Deterioration behavior of aged magnetorheological elastomer under harsh marine environment
Nursyafiqah Zaini , Saiful Amri Mazlan
, Saiful Amri Mazlan , Siti Aishah Abdul Aziz
, Siti Aishah Abdul Aziz , Mohd Aidy Faizal Johari
, Mohd Aidy Faizal Johari , Ubaidillah Ubaidillah, Nur Azmah Nordin, Muntaz Hana Ahmad Khairi, Megat Ahmad Kamal Megat Hanafiah
, Ubaidillah Ubaidillah, Nur Azmah Nordin, Muntaz Hana Ahmad Khairi, Megat Ahmad Kamal Megat Hanafiah
 , Saiful Amri Mazlan
, Saiful Amri Mazlan , Siti Aishah Abdul Aziz
, Siti Aishah Abdul Aziz , Mohd Aidy Faizal Johari
, Mohd Aidy Faizal Johari , Ubaidillah Ubaidillah, Nur Azmah Nordin, Muntaz Hana Ahmad Khairi, Megat Ahmad Kamal Megat Hanafiah
, Ubaidillah Ubaidillah, Nur Azmah Nordin, Muntaz Hana Ahmad Khairi, Megat Ahmad Kamal Megat HanafiahVol. 18., No.7., Pages 728-741, 2024
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.54
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2024.54
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
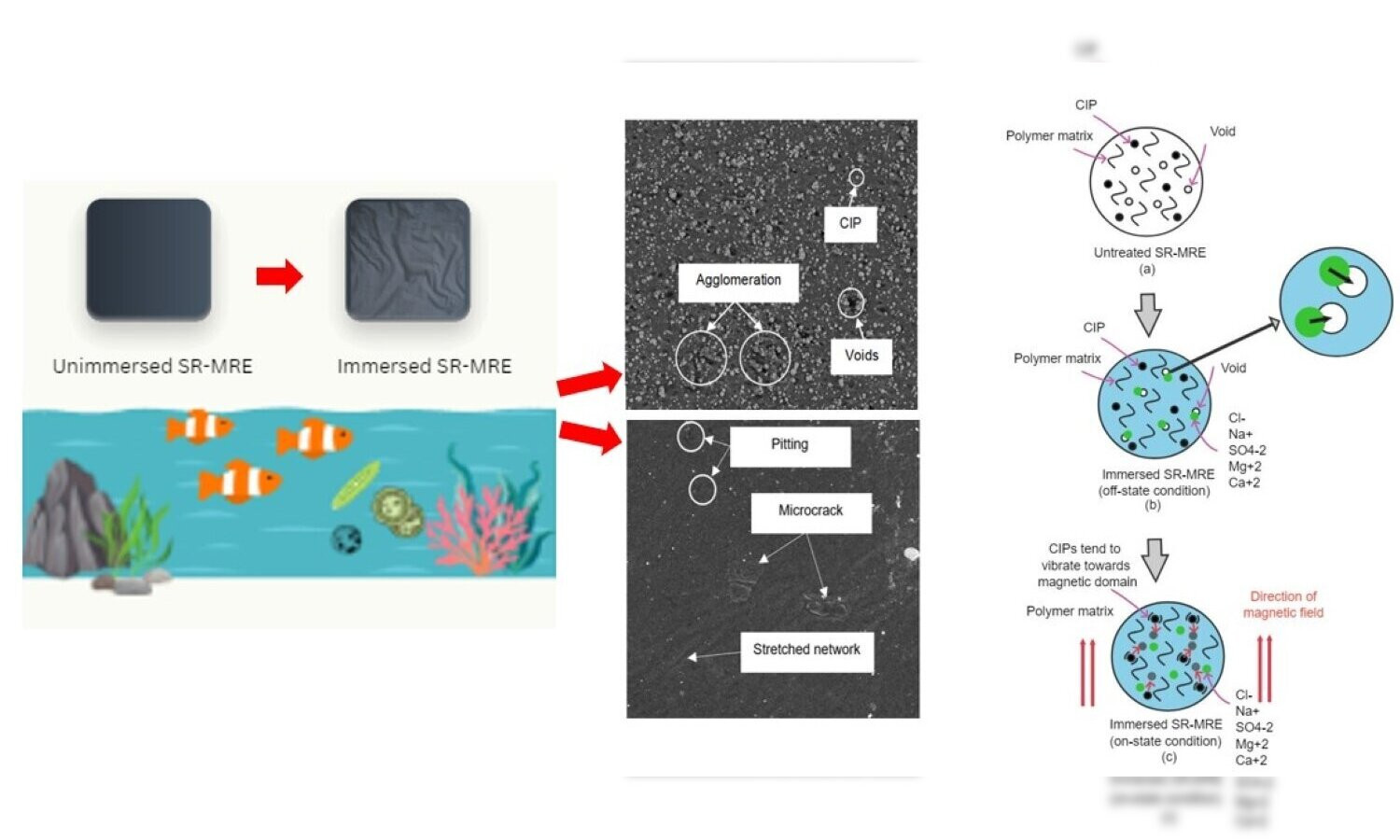
ABSTRACT
Silicone rubber magnetorheological elastomers (SR-MREs) are increasingly recognized for their resilience in marine conditions, offering prolonged service life and durability. This study evaluates the one-month durability of silicone rubber magnetorheological elastomers (SR-MREs) under seawater conditions. Results revealed a 6% reduction in hardness and an 8% decrease in Young’s modulus compared to unimmersed samples. Morphological and attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) analyses supported these findings, revealing surface defects and chemical bonding changes. The immersed SR-MRE displayed a notable 250% increase