Content
All issues / Volume 20 (2026) / Issue 3 (March)
Szabolcs Krizsma, Lóránt Kiss, László Mészáros
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 215-216, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.17
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 215-216, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.17

This is an editorial article. It has no abstract.
Joanna Smorawska-Kliza, Julia Habaj, Ewa Głowińska
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 217-232, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.18
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 217-232, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.18
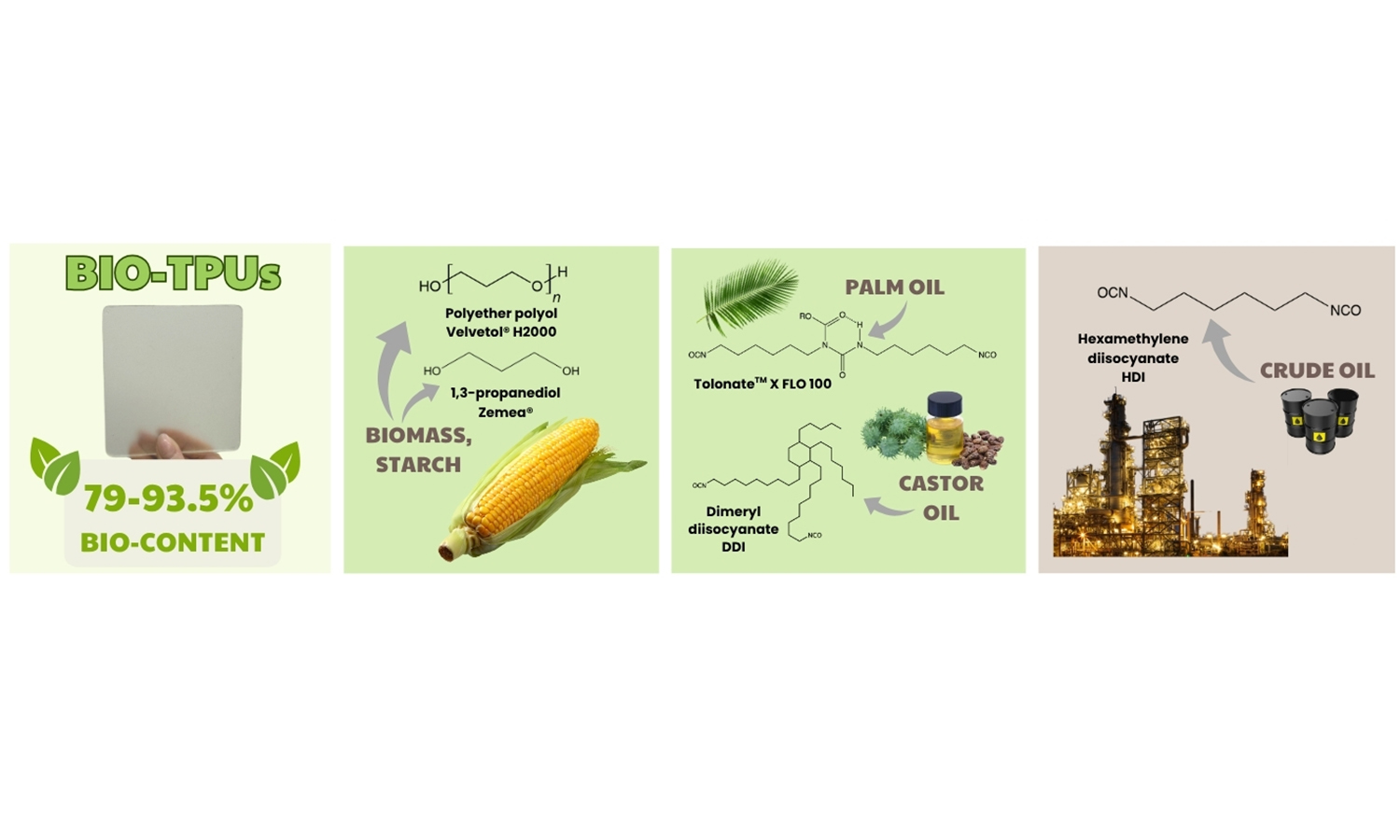
Modification of the hard segment structure in polyurethanes using isocyanate mixtures has emerged as one of the most effective strategies for developing new materials with enhanced properties and a high content of bio-based carbon. In this work, next-generation sustainable thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers (bio-TPUs) were synthesized using aliphatic isocyanate mixtures based on bio-derived diisocyanates Tolonate™ X FLO 100 and dimeryl diisocyanate (DDI) alongside hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI). Poly(trimethylene ether) glycol (PO3G) and bio-based 1,3-propanediol served as renewable hydroxyl-terminated components. The bio-TPUs were prepared using the common ‘one-shot’ method. The resulting materials were analyzed to assess phase separation, morphology, as well as mechanical, thermal and thermomechanical properties. The results confirm the significant influence of the type of diisocyanate mixture on the properties of bio-TPU, improving their thermal stability (up to 300 °C) and reducing the melting temperature to 140 °C, which makes them suitable for low-temperature processing.
