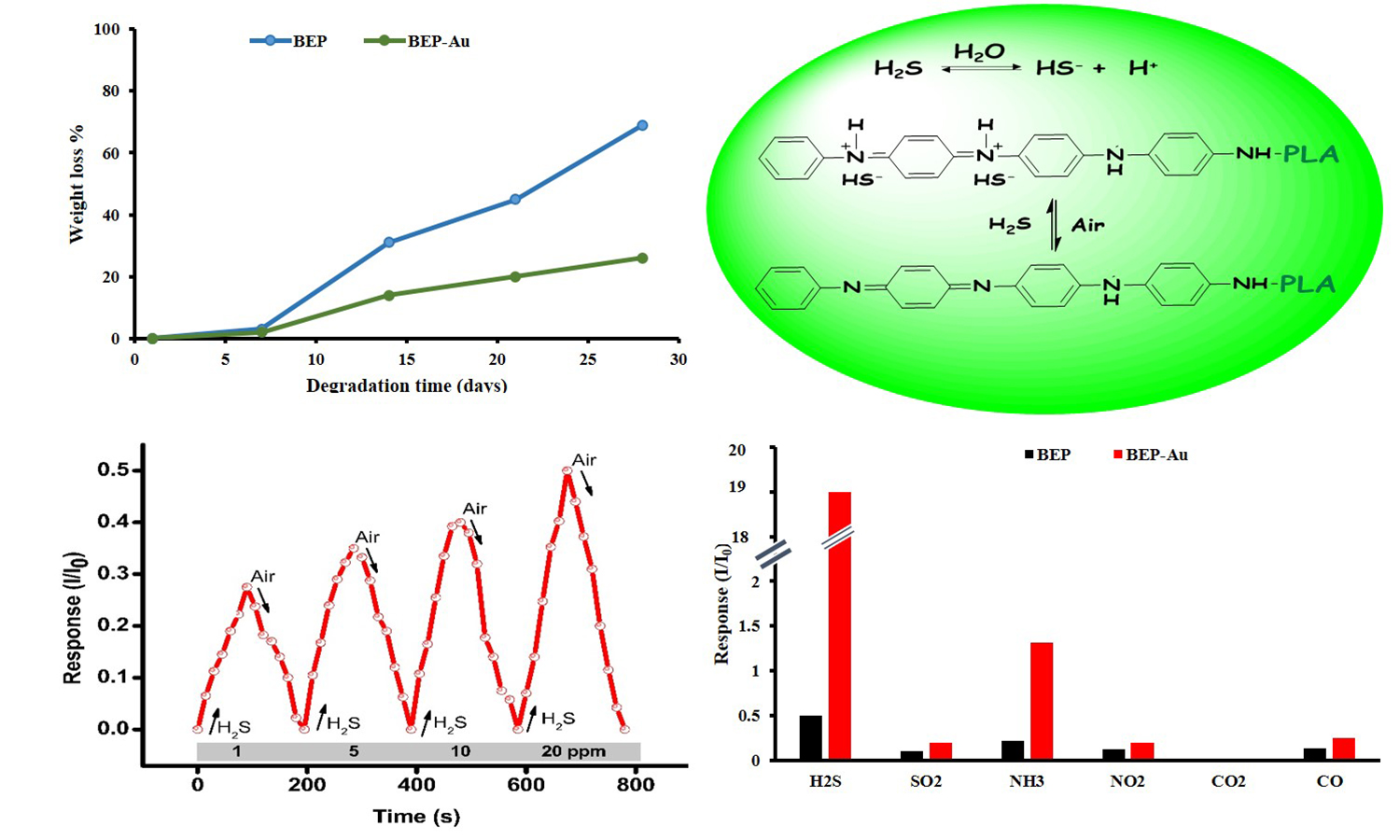
In this paper, a series of biodegradable-electroactive polymers (BEP) and its composite with gold nanoparticles (BEPAu) were prepared and used in the detection of H2S gas. First, the starting materials which included the electroactive aniline tetramer (ACAT) and biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA) were synthesized and characterized. The BEP was then prepared by reacting tri-isocyanate (N-3300) with the synthesized ACAT and PLA at a specific feeding ratio. In this case, ACAT served as a pendant group. The BEP-Au composite was subsequently prepared by immersing a specific amount of BEP in a certain concentration of HAuCl4·3H2O solution for 6 h, followed by characterization. The gas sensing performances of as-prepared sensors were tested. Results revealed that the BEP sensor has a good sensitivity of 0.0114 ppm–1 towards increasing concentrations of H2S gas (1–20 ppm), which was observed to have increased up to 0.907 ppm–1 after the addition of gold nanoparticles, i.e., BEP-Au. Furthermore, the said sensors also showed rapid response and recovery rates, good repeatability, and high selectivity. To fully evaluate the feasibility of BEP and BEP-Au for the detection of H2S gas, the adsorption was further investigated via the ab initio density functional. theory (DFT). The DFT calculations complemented the experimental gas sensing results.
