Reversibly interlocked polymer networks: a technology that can do more than eliminating phase separation in polyblends
Vol. 18., No.6., Pages 559-560, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.41
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.41
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

RELATED ARTICLES
Andrea Toldy
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 350-350, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.25
Vol. 19., No.4., Pages 350-350, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.25

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Wenxin Gan, Hanyu Xue, Hongyi Lin, Renjin Gao, Yuchi Zhang, Liwei Wang, Jiuping Rao
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 311-325, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.22
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 311-325, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.22
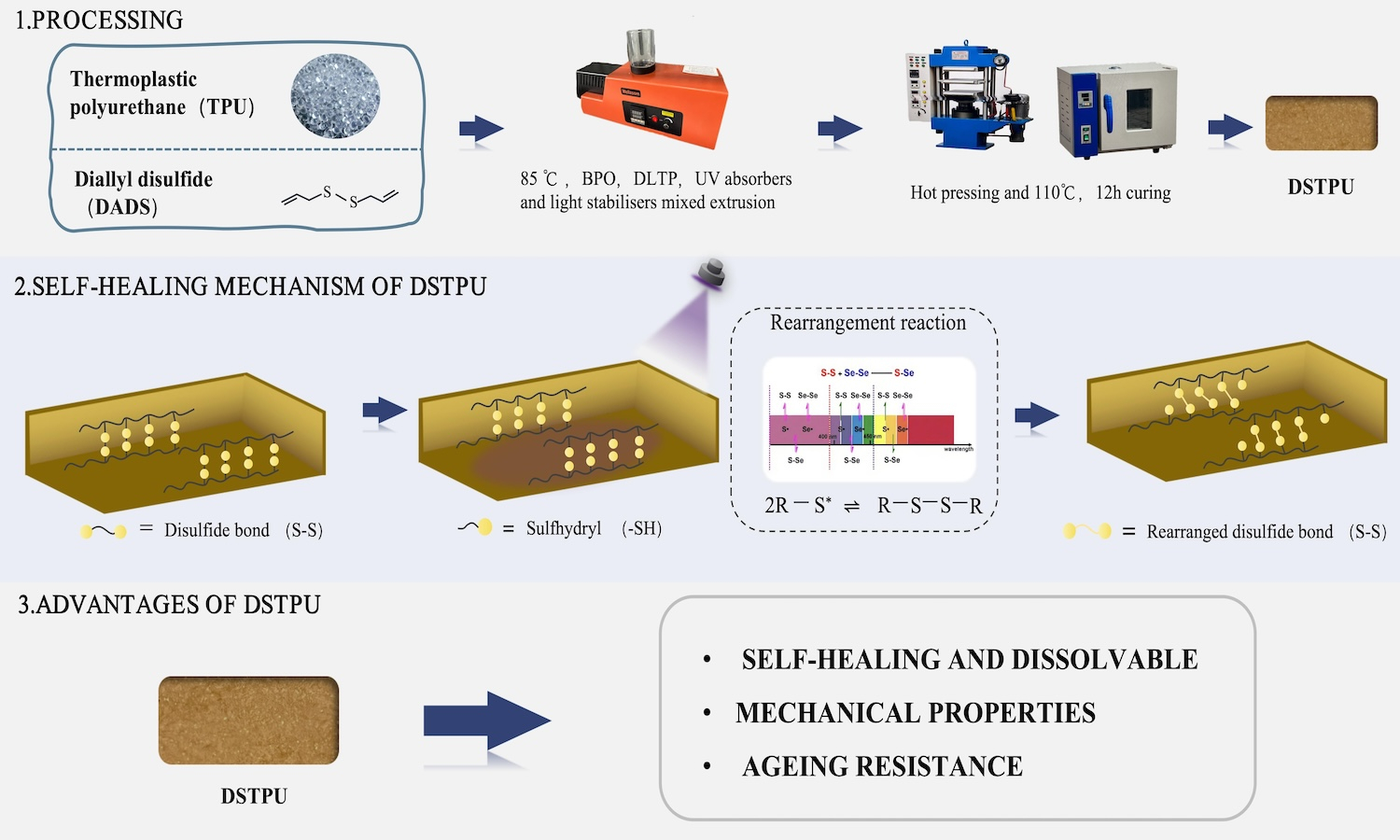
Cross-linking frequently enhanced the mechanical properties of linear polymeric materials; however, it also resulted in the transition from thermoplastic to thermosetting materials, which posed issues from an environmental perspective. Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) elastomers were extensively applied across various industries. To improve the mechanical properties of TPU while preserving its environmental benefits, this study integrated radical copolymerization technology to develop a reversible crosslinked TPU. Specifically, the linear polyurethane molecular chains were crosslinked using diallyl disulfide (DADS) as a functional cross-linking monomer. Through radical copolymerization reactions, reversible crosslinks formed from disulfide bonds were created between the linear polyurethane molecular chains, yielding a self-healing reversible crosslinked thermoplastic polyurethane (DSTPU). The study showed that DSTPU could self-heal and dissolve under UV light and alkaline N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) conditions, achieving 82.2% self-healing efficiency at 3 phr DADS. It dissolved into fine particles in alkaline DMF. Disulfide bonds in DSTPU enhanced cross-linking, boosting 19% oxygen permeability, thermal conductivity (0.218 W/(m·K)), and mechanical properties like tensile stress (11.18 MPa), force (134.13 N), and elongation (548%). These bonds also enhanced aging resistance, cutting ΔYI to 6.0%.
Shengao Yang, Yan Wang, Fang Wang, Kaiyi Zhang, Xinxin Lv, Hao Teng, Rui Zheng, Faliang Luo, Qian Xing
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 94-106, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.7
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 94-106, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.7
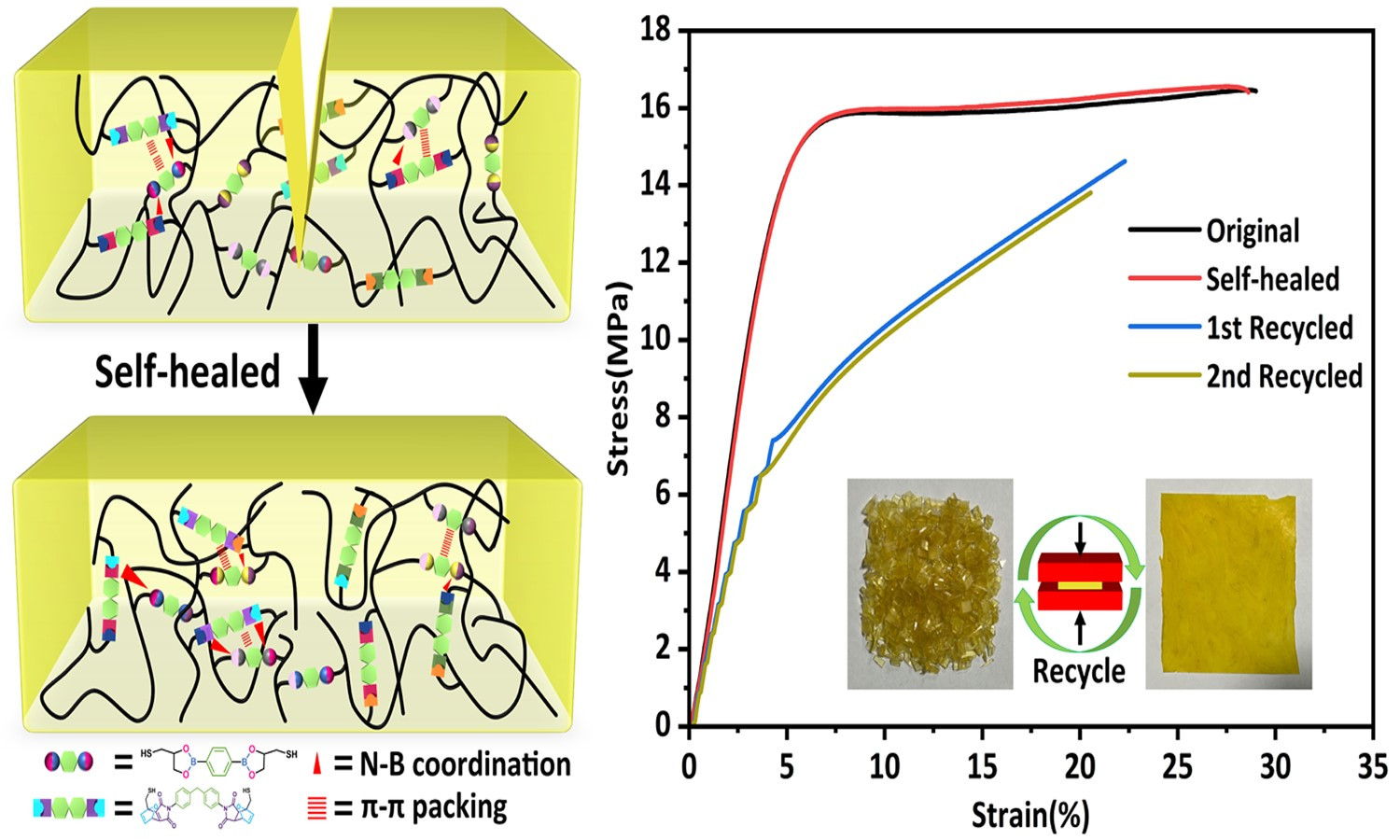