Paulina Bednarczyk, Kamil Rożniakowski
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 233-245, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.19
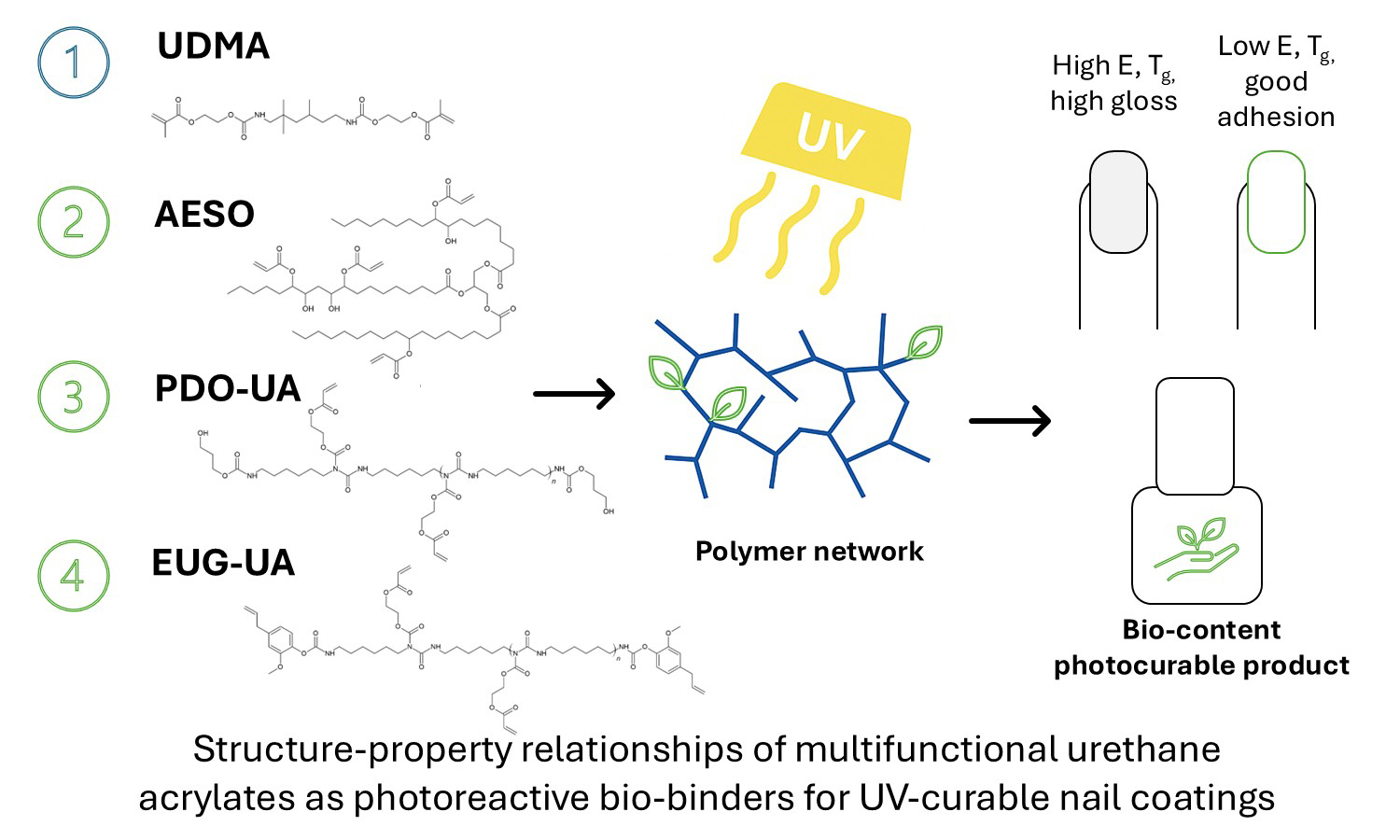
This study investigates the structure–property relationships of multi-functional urethane acrylate resins designed as photoreactive binders for UV-curable nail coatings. Four systems were examined: a commercial resin urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA), a bio-based acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO), and two newly synthesized bio-based urethane acrylates derived from 1,3-propanediol (PDO–UA) and eugenol (EUG–UA). Photopolymerization kinetics were analyzed by realtime FTIR, while the properties of the cured coatings were also determined. The mechanical and thermal behavior of selfsupporting polymer films was evaluated by tensile testing and DSC analysis. The UDMA network exhibited the highest crosslink density, reflected in its high modulus (≈0.5 GPa), tensile strength (≈15 MPa), and Tg (≈60°C), making it suitable for use as a top coat. AESO showed moderate stiffness and flexibility, whereas PDO–UA and EUG–UA formed soft, low-Tg (–12 and –17°C) and highly deformable networks typical of elastomeric materials. The combined mechanical and thermal results confirmed that crosslink density strongly governs coating performance and applicability. This study demonstrates that blending UDMA with bio-based oligomers enables the design of sustainable, UV-curable nail lacquers with an optimal balance of hardness, flexibility, and adhesion to the natural nail plate.