Sanjay Kumar, Chang-Mou Wu, Po-Chun Lin, Jieng-Chiang Chen, Yoshinobu Shimamura
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1038-1051, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.76
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1038-1051, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.76
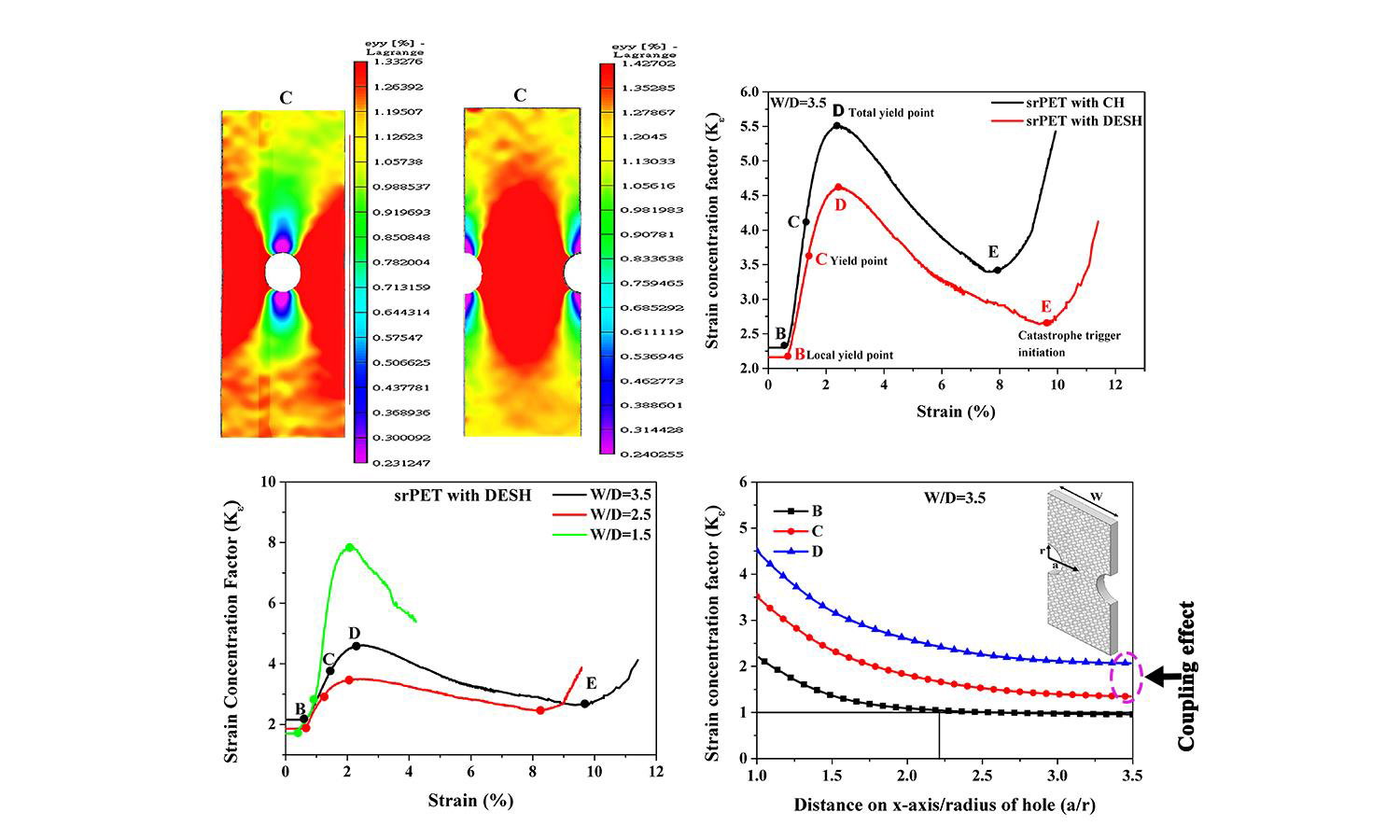
This study investigated variations in strain concentration factors (Kɛ) within the full deformation range of self-reinforced poly(ethylene terephthalate) composites (srPETs) with double-edge semicircular holes (DESH) using digital image correlation (DIC) at different width-to-diameter (W/D) ratios. The value of Kɛ agrees with the theoretical concentration factor (Kt) within the elastic deformation range; then, it increases rapidly to a peak because of plastic deformation. Therefore, the change in Kɛ was divided into different stages based on the spread of the yield extent (beginning from the hole edge). These results will help improve the understanding of the yielding phenomenon of open-hole materials and provide early warnings before final material damage. Kɛ decreased in both the elastic and plastic regions with a decrease in W/D; however, there was an exception when the W/D ratio = 1.5. Therefore, the geometric