in elongation at break, highlighting enhanced elasticity. Rheological properties revealed complex mechanical behavior, with an initial increase in storage modulus from 0.25 to 0.38 MPa in the presence of a magnetic field, followed by a gradual decrease to 0.15 MPa at 0 A and 0.52 Mpa at 5 A with strain. Additionally, this study proposes an illustrative mechanism to elucidate the relationship between seawater elements and SR-MRE behavior, enhancing our understanding of its mechanical properties and degradation in marine environments, thus highlighting SR-MRE’s potential as a durable material compared to traditional rubber composites.
RELATED ARTICLES
Liu Yang, Xuan Zhao, Sun Xinyu, Shuai Yuan, Lei Zhu
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60
Vol. 19., No.8., Pages 783-795, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.60

Waste tire rubber poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and complex crosslinkedvstructure. In this sense, this study aims to examine the utilization of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) in the desulfurizationvprocess of ground tire rubber (GTR). A range of hydrogen bond donors (HBDs), including ethylene glycol, malonic acid,vimidazole, toluene sulfonic acid, and urea, were combined with choline chloride, which serves as a hydrogen bond acceptorv(HBA), to synthesize deep eutectic solvents. Subsequently, these DESs are used in the modification of rubber devulcanizationvprocesses. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Horikx analysis werevused to confirm the occurrence of devulcanization. The studies confirmed that the devulcanization process was selective invnature, effectively reducing random chain scission while maintaining the integrity of the polymer. Furthermore, the vulcanizatesvobtained post-treatment demonstrated enhanced properties, including increased tensile strength, modulus, tear strength, hardness, and durability, with ethylene glycol-based DES (DES-E) exhibiting the most pronounced enhancements.
Jose James, George Vazhathara Thomas, Sisanth Krishnageham Sidharathan, Mohammad Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 697-705, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.53
Vol. 19., No.7., Pages 697-705, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.53
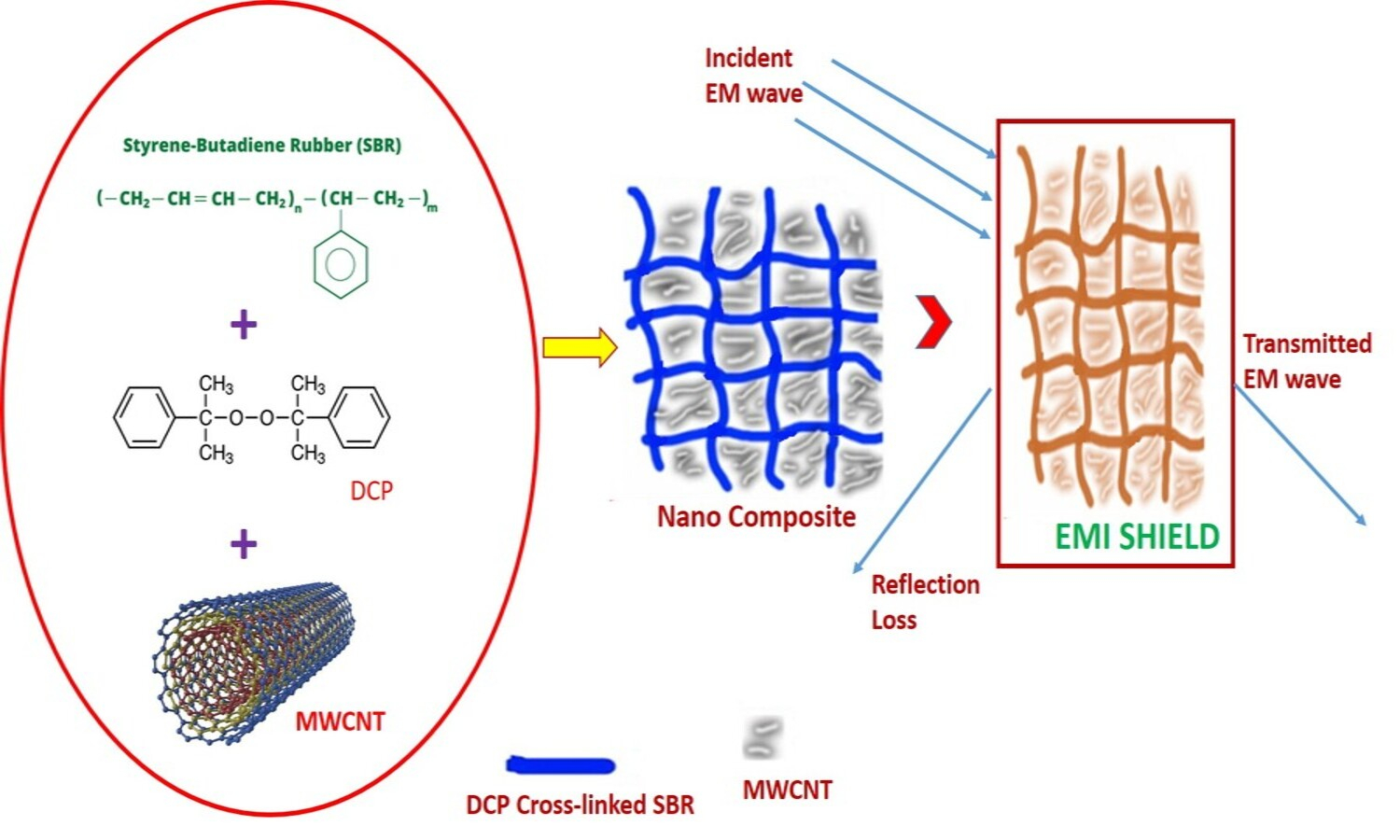
A nanocomposite of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) was fabricated using an internal melt mixer. Systematically investigated the role of MWCNT loading on the mechanical, dielectric, electrical and Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding characteristics of developed nanocomposites. The fine dispersion of MWCNTs in the SBR matrix was clearly observed from high-resolution transmission electron microscope images. The nanocomposites exhibited outstanding electrical, dielectric and EMI shielding behaviours (~45 dB at 20 phr of MWCNT). A high conductivity of 0.92 S/cm was attained in the nanocomposites and is attributable to the establishment of percolation networks of MWCNT in the SBR matrix. These composites displayed reasonably good mechanical properties because of the reinforcing effect of MWCNT. The economically viable and easy fabrication protocol of this nanocomposite can act as a platform for the synthesis of low-cost and highly effective composite for EMI shielding applications.
Cristian Valdés, Valentina Guzmán, Camila Ponce, Maribel Mamani, Juan Guevara, Claudia Vergara, Rodrigo Andler
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
Vol. 19., No.6., Pages 594-609, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.45
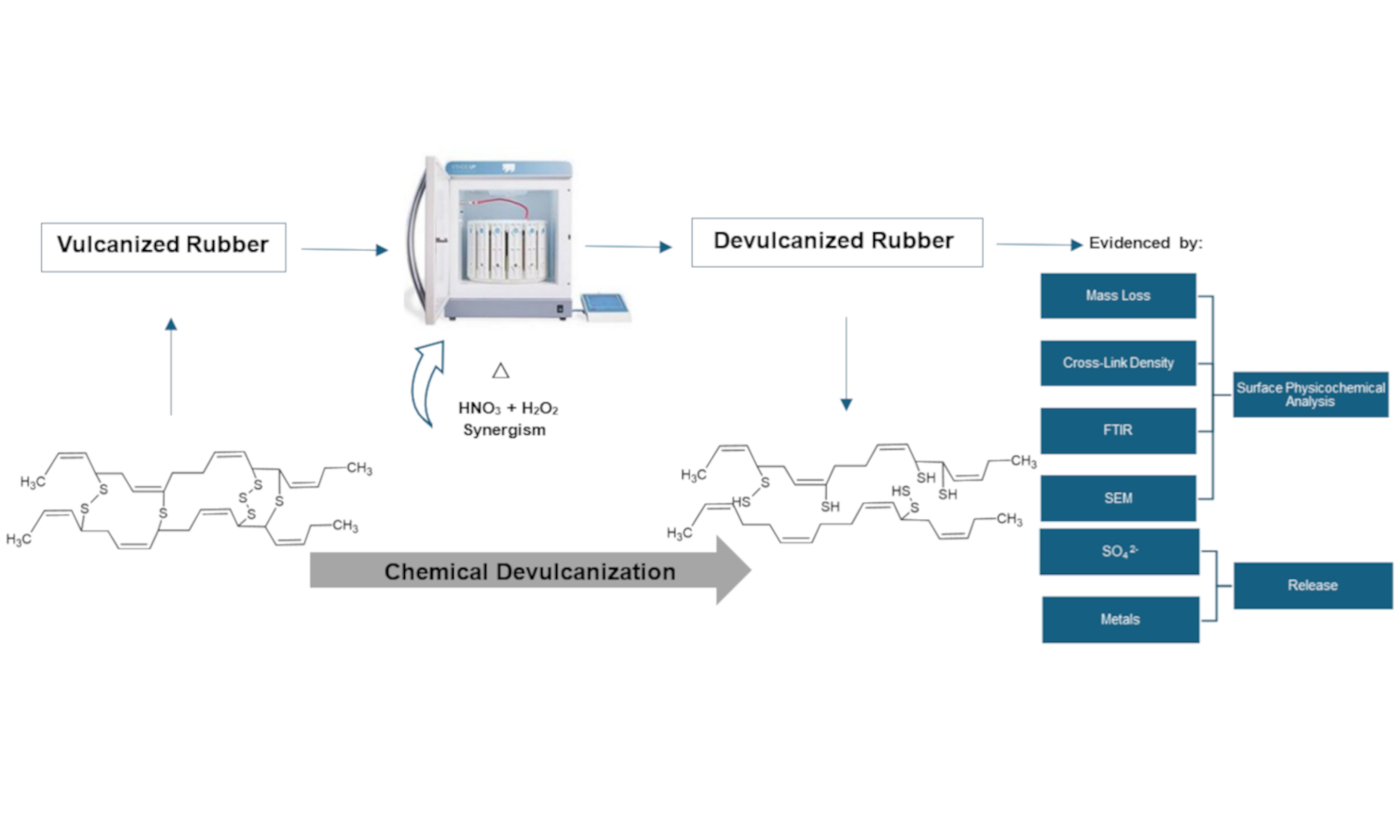
Waste rubber disposal causes considerable negative environmental impacts due to its increase worldwide, mainly in the automotive industry. Therefore, the search for technological solutions for rubber waste is a priority, and the first step in this material degradation is devulcanization due to its difficult degradation. This study evaluated rubber devulcanization using a closed vessel microwave digestion system with nitric acid (HNO3) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) through chemical characterization, aiming at verifying the synergistic effect between these oxidizing agents. Microwave irradiation was applied as a heating method to facilitate the chemical reactions, focusing on the synergism between HNO3 and H2O2. Results showed that 5 M H2O2 in combination with 1% HNO3, presented better results. A greater decrease in cross-link density was demonstrated as the concentration of H2O2 increased (3.96·10–5±1.99·10–6 mol/cm3), likewise, higher sulfates released (926.8±53.4 mg/L), increased mass loss (12.184±1.06%), rubber surface fragmentation, and important variations in the C–S, C=O bands, showing better results when devulcanization is carried out in synergism between HNO3 and H2O2.
Nabil Hayeemasae, Sitisaiyidah Saiwari, Siriwat Soontaranon, Mohamad Irfan Fathurrohman, Abdulhakim Masa
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 339-349, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.24
Vol. 19., No.3., Pages 339-349, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.24
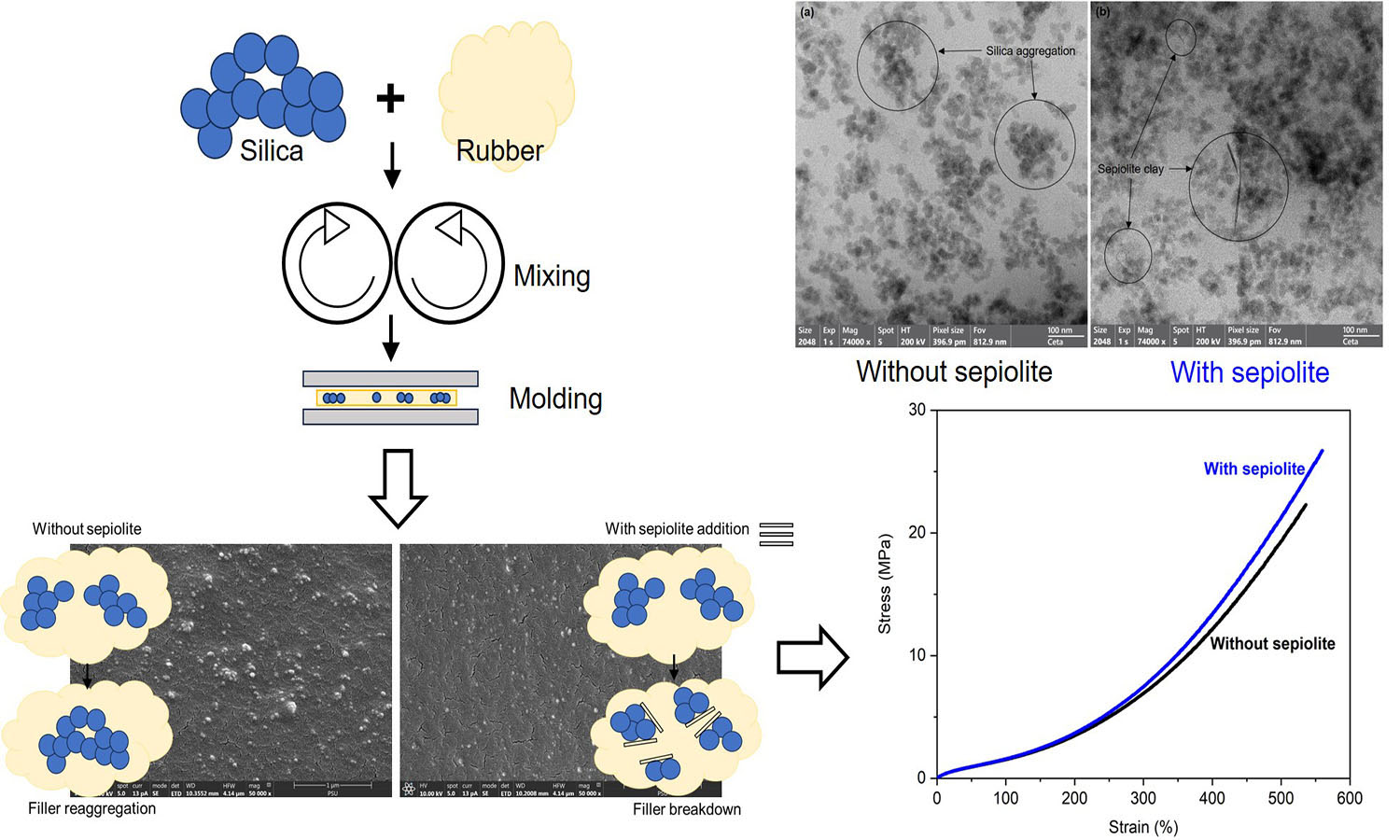
Natural rubber (NR) composites filled with silica and crosslinked with phenolic resin were prepared in this study. The influence of a small sepiolite addition (1–5 part(s) per hundred parts of rubber, phr) on the properties of NR composites was studied. It was found that sepiolite reduced silica aggregate size, allowing improved dispersion in the NR matrix. Sepiolite facilitates silica dispersion by locating at the silica surfaces and acting as a barrier that prevents agglomeration of silica filler. The swelling resistance, crosslink density, tensile strength, and strain-induced crystallization were all strengthened by incorporating sepiolite because of the improved silica dispersion. The greatest tensile strength was achieved at a 2 phr sepiolite addition level. The improvement was about 18% over the reference composite due to the greatest filler-rubber interactions and the finest filler dispersion. The results clearly indicate that sepiolite clay can be applied as a dispersing agent in silica-containing rubber composites.
Mohammad Mehdi Alighanbari, Firoozeh Danafar, Araam Namjoo, Asma Saeed
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 15-46, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
Vol. 19., No.1., Pages 15-46, 2025
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2025.3
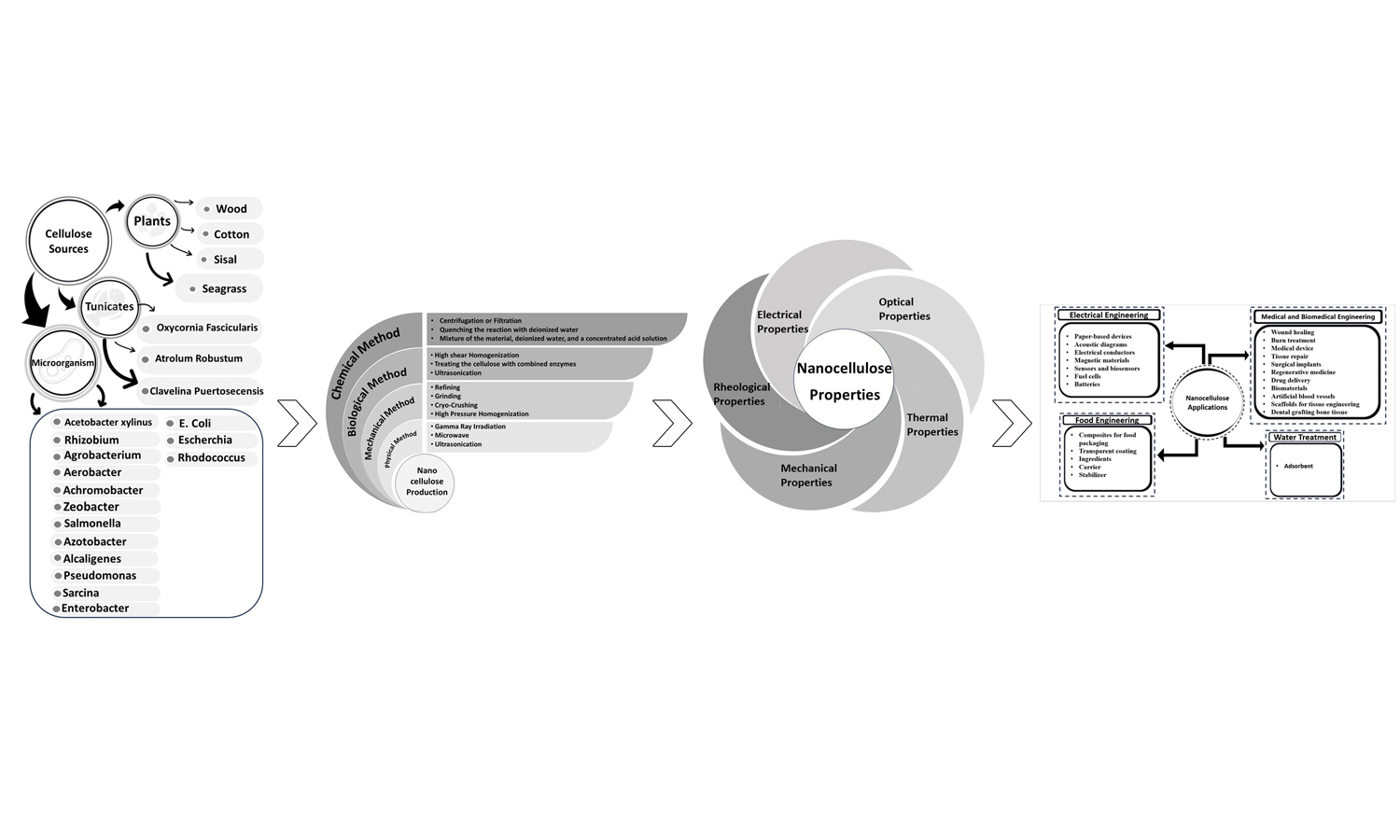
The environmental and ecological concerns drive researchers to synthesize functional materials using components from natural resources. Nanocellulose (NC), derived from plants, marine animals, or microorganisms, is a green material attracting attention due to its abundance, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. NC’s interstice properties enable the synthesis of functional nanocomposites in forms like aerogels, foams, paper, sheets, or hollow filaments. This review briefly describes NC classification and production while comprehensively presenting its mechanical, rheological, optical, and electrical properties, offering foundational knowledge for future research. Additionally, it highlights recent developments in NC-based products across fields such as papermaking, water treatment, civil engineering, electronics, cosmetics, food, and medicine. For the first time, this paper explores recent advances in NC molecular simulation, providing insights into structure, arrangement, and interactions through molecular dynamic simulation. Finally, future prospects for NC-based applications are discussed to encourage studies addressing current challenges.