Dam Xuan Thang, Tong Khanh Linh
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 246-263, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.20
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 246-263, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.20
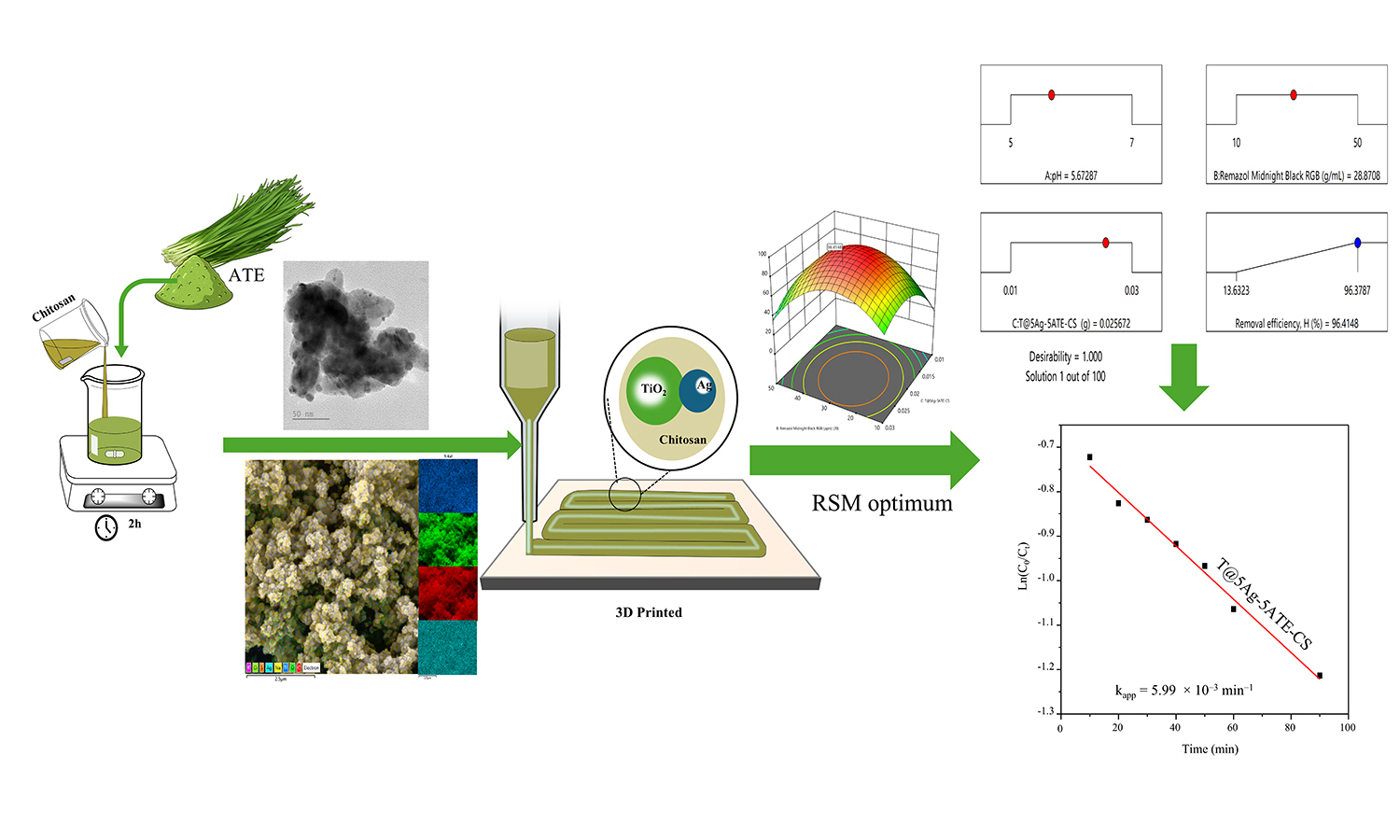
We report a green route to Ag–TiO2 nanocomposites using an Allium tuberosum extract, rich in organosulfur and polyphenolic constituents, as a dual-function biogenic reducer and stabilizer, enabling efficient Ag+→Ag0 conversion and capping of Ag–TiO2 without the use of harsh reagents. The nanocomposites are formulated into chitosan-based inks for direct ink writing (DIW) of porous, mechanically robust, reusable membranes (optimal formulation T@5Ag–5ATE–CS) with a homogeneous Ag dispersion. Multiscale characterization (SEM/TEM, XRD, FTIR, UV–vis DRS, EDS mapping) confirms metallic Ag0 uniformly decorating TiO2 and an extended visible-light response attributable to strong localized surface plasmon resonance. Under near-UV/visible irradiation, the membranes decolorize Remazol Midnight Black RGB dye with pseudo-first-order kinetics, yielding kapp up to 5.99·10–3 min–1 with R2 ≈ 0.99 and outperforming