configuration W/D > 1.5 was recommended for designing secure structural ductile composites. The Kɛ of DESH is lower than that of circular holes (CH) in both the elastic and plastic regions for the hole effect. Thus, composites with DESH should be preferred as an alternative for structural applications.
Thawanrat Chaisit, Punnanee Sumpavapol, Kittisak Jantanasakulwong, Thorsak Kittikorn
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1052-1064, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.77
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1052-1064, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.77
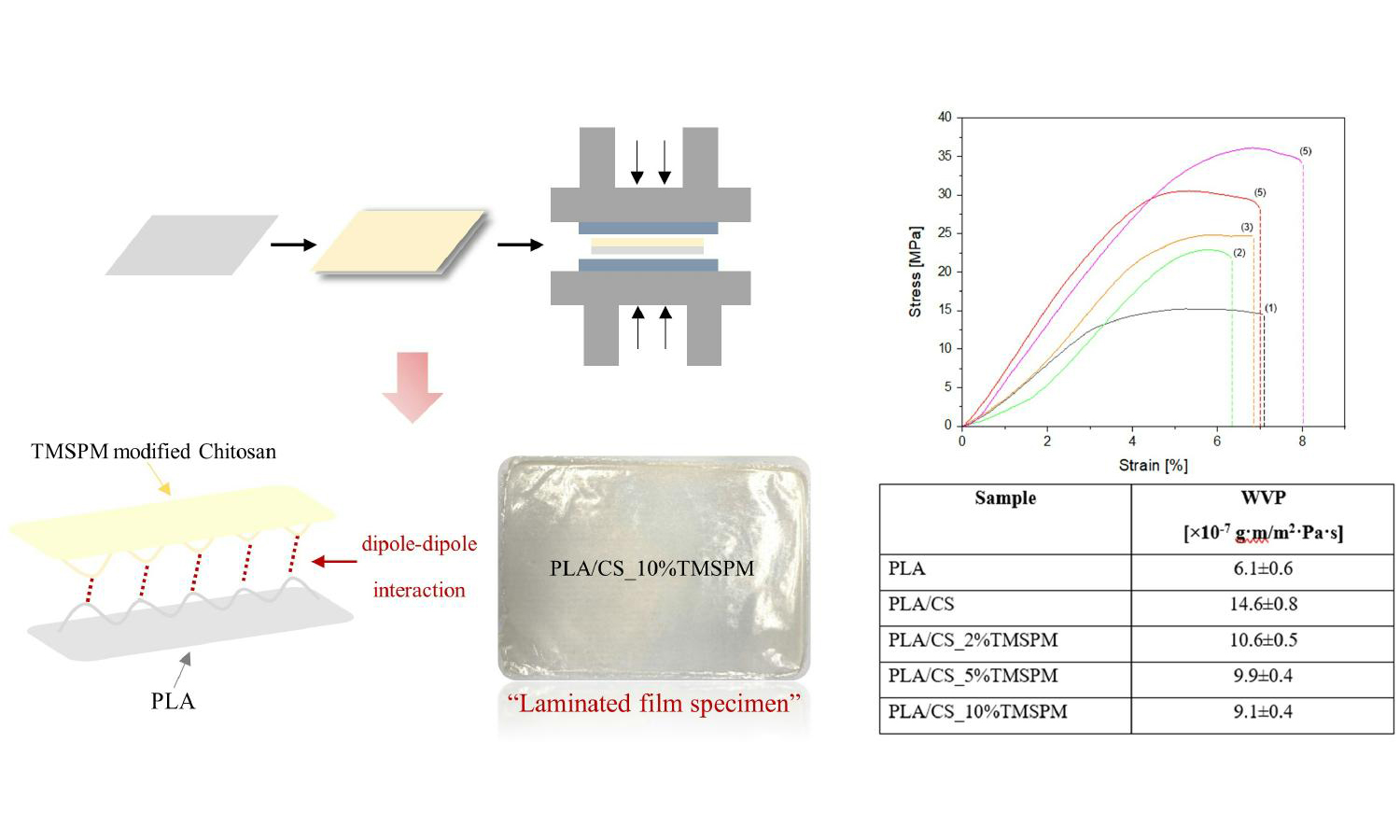
Nowadays, there has been an increase in demand for using biodegradable food packaging due to its sustainable and environmentally friendly. Poly(lactic acid) is an interesting alternative. To increase the potential use of packaging, the development of a bioactive packaging by using a natural antimicrobial like chitosan has gained considerable attention due to its excellent antimicrobial activity and performance meanwhile, both layers have different surface properties that result in poor interfacial adhesion. So, this research aims to improve the interfacial adhesion between PLA and chitosan by grafting chitosan with 