Eugenol and cloves as plant-origin stabilizers in epoxidized natural rubber compositions
Vol. 18., No.10., Pages 1039-1050, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.79
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.79
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
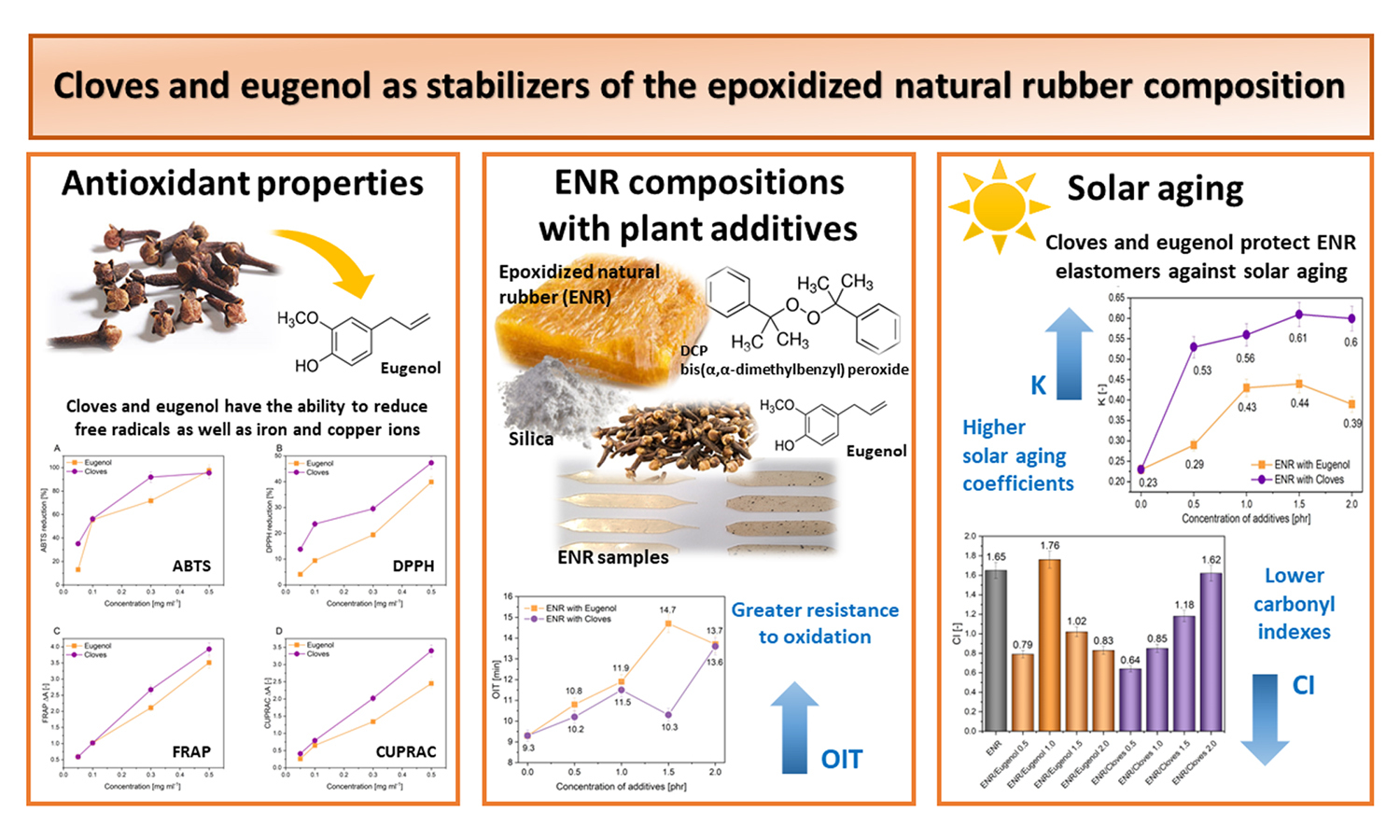
In polymer materials technology, replacing synthetic stabilizers with natural antioxidants is a current and developing issue. Cloves have antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, which is why they are often used in medicine and in gastronomy. Eugenol – the main component of clove oil, is also a strong antioxidant. The aim of the study was to analyze and compare the anti-aging effects of eugenol and cloves in epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) compositions. The 2,2′-azinobis- (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate (ABTS), 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) and CUPric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) tests showed the ability of plant materials to reduce free radicals, as well as iron and copper ions. ENR compositions with additives were characterized by a longer oxidation induction time (OIT). The samples after solar aging showed better resistance to elevated temperature and solar radiation, as evidenced by aging coefficients (K) calculated on the basis of mechanical properties and carbonyl indexes of samples with eugenol and cloves. Cloves and eugenol can be successfully used as natural stabilizers in elastomeric materials.
RELATED ARTICLES
Azizon Kaesaman, Tassaneeya Khunrang, Charoen Nakason
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 753-772, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 753-772, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.58
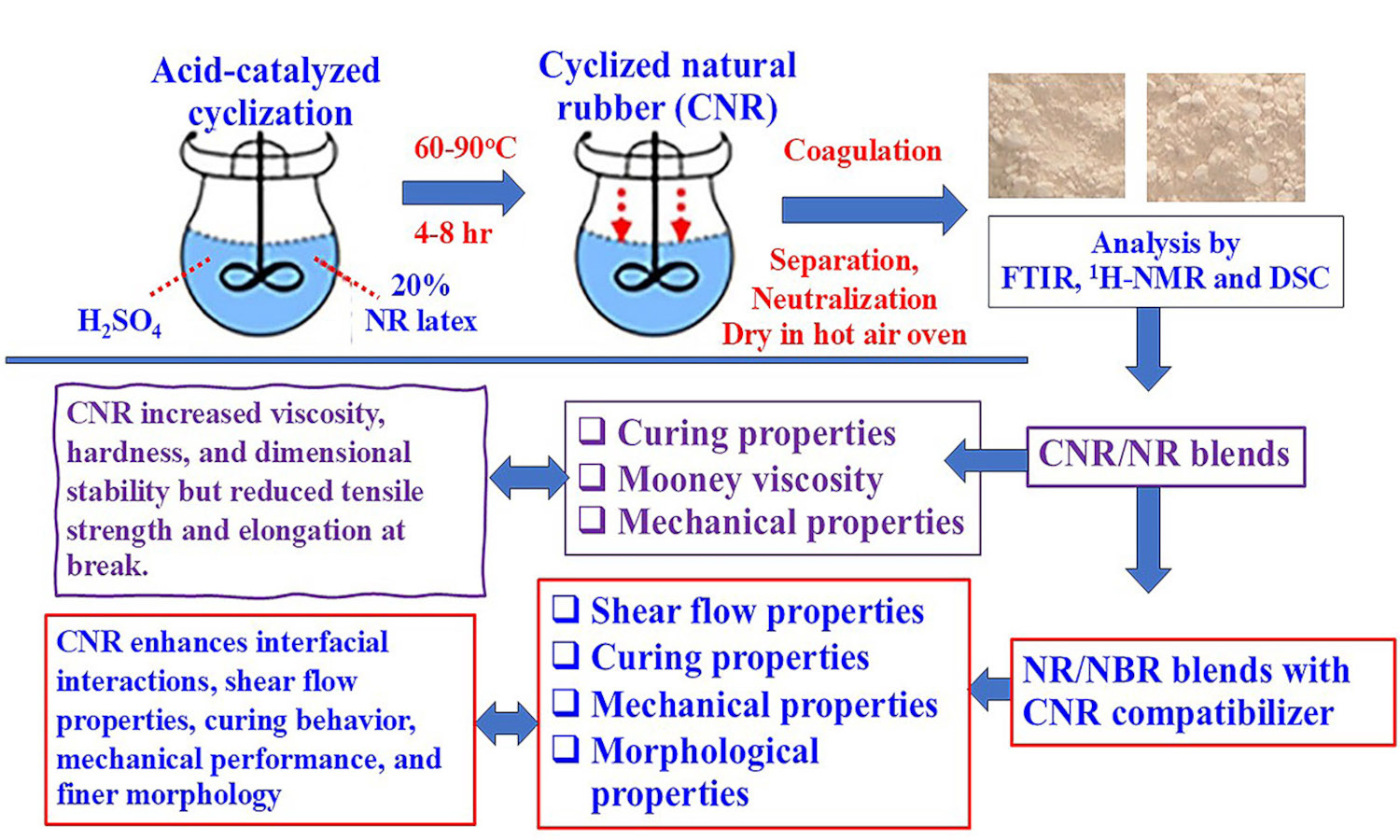
Cyclized natural rubber (CNR) was synthesized through the acid-catalyzed reaction of natural rubber (NR) latex using sulfuric acid as a catalyst and stabilized with a non-ionic surfactant. Cyclization was evaluated by iodine numbers under varying reaction times, temperatures, and NR-to-acid ratios. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-NMR) confirmed the formation of cyclic structures in CNR molecules. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that the glass transition temperature (Tg) of CNR increased with cyclization, indicating greater rigidity and less chain flexibility. CNR was then blended with NR and used as a compatibilizer in NR/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR)blends. It increased blend viscosity, hardness, and dimensional stability but reduced tensile strength and elongation due to its rigid cyclic domains. In NR/NBR blends, CNR outperformed a commercial homogenizer in enhancing interfacial interactions, leading to superior shear flow properties, curing behavior, and mechanical performance. This is attributed to the polar groups in CNR, which enhance intermolecular interactions and phase compatibility, resulting in finer phase morphology. This study highlights the potential of CNR as a versatile material for enhancing the performance of rubber compounds, with promising applications in advanced industrial formulations.
Abdulhakim Masa, Nureeyah Jehsoh, Sawitree Dueramae, Nabil Hayeemasae
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 653-669, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.50
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 653-669, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.50

An antibacterial natural rubber (NR) latex film was successfully prepared in this study. This was done by coating silver (Ag) nanoparticles onto the surface of the NR latex film. The Ag nanoparticles were synthesized using green tea (GT) extract as a bio-reducing agent. The corresponding Ag nanoparticles were then deposited onto the NR latex film. Before synthesis, the phenolic compounds were identified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The Ag nanoparticles were found to be smaller than 25 nm in size. Subsequently, an experimental evaluation was conducted to determine the influence of deposition time, namely 1 to 20 min, on the film’s overall performance. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) confirmed that the Ag content was higher over the deposition time. The surface roughness of the samples was also screened by atomic force microscopy (AFM), where the films became rougher over the deposition time, confirming that Ag nanoparticles dispersed over the surface. As for the antibacterial activities, both qualitative and quantitative tests showed significant outputs. The clear zones of S. aureus and E. coli increased over the deposition time, and a shorter contact time was used to kill the bacteria. This study offers a scientific foundation that supports the development of future rubber products utilizing these findings.
Nabil Hayeemasae, Sitisaiyidah Saiwari, Siriwat Soontaranon, Mohamad Irfan Fathurrohman, Abdulhakim Masa
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 339-349, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.24
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 339-349, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.24
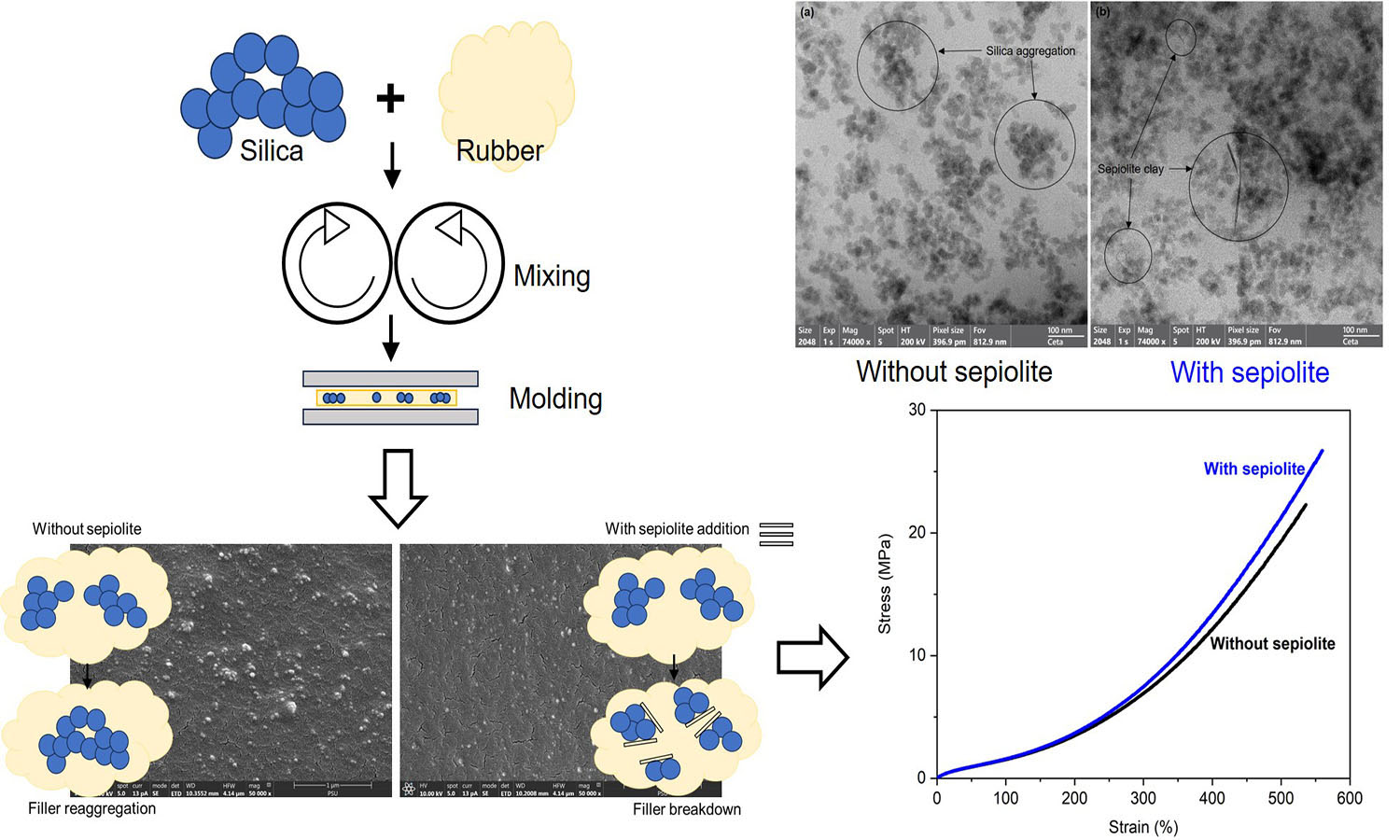
Natural rubber (NR) composites filled with silica and crosslinked with phenolic resin were prepared in this study. The influence of a small sepiolite addition (1–5 part(s) per hundred parts of rubber, phr) on the properties of NR composites was studied. It was found that sepiolite reduced silica aggregate size, allowing improved dispersion in the NR matrix. Sepiolite facilitates silica dispersion by locating at the silica surfaces and acting as a barrier that prevents agglomeration of silica filler. The swelling resistance, crosslink density, tensile strength, and strain-induced crystallization were all strengthened by incorporating sepiolite because of the improved silica dispersion. The greatest tensile strength was achieved at a 2 phr sepiolite addition level. The improvement was about 18% over the reference composite due to the greatest filler-rubber interactions and the finest filler dispersion. The results clearly indicate that sepiolite clay can be applied as a dispersing agent in silica-containing rubber composites.
Marek Pöschl, Radek Stoček, Petr Zádrapa, Martin Stěnička, Gert Heinrich