pristine TiO2. Response surface methodology identifies an optimum at pH 5.67, 28.87 mg·L–1 dye, and 0.0257 g catalyst, delivering a predicted 96.41% versus experimental 95.07% removal (validation error 1.39%) with excellent model statistics (R2 ≈ 0.995). The combined effects of Allium-tuberosum-assisted Ag plasmonics, TiO2 photocatalysis, and chitosan-enhanced adsorption underpin the high photocatalytic activity and reusability, highlighting a scalable, eco-friendly pathway to printable photocatalytic/antimicrobial membranes for wastewater treatment.
Cláudia Andréa Batista dos Santos, Bartłomiej Kryszak, Rafał Malinowski, Aleksandra Ujćič, Konrad Szustakiewicz
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 264-278, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.21
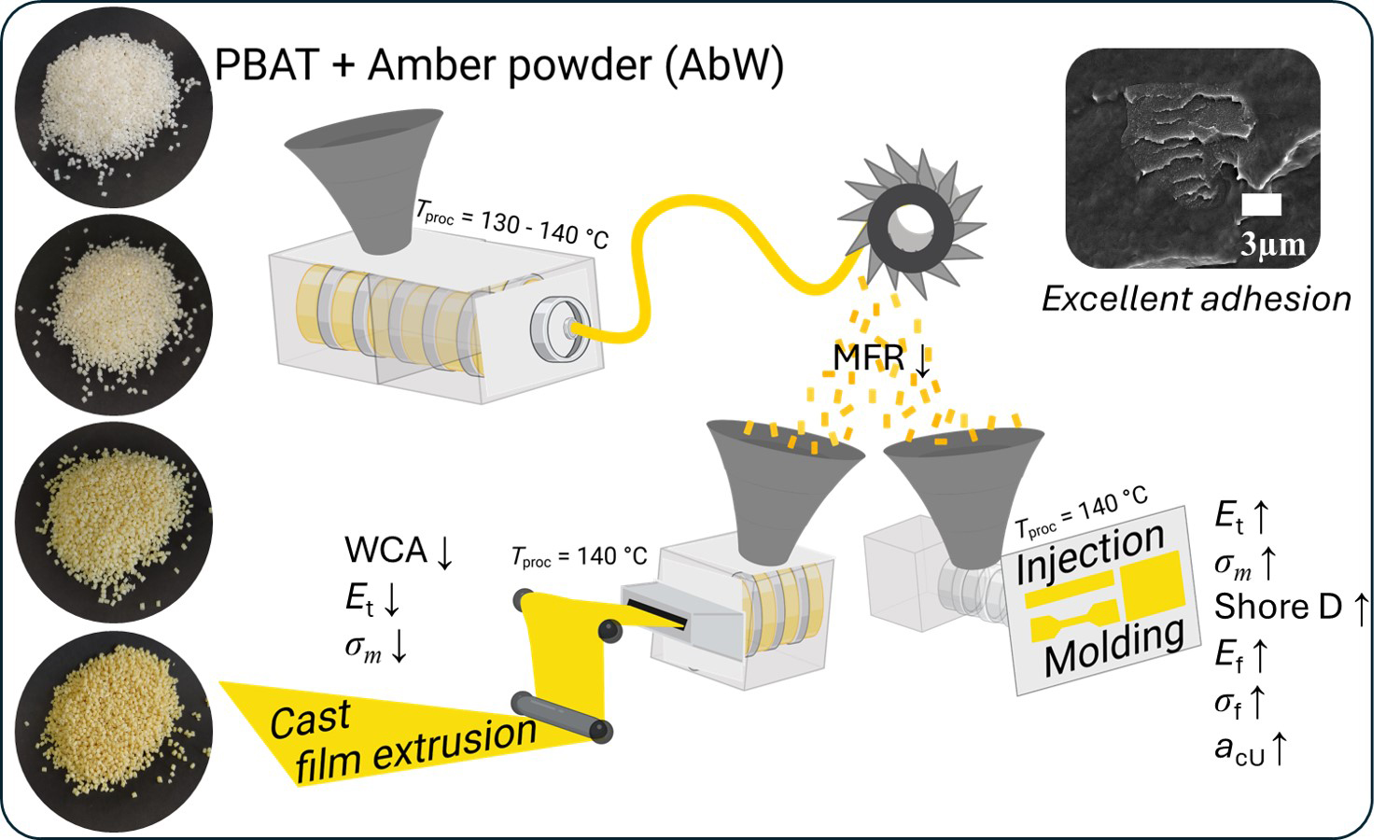
This study investigates the interaction between poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) and amber powdered waste (AbW) from jewelry at different filler concentrations (0, 1, 2.5, and 5 wt%) obtained via melt mixing in a corotating twin screw extruder. The resulting materials were pelletized and processed using two techniques: 1) cast film extrusion and 2) injection