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate (TMSPM) using ultrasonic vibration and to study the preparation of the laminated film via lamination technique. From the FTIR results, the characteristic peaks at a wavenumber of 1701 and 877 cm–1 corresponding to the C=O vibration in the methacrylate and Si–O stretching groups of TMSPM were observed. This indicates that the grafting reaction occurs completely. Interestingly, the PLA/CS_10%TMSPM laminated film revealed an improved interfacial adhesion and hydrophobicity. This was observed from the strength value that increased from 21.9 to 35.8 MPa and the water vapor permeability value that decreased from 14.6·10–7 to 9.1·10–7 (g·m)/(m2·Pa·s) when compared to the PLA/CS laminated film. In addition, the PLA/CS_10%TMSPM laminated film also showed excellent antimicrobial activity against E. coli as well.
Rikanari R. Choudhury, Jaydevsinh M. Gohil, Akshaya K. Palai, Kingshuk Dutta, Smita Mohanty
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1065-1082, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.78
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1065-1082, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.78
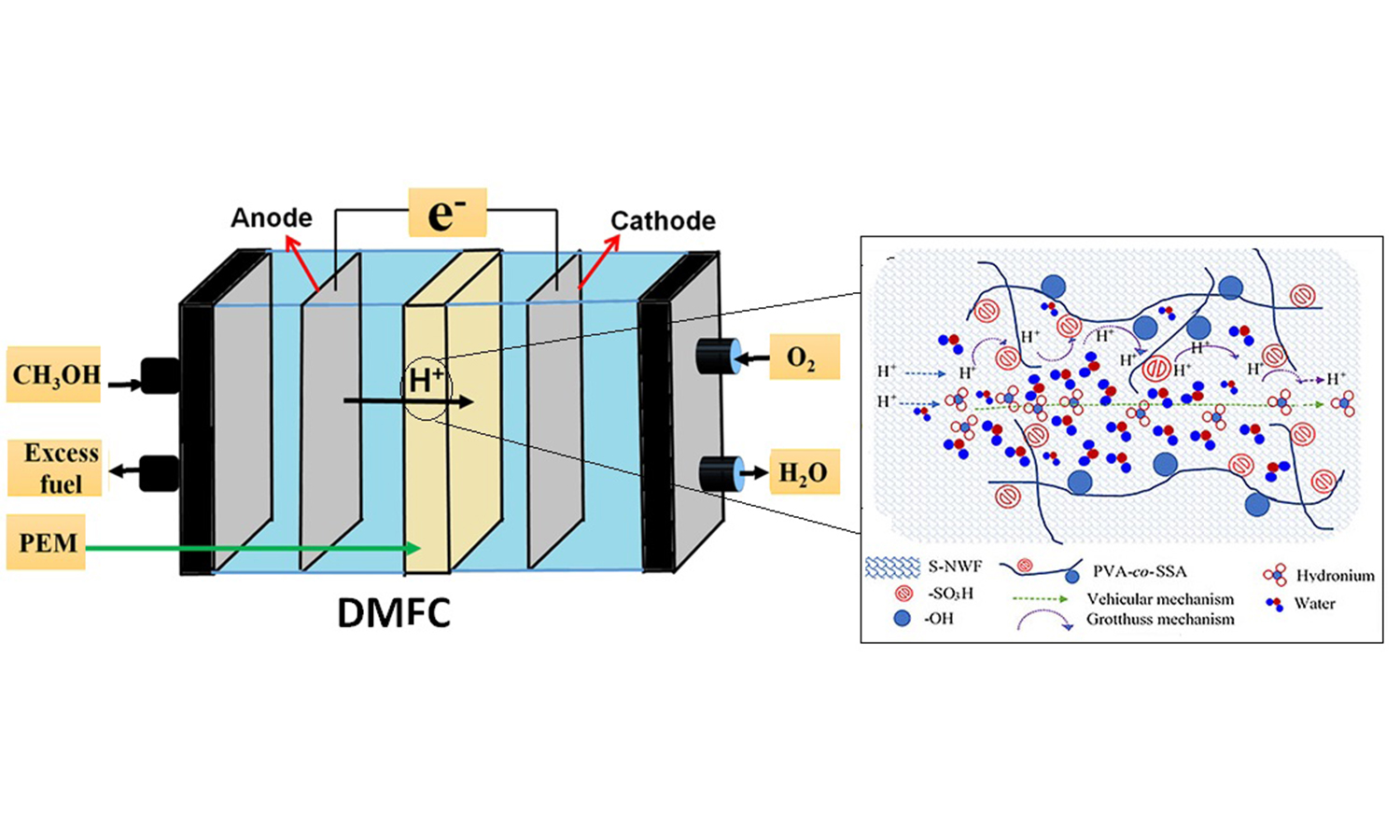
Various materials have been examined over the last several decades to fabricate proton exchange membranes (PEMs) for direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs), with the objective of achieving high selectivity (i.e., the ratio of proton conduction to fuel permeability). Ideally, a PEM for DMFC must demonstrate higher proton conductivity, as well as lower methanol permeability, in comparison to the commercial Nafion membranes. With these objectives, this research paper reports the fabrication of a composite PEM comprising glutaraldehyde-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol-co-styrenesulfonic acid) and sulfonated polypropylene-based non-woven fabric (S-NWF) by deep coating technique. The resulting PEMs were thoroughly characterized to find physicochemical and electrochemical properties. Key findings obtained with these composite PEMs are (a) exhibition of dimensional stability in hot water (at 80 °C), (b) improved proton conductivity (i.e., 0.12 S·cm–1 at 80 °C), and reduced methanol permeability (i.e., 3.91·10–8 cm2·s–1) upon increasing the number of coating layers on the S-NWF, (c) achievement of a membrane selectivity value of 2.61·106 S·s·cm–3, and (d) the fact that 6 layers of coating resulted in producing the highest peak power density of 62.32 W·m–2 and a current density of 540 A·m–2.