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1178-1190, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.90
Vol. 18., No.12., Pages 1178-1190, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.90
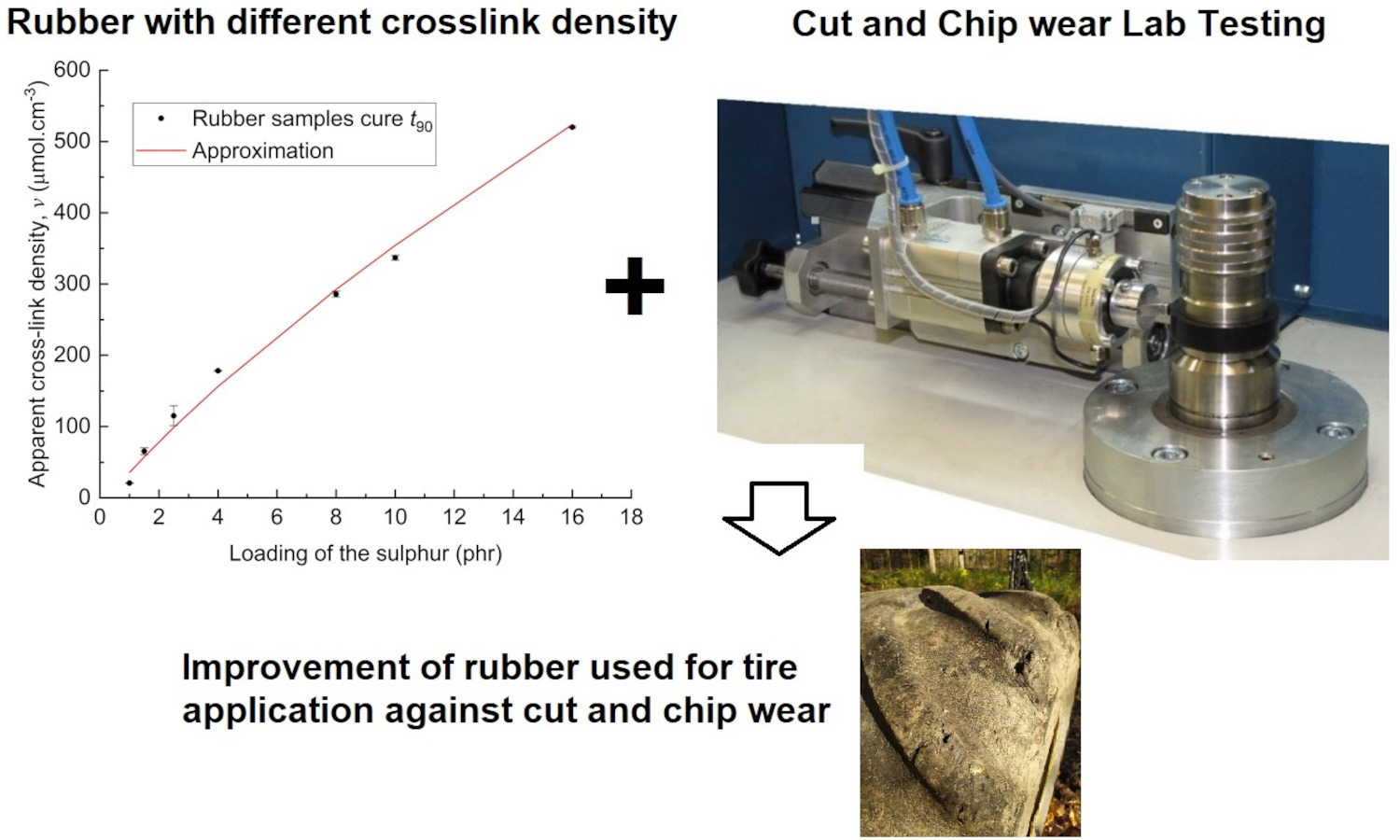
This paper extends previous studies by the authors that aimed to describe the effect of apparent cross-link density (CLD) of the rubber polymer networks on the fracture mechanism caused by cut and chip (CC) wear of natural rubber (NR), demonstrating the positive effect of conventional vulcanization (CV). This work is focused on the determination of the effect of CLD while keeping constant the accelerator-to-sulfur ratio A/S = 0.2, typical for CV systems. For this ratio, different sulfur quantities were chosen, and the concentration of the accelerator N-tert-butyl-benzothiazole sulphonamide (TBBS) was calculated to achieve CLDs in a range from 35 to 524 μmol・cm–3. Standard analyses such as tensile tests, hardness, rebound resilience and DIN abrasion were performed. From these analyses, the optimum physical properties of the NR-based rubber were estimated to be in the CLD range of approximately 60 to 160 μmol・cm–3. A CC wear analysis was performed with an Instrumented cut and chip analyzer (ICCA) and it was found that the highest CC wear resistance of the NR is in the CLD range of 35 to 100 μmol・cm–3. Furthermore, the effect of straininduced crystallization (SIC) of NR on CC wear and its dependence on the CLD region was discussed. For the first time, we determine a CLD range for a CV system in which the material achieves both optimal mechanical properties and CC wear resistance.
Rattanawadee Ninjan, Bencha Thongnuanchan, Natinee Lopattananon, Subhan Salaeh, Phakawat Thongnuanchan, Pornsuwan Buangam
Vol. 18., No.11., Pages 1077-1093, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.83
Vol. 18., No.11., Pages 1077-1093, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.83
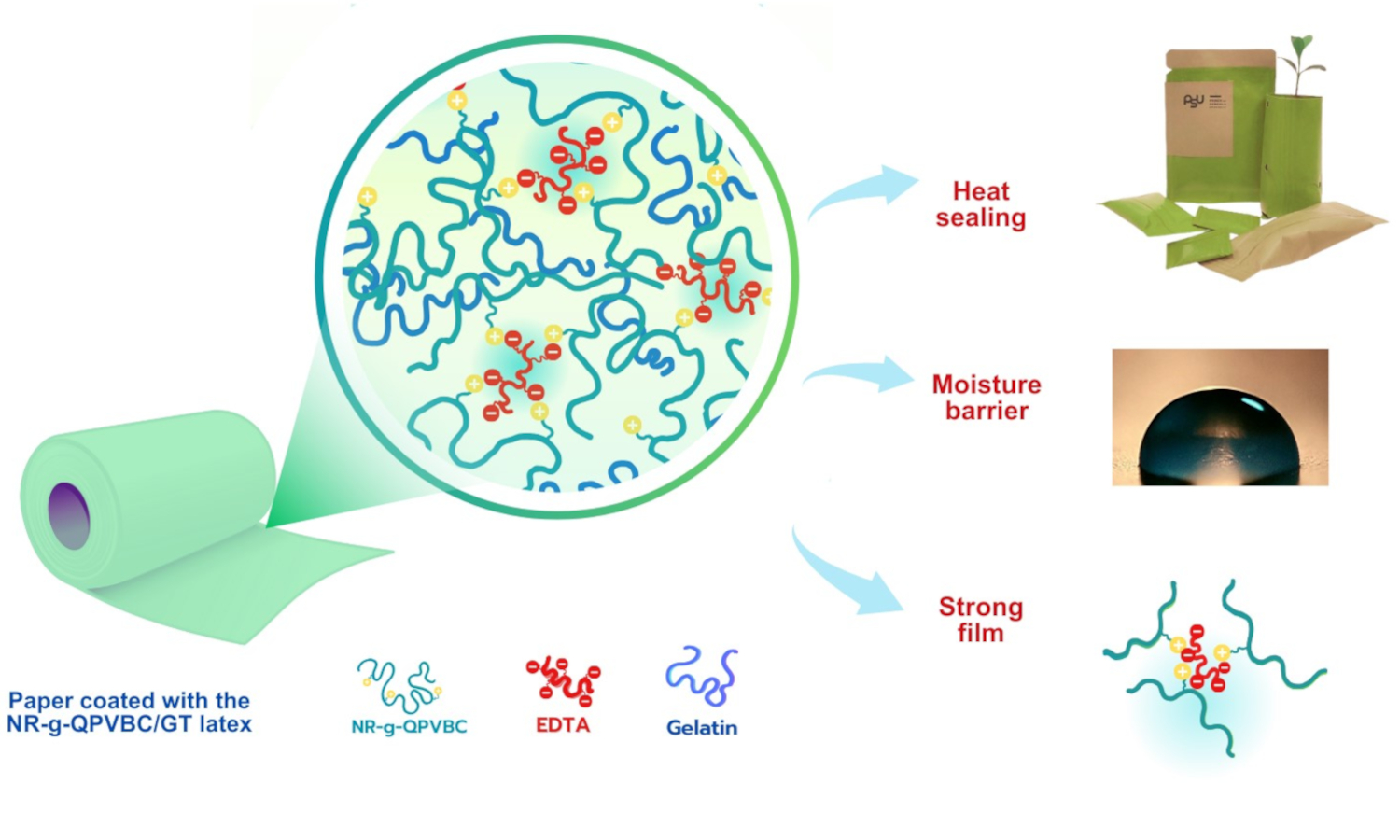
Research into sustainable packaging materials has gained increasing importance due to the pressing environmental concerns related to plastic waste. The present study focused on developing a sustainable paper coating based on modified natural rubber (NR) latex filled with gelatin (GT). The graft copolymer latex of NR and poly(vinylbenzyl chloride) bearing quaternary ammonium groups, abbreviated as NR-g-QPVBC, was first synthesized. GT was then incorporated into the latex, and the combination of these materials resulted in a heat-sealable film with good tensile properties and a water barrier. The ionic crosslinking of the latex film was achieved by the reaction with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Heat-sealing studies of the NR-g-QPVBC latex film filled with GT (NR-g-QPVBC/GT) revealed its heat-sealability at 160 °C. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis further confirmed the diffusion of the chains across the interface during heat sealing. Dip coating was a method for depositing latex film on kraft paper. The paper coated with the NR-g-QPVBC/GT latex showed a significant increase in dry and wet-tensile strength compared to the uncoated paper. The sealing process was optimized to achieve a heat-seal strength of 755.31 N/m at a dwell time of 3 s and a temperature of 160 °C. The research's practical application was demonstrated by transforming the coated paper into various heat-sealable bags using a handheld bag sealer.