molding. The shaped specimens exhibited excellent interfacial adhesion. Thermal behavior, as assessed by Vicat softening temperature (VST), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), showed minimal variation among the composites. Despite similar melt flow rate (MFR) values among the samples, the incorporation of AbW affected the behavior of the polymer during cast film extrusion. Consequently, the composite films exhibited lower tensile mechanical parameters (tensile strength, Young’s modulus, stress and strain at break) compared to the neat PBAT film. In turn, the injection molded composites showed improved tensile, flexural, and impact parameters compared to their neat counterpart. Additionally, a slight decrease in water contact angle (WCA) suggested increased surface hydrophilicity of the extruded films. These findings demonstrate the potential of AbW as an additive for biopolymer composites with enhanced mechanical performance. The increased surface hydrophilicity is particularly relevant for applications targeting biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Shuang Gao, Yuan Lyu, Jieting Geng, Lin Xia
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 279-291, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.22
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 279-291, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.22
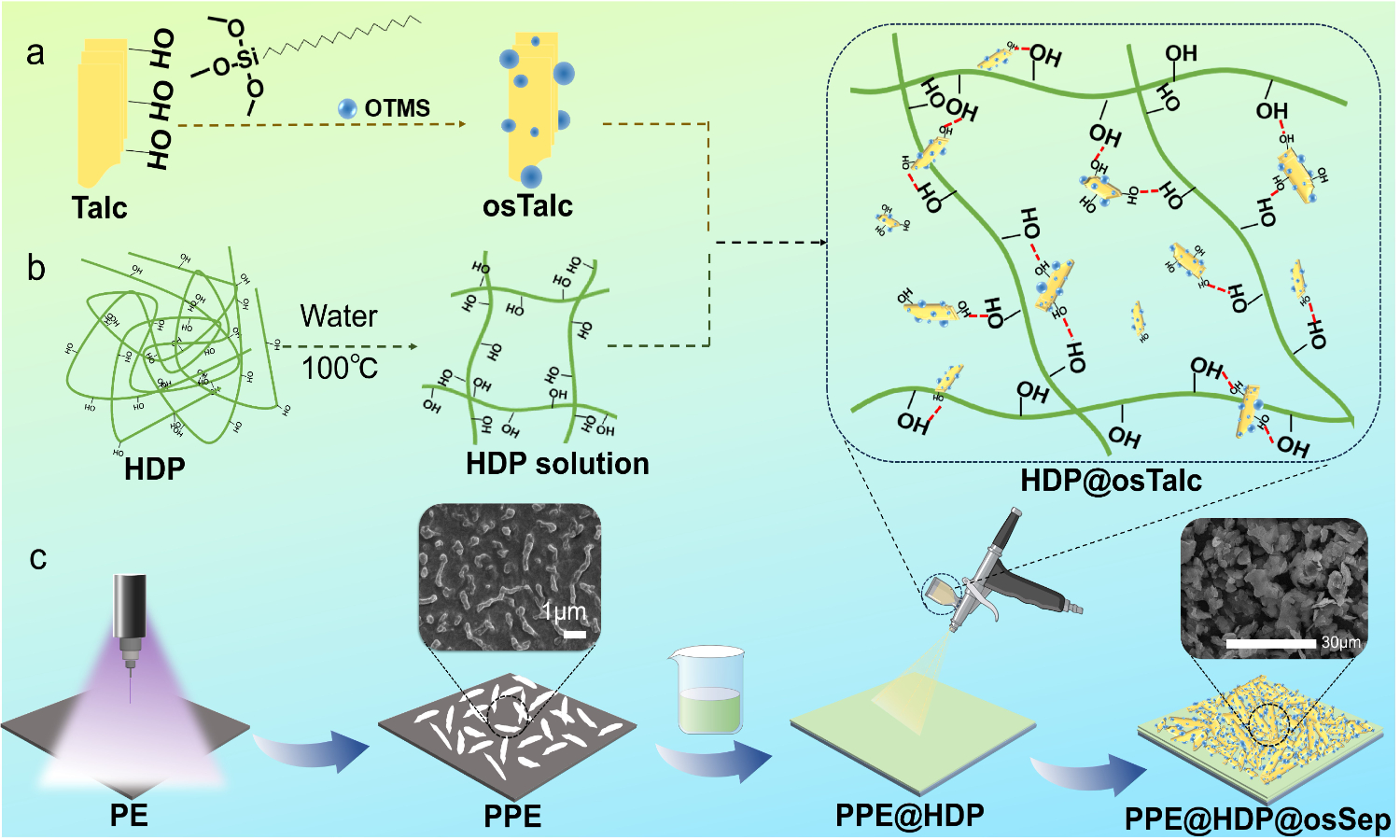
Inspired by natural structures, this study successfully developed innovative composites through the strategic integration of biomimetic concepts and advanced material engineering techniques. Using plasma-treated polyethylene (PPE) film as the substrate, hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (HDP) as the bioinspired adhesive layer, and modified talc (osTalc) as the functional modifier, a series of PPE@HDP@osTalc composites were fabricated via an optimized spray-coating process. The as-prepared composite demonstrates exceptional superhydrophobicity and mechanical flexibility. Chemical stability assessment of the PPE@HDP@osTalc composites demonstrated strong interfacial bonding between the PPE, HDP, and osTalc components. The development of this bioinspired smart composite not only provides new insights for designing functional materials but also demonstrates significant potential for applications in emerging fields such as flexible electronics, marine engineering, and biomedical devices.