Dynamic cross-linked networks (DCNs) endow thermoset rubber with self-healability and recyclability to extend its lifetime and alleviate environmental pollution. However, the contradiction between high self-healing and mechanical properties in DCNs rubber is always difficult to be resolved. Herein, we used boronic ester (BO) and Diels-Alder dynamic covalent bonds (DA) to synthesize polybutadiene-based dual networks rubber (PB-BO-DA) via thiol-ene reaction. This approach achieved a tensile strength of 16.46 MPa and 99% self-healing efficiency, facilitated by extensive intermolecular interactions (π-π packing and N-B coordination) and fully dynamic cross-linking. In addition, multiple dynamic cross-linked networks (MDCNs) polybutadiene-based rubber also show excellent shape memory ability and recyclability. This strategy might open a helpful pathway to fabricate intelligent multifunctional polymers with high strength and high self-healing efficiency.
Yiting Jing, Sufang Chen, Zejun Xu, Tingcheng Li, Daohong Zhang
Vol. 17., No.12., Pages 1200-1211, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.91
Vol. 17., No.12., Pages 1200-1211, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.91
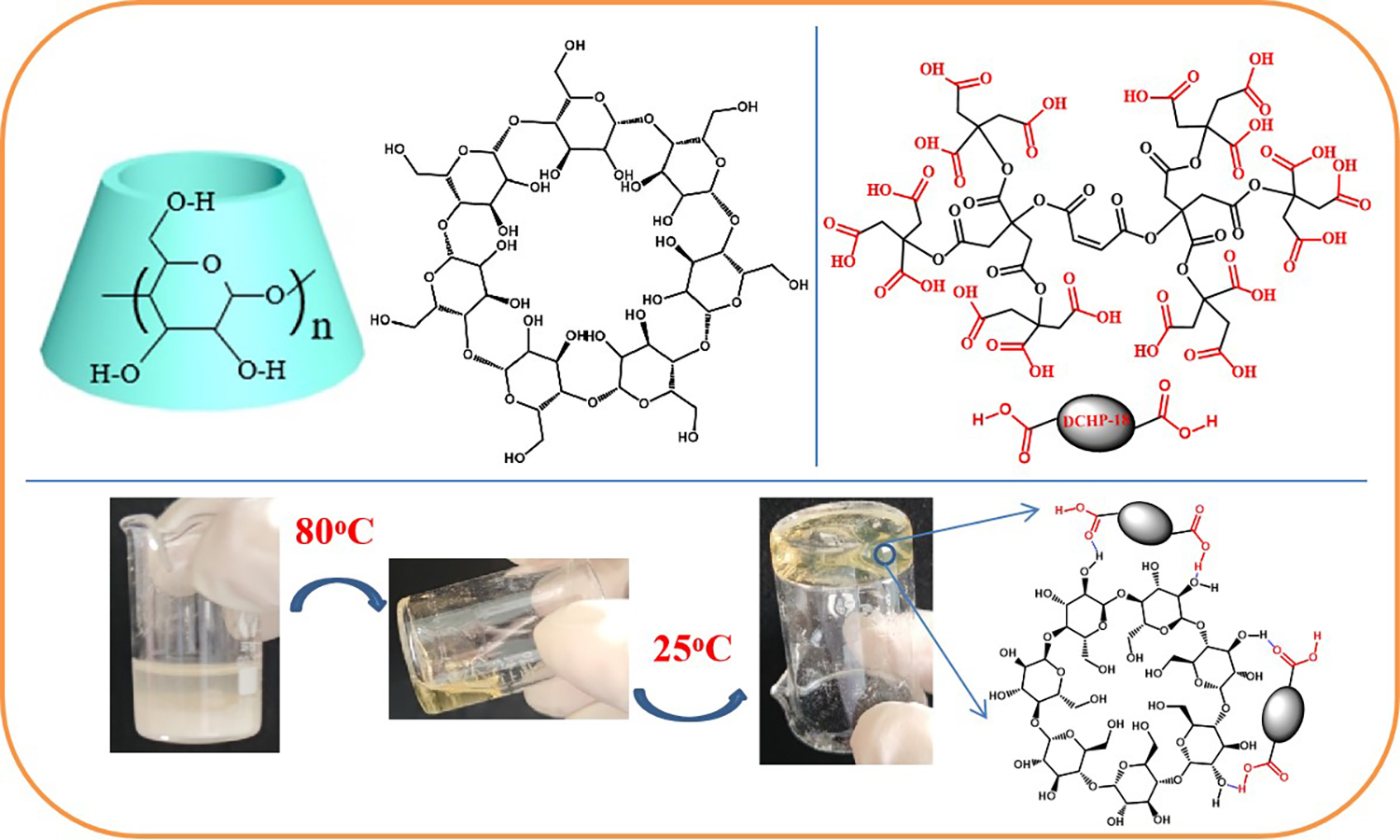
Adhesives have been widely applied in various fields. However, most industrial adhesives contain organic solvents, which are toxic and difficult to clean after use. Importantly, most adhesives are used in a relatively small temperature range (0–50 °C), which is due to the fragmentation of the morphology and properties of supramolecular polymer gels at low temperatures. Most of the supramolecular adhesives need to be heated during the bonding process, which cannot meet the requirements of low-temperature adhesion in daily life and industry. In this study, based on the concept of using deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as a platform, cyclodextrin (β-CD) and carboxyl terminated hyperbranched polyester (DCHP) were used to prepare solvent-free supramolecular polymer gel (CD-DCHP), which was non-toxic and easy to clean. Due to the joint action of deep eutectic solvent and supramolecular polymer structure, CD-DCHP showed excellent mechanical properties, super strong adhesion (up to 4.55 MPa on glass surface), and excellent low-temperature performance (up to 1.64 MPa at –60 °C). This supramolecular polymer gel also showed excellent tolerance to acids, alkalis, and various organic solvents. It greatly expanded the application of DES and provided a new approach to the development of supramolecular adhesives.
Ferenc Ronkay
Vol. 17., No.12., Pages 1180-1181, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.89
Vol. 17., No.12., Pages 1180-1181, 2023
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2023.89

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.