Francesco Lopresti, Luigi Botta, Vincenzo La Carrubba, Giuseppe Attinasi, Luca Settanni, Giuliana Garofalo, Raimondo Gaglio
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1083-1098, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.79
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1083-1098, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.79
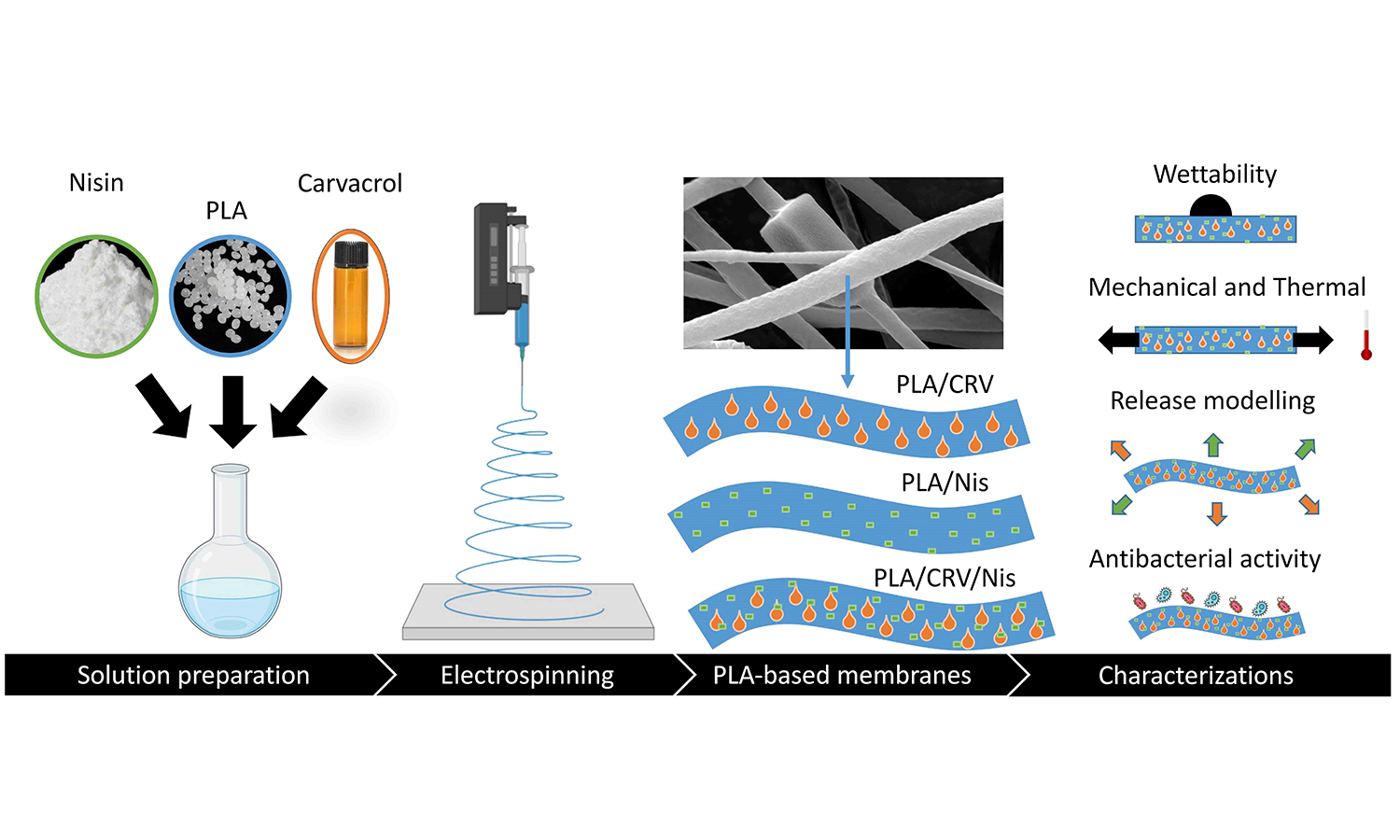
Functional, biopolymeric electrospun structures for the controlled release of antimicrobial agents are gaining increasing interest in food packaging applications. In this study, the physical and antibacterial performances of ternary systems composed of polylactic acid (PLA) electrospun mats loaded with 20 wt% of different relative amounts of carvacrol (CRV) and a commercial nisin formulation (Nis) were assessed. Scanning electron micrographs displayed micro-scaled fibers with different diameter size distributions depending on the relative concentrations of the additives. The PLA/CRV/Nis membranes’ wettability was affected by the relative amount of CRV and Nis loaded, switching from hydrophobic to hydrophilic at the highest Nis concentrations. Thermal and tensile tests assessed the plasticizer action of CRV on PLA, while the Nis formulation was found to modify the mechanical behavior of the membranes from ductile to brittle. The release profiles of CRV and Nis from PLA/CRV/Nis structures, assessed via spectroscopical measurements and fitted with a power-law model, permitted to investigate of the different release mechanisms of the additives as a function of their relative concentration. The determination of the antibacterial activity of the electrospun material clearly indicated that the most effective inhibition of food-borne pathogenic bacteria was registered with PLA containing 20% of CRV.