Xin Liu, Liang Xu, Yu Bai, Wei Wang, Zheng Li, Jizhou Du, Jing Zhang, Junfeng Qian, Mingyang He
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 292-310, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.23
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 292-310, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.23
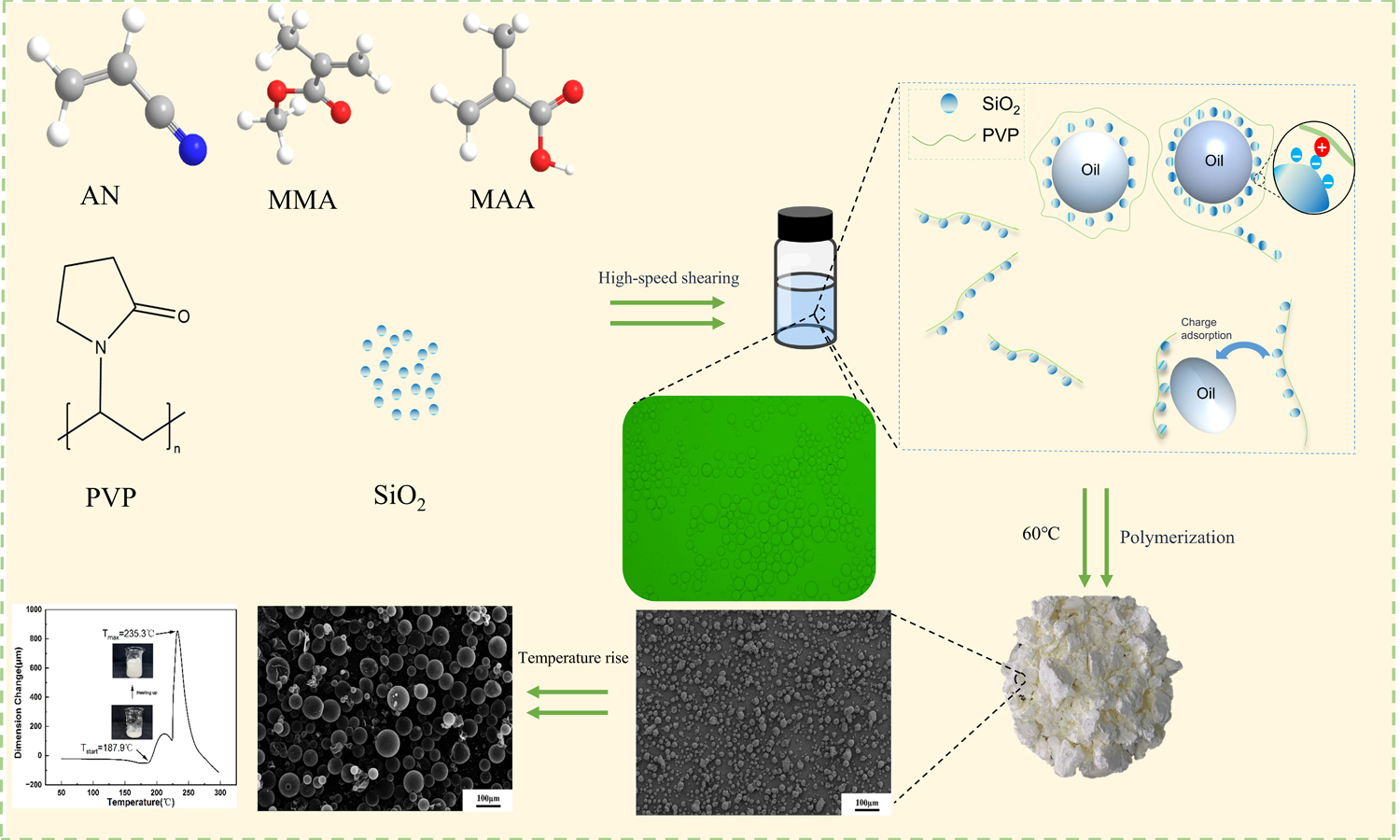
Thermally expandable microspheres (TEMs) are 5–50 μm core–shell particles that expand near the shell’s glass transition temperature (Tg). They are widely used as blowing agents in polymer foaming. Typically, TEMs are prepared by Pickering emulsion–based suspension polymerization. In this process, the oil phase contains monomers, a volatile blowing agent, and an initiator, and it is dispersed as oil-in-water droplets. The aqueous phase contains inorganic particles and an organic dispersant to stabilize the interface. However, solely regulating the oil phase has failed to deliver TEMs that couple a high onset expansion temperature (Tstart) with a large expansion ratio. Therefore, these materials remain unsuitable as blowing agents for high-processing-temperature polymers. This study systematically investigates how regulating the aqueous-phase environment affects Tstart and the expansion ratio of TEMs. Specifically, we tune silica concentration, pH, and ionic strength. By enhancing emulsion stability and optimizing emulsion morphology, we obtain TEMs that combine a high Tstart (188 °C) and a 12× diameter expansion. These findings highlight the importance of aqueous-phase regulation in controlling the Tstart and expansion ratio of TEMs, providing a promising route to microspheres suited for high-temperature polymer foaming.
Kazem Honarkar, Mohammad Karrabi
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 311-323, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
Vol. 20., No.3., Pages 311-323, 2026
DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2026.24
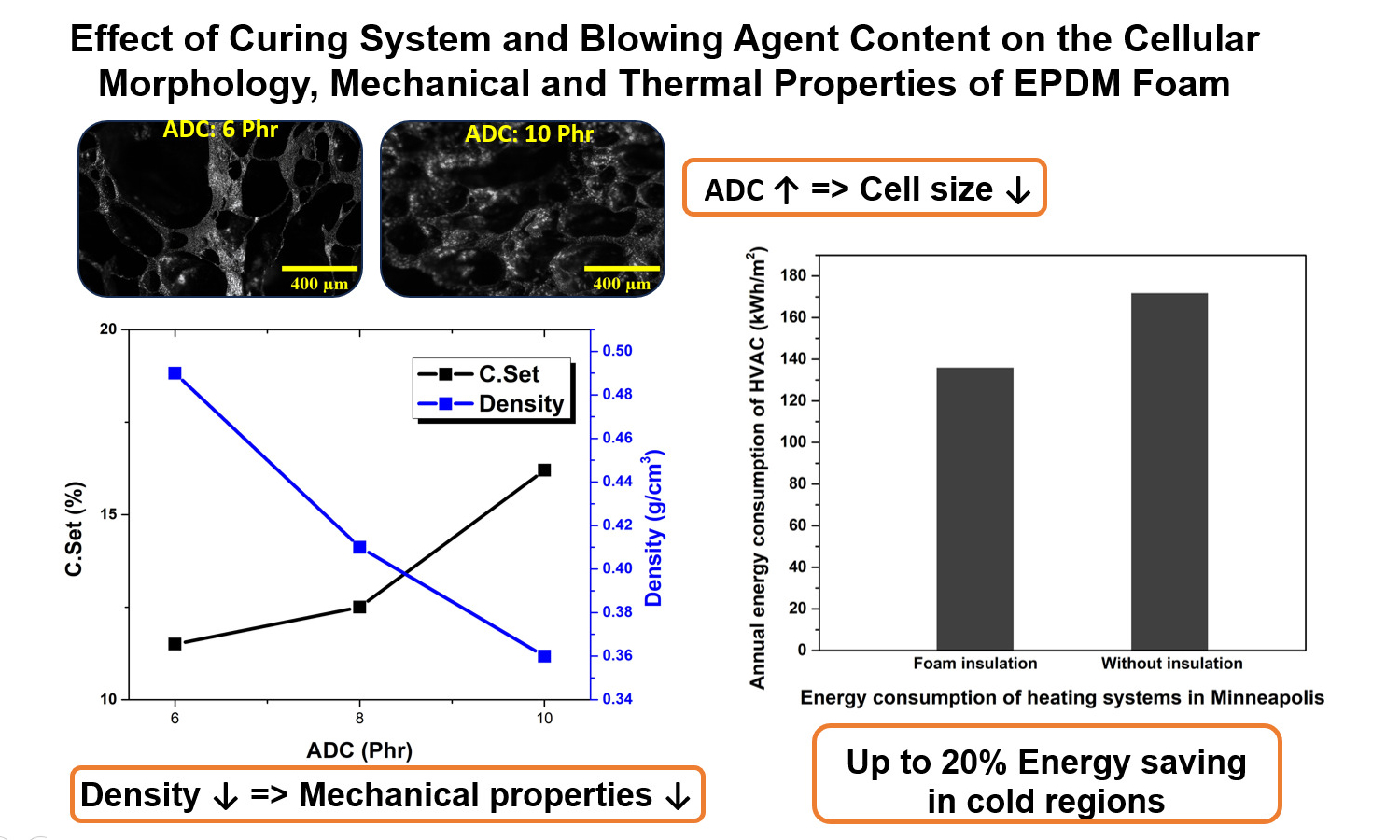
In this study, the effect of the amount of blowing agent and the type of sulfur curing system on the cellular structure, thermal, and mechanical properties of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer (EPDM) foam was investigated. Three types of sulfur curing systems including efficient, semi-efficient and conventional and three variable levels of azodicarbonamide (ADC) were considered; as a result, nine EPDM foam formulations were evaluated. Curing process parameters were measured using cure rheometry and cellular structure was examined by optical microscopy images, determining the average cell size and size distribution. For evaluating physical and mechanical properties, density and compression set tests were performed. Thermal conductivity tests were conducted on selected samples. Building energy modeling was performed using DesignBuilder software to evaluate the thermal insulation performance of the foams. The results showed that the type of curing system and the amount of ADC significantly affect cell morphology, density, and mechanical properties. Overall, a decrease in density leads to reduced mechanical properties. The modeling results indicated that using EPDM foams as building thermal insulation can reduce the energy consumption of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems by up to 20%.