Agata Zubkiewicz, Izabela Irska, Konrad Walkowiak, Jerzy Dryzek, Sandra Paszkiewicz
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1099-1112, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.80
Vol. 16., No.10., Pages 1099-1112, 2022
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.80
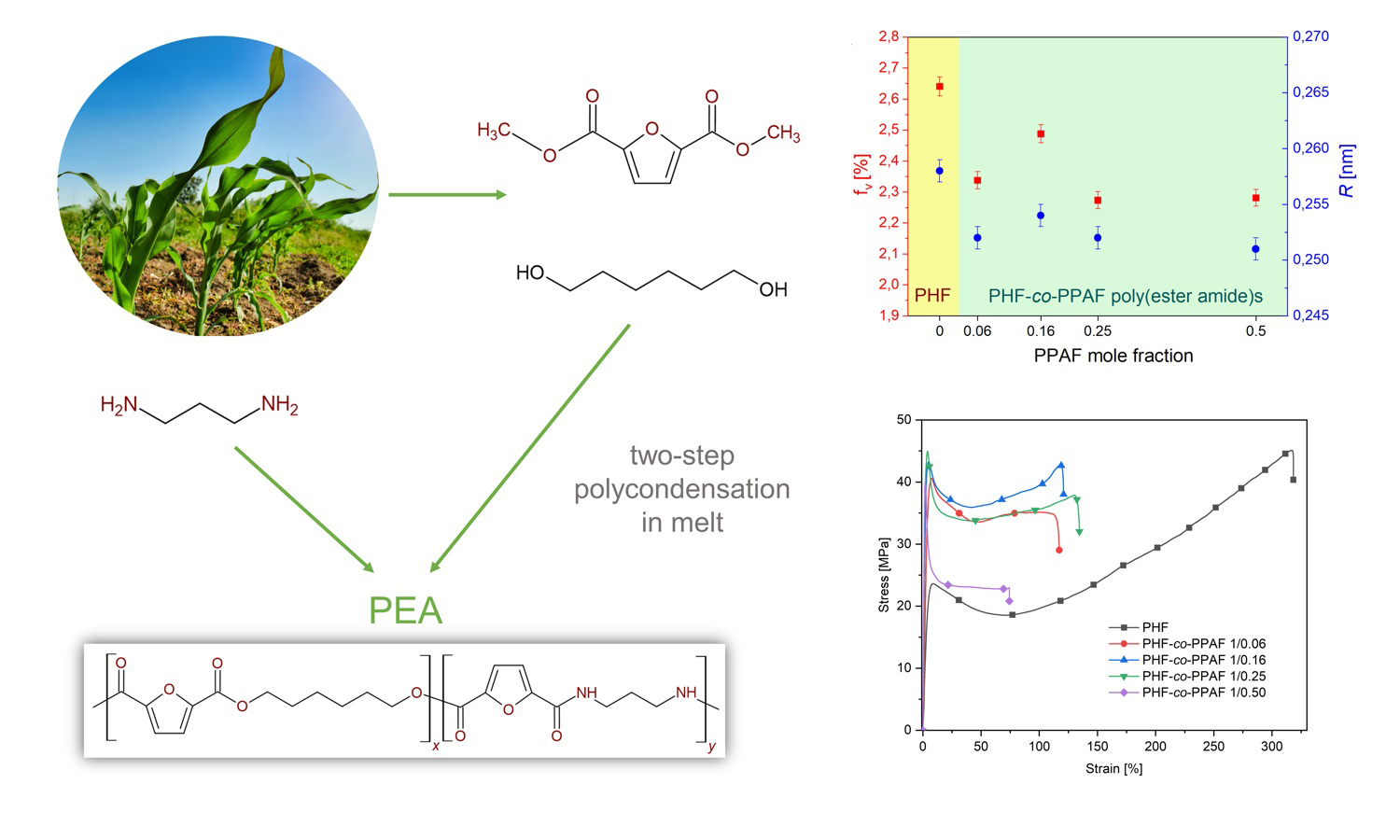
In this work, new furan-based poly(ester amide)s of various compositions were synthesised by the melt polycondensation method. The chemical structure and composition were determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analyses. The optical properties were studied by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The thermal properties were investigated by means of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The thermo-oxidative stability of PEAs was also tested. Additionally, the free volume by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) technique and mechanical properties were examined. It was found that the incorporation of poly(propylene furanamide) (PPAF) units significantly affects the thermal and mechanical properties of co-polymers based on poly(hexylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate) (PHF). Depending on the composition, both semi-crystalline and amorphous co-polymers were obtained. Moreover, the values of the free volume radius (R) and the free volume fractions (fv) were strongly affected by the mole fraction of PPAF